|
Hermann De Pourtalès
Count Hermann Alexander de Pourtalès (31 March 1847 – 28 November 1904) was a Swiss sailor who competed in the 1900 Summer Olympics. Early life Pourtalès was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland on 31 March 1847. He was a son of Count Alexandre Joseph de Pourtalès (1810–1833) and the former Auguste Saladin (1815–1885). His sister, Isabelle Marguerite de Pourtales, was the wife of archaeologist Henri Édouard Naville, a prominent Egyptologist who found a statue of Ramesses II at Bubastis. His paternal grandparents were Louis de Pourtalès (a brother of James-Alexandre de Pourtalès and Frédéric de Pourtalès, grandfather of Friedrich von Pourtalès) and Sophie de Guy d'Audanger. His nephew was Bernard de Pourtalès. The Pourtalès family were French Huguenots who settled in Neuchâtel following the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. His maternal grandfather was Antoine Charles Guillaume Saladin. Career Pourtalès was a captain of the Cuirassiers of the Guar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
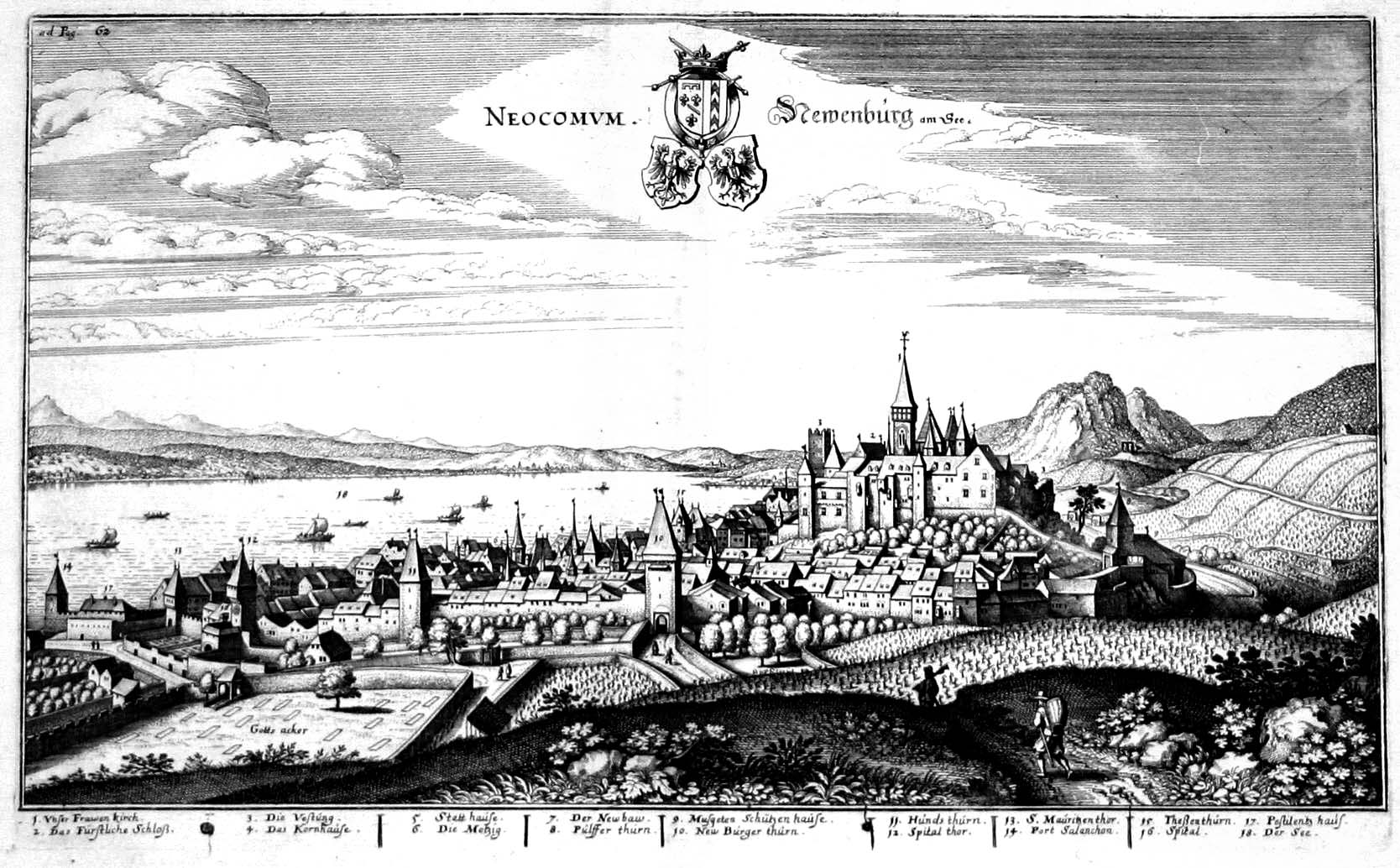
Neuchâtel
Neuchâtel (, ; ; ) is a list of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital (political), capital of the cantons of Switzerland, Swiss canton of Neuchâtel (canton), Neuchâtel on Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, Neuchâtel, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 33,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". The castle after which the city is named was built by Rudolph III of Burgundy and completed in 1011. Originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the city was absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033. The domain of the counts of Neuchatel was first referred to as a city in 1214. The city came under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1806 to 1814. In 1848, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard De Pourtalès
Bernard Alexandre George Edmond de Pourtalès (5 June 1870 – 5 July 1935) was a Swiss infantry captain and sailor who competed in the 1900 Summer Olympics. In 1900 he was a member of the Swiss boat ''Lérina'', which won the gold medal in the first race and silver medal in the second race of the 1 to 2 ton class. He also participated in the open class, but did not finish. His uncle Hermann and uncle's wife Hélène were also crew members. He was born in Bellevue, Switzerland, and died in Casablanca, French Morocco The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when Sultan Abd al-Hafid signed the .... Further reading * * References External links * 1870 births 1935 deaths Swiss male sailors (sport) Sailors at the 1900 Summer Olympics – 1 to 2 ton Olympic sailors for Switzerland Olympic gold meda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clio
In Greek mythology, Clio ( , ; ), also spelled Kleio, Сleio, or Cleo, is the muse of history, or in a few mythological accounts, the muse of lyre-playing. Etymology Clio's name is derived from the Greek root κλέω/κλείω (meaning "to recount", "to make famous" or "to celebrate"). The name's traditional Latinisation is Clio, Lewis and Short, ''A Latin Dictionary: Founded on Andrews' Edition of Freund's Latin Dictionary: Revised, Enlarged, and in Great Part Rewritten by Charlton T. Lewis, Ph.D. and Charles Short, LL.D''. The Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1879, ''s.v.'' but some modern systems such as the American Library Association-Library of Congress system use ''K'' to represent the original Greek '' kappa'', and ''ei'' to represent the diphthong ''ει'' ( epsilon iota), thus ''Kleio''. Depiction Clio, sometimes referred to as "the Proclaimer", is often represented with an open parchment scroll, a book, or a set of tablets. She is also shown with the heroic trum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Geneva
The Canton of Geneva, officially the Republic and Canton of Geneva, is one of the Cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons of the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of forty-five Municipality, municipalities, and the seat of the government and parliament is in the Geneva, city of Geneva. Geneva is the French-speaking westernmost canton of Switzerland. It lies at the western end of Lake Geneva and on both sides of the Rhone, its main river. Within the country, the canton borders Vaud to the east, the only adjacent canton. However, most of Geneva's border is with France, specifically the region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. As is the case in several other Swiss cantons (Ticino, canton of Neuchâtel, Neuchâtel, and canton of Jura, Jura), Geneva is referred to as a republic within the Swiss Confederation. One of the most populated cantons, Geneva is considered one of the most cosmopolitan regions of the country. As a center of the Calvinism, Calvinist Protestant Reformation, Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Versoix
Versoix () is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Canton of Geneva, in Switzerland. It is located in the northern suburbs of Geneva. Geography Versoix has an area, , of . Of this area, or 29.1% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 38.1% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 32.4% is settled (buildings or roads), or 0.8% is either rivers or lakes and or 0.1% is unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 19.4% and transportation infrastructure made up 8.7%. while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 2.8%. Out of the forested land, 36.1% of the total land area is heavily forested and 2.0% is covered with o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Meteorological Society
The Royal Meteorological Society is an organization that promotes academic and public engagement in weather and climate science. Fellows of the Society must possess relevant qualifications, but Members can be lay enthusiasts. It publishes various journals, including the '' Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society''. The chief executive officer is Liz Bentley. Constitution The Royal Meteorological Society traces its origins back to 3 April 1850 when the British Meteorological Society was formed as "a society the objects of which should be the advancement and extension of meteorological science by determining the laws of climate and of meteorological phenomena in general". Along with nine others, including James Glaisher, John Drew, Edward Joseph Lowe, The Revd Joseph Bancroft Reade, and Samuel Charles Whitbread, Dr John Lee, an astronomer, of Hartwell House, near Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire founded in the library of his house the British Meteorological Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Marcet
William Marcet FRS FRCP (13 May 1828 – 4 March 1900) was President of the Royal Meteorological Society He was born the son of Francis Marcet, FRS and the grandson of Alexander Marcet, FRS in Geneva, Switzerland. He graduated M.D. as a physician from Edinburgh University in 1850 with the thesis ''"Fermentation"''. He was appointed Assistant Physician at the Westminster Hospital in 1853. He was then Lecturer on Chemistry and Forensic Medicine at the Westminster Hospital Medical School and Assistant Physician at Brompton Hospital from 1867. He carried out a number of field experiments in the Alps and the island of Tenerife on the effect of altitude on respiration and delivered the Croonian Lecture to the Royal College of Physicians in 1895 on the subject. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the Fellows of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hélène De Pourtalès
Countess Hélène de Pourtalès (born Helen Barbey; April 28, 1868 – November 2, 1945) was an American-born Swiss sailor who competed in the 1900 Summer Olympics in Paris representing Switzerland and became the first woman to win an Olympic gold medal. She was also the first woman to represent Switzerland at the Olympics. Early life Helen Barbey was born on April 28, 1868, in New York City, the daughter of Henry Isaac Barbey and Mary (née Lorillard) Barbey. Her maternal grandparents were Pierre Lorillard III and Catherine Anne () Lorillard. Her sister Eva was married to André Poupart, Baron de Neuflize in 1903, the older brother of Roberte Ponsonby, Countess of Bessborough. Her father, a financier and a director of the Buffalo, Rochester and Pittsburgh Railway, was a nephew of Adrian Georg Iselin and cousin of Charles Oliver Iselin. Her family included her uncle Pierre Lorillard IV; aunt Catherine Lorillard; uncle George Lyndes Lorillard, who married Marie Louise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Emperor
The German Emperor (, ) was the official title of the head of state and Hereditary monarchy, hereditary ruler of the German Empire. A specifically chosen term, it was introduced with the 1 January 1871 constitution and lasted until the abdication of Wilhelm II was announced on 9 November 1918. The Holy Roman Emperor is sometimes also called "German Emperor" when the historical context is clear, as derived from the Holy Roman Empire's official name of "Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation" from 1512. Following the German Revolution of 1918–1919, revolution of 1918, the head of state was the President of Germany (1919–1945), president of the Reich (), beginning with Friedrich Ebert. German Empire (1848–1849) In the wake of the German revolutions of 1848–1849, revolutions of 1848 and during the German Empire (1848–1849), Frederick William IV of Prussia, King Friedrich Wilhelm IV of Prussia was offered the title "Emperor of the Germans" () by the Frankfurt Parliament in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm I Of Germany
Wilhelm I (Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 1861 and German Emperor from 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the first head of state of a united Germany. He was regent of Prussia from 1858 to 1861 for his brother Frederick William IV. During the reign of his grandson Wilhelm II, he was known as Emperor Wilhelm the Great (German: ''Kaiser Wilhelm der Große''). The second son of Prince Frederick William and Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Wilhelm was not expected to ascend to the throne. His grandfather, King Frederick William II died the year he was born, and his father was crowned Frederick William III. Wilhelm fought with distinction during the War of the Sixth Coalition, and afterwards became a prominent figure within the Prussian Army. In 1840, his childless elder brother became King of Prussia, making him heir presumptive. Wilhelm played a major role in crushing the Revolutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of Prussia
The monarchs of Prussia were members of the House of Hohenzollern who were the hereditary rulers of the former German state of Prussia from its founding in 1525 as the Duchy of Prussia. The Duchy had evolved out of the Teutonic Order, a Roman Catholic crusader state and theocracy located along the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. The Teutonic Knights were under the leadership of a Grand Master, the last of whom, Albert, converted to Protestantism and secularized the lands, which then became the Duchy of Prussia. The Duchy was initially a vassal of the Kingdom of Poland, as a result of the terms of the Prussian Homage whereby Albert was granted the Duchy as part of the terms of peace following the Prussian War. When the main line of Prussian Hohenzollerns died out in 1618, the Duchy passed to a different branch of the family, who also reigned as Electors of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire. While still nominally two different territories, Prussia under the suzerainty o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guards Cuirassiers (Prussia)
The Guards Cuirassiers () were a heavy cavalry regiment of the Royal Prussian Army. Formed in 1815 as an Uhlans regiment, it was reorganized as a cuirassiers unit in 1821. The regiment was part of the Guards Cavalry Division and fought in the Second Schleswig War, the Austro-Prussian War, the Franco-Prussian War and World War I. The regiment was disbanded in September 1919. See also *List of Imperial German cavalry regiments Cavalry regiments of Germany, Regiments of the German Army in World War I, Lists of military units and formations of World War I, German Lists of military units and formations of Germany, Imperial German cavalry regiments ... References * External links *http://www.kuerassierregimenter.de/ {{Authority control Guards cavalry regiments of the Prussian Army Military units and formations established in 1815 Military units and formations disestablished in 1919 Royal guards 1815 establishments in Prussia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |