|
Henriette L'Hardy
Henriette Marie Françoise L'Hardy (9 December 1768– 27 January 1808) was the lady's companion from the Principality of Neuchâtel of the countess Sophie von Dönhoff, the Prussian lady-in-waiting and a morganatic spouse by bigamy to King Frederick William II of Prussia. She made a self-portrait. L'Hardy, born in Auvernier, was the eldest daughter of the officer in the French military François Nicolas L'Hardy (1715-1788) and Marie Henriette Rossel (1744-1821). She was a friend of Isabelle de Charrière since August 1791, with whom she exchanged over 240 letters and whose letters and manuscripts she inherited. In her letters Isabelle de Charrière called her often ''Lucinde'' after the heroine of Moliere's farce Le Médecin malgré lui. She was the lady's companion of Sophie von Dönhoff in Prussia: Berlin, Potsdam, Charlottenburg and Sanssouci since September 1791. In June 1792 they went together with the son Friedrich (born 24 January 1792) to the Principality of Neuch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady's Companion
A lady's companion was a woman of genteel birth who lived with a woman of rank or wealth as Affinity (medieval), retainer. The term was in use in the United Kingdom from at least the 18th century to the mid-20th century but it is now archaism, archaic. The profession is known in most of the Western world. The role was related to the position of lady-in-waiting, which by the 19th century was applied only to the female retinue, retainers of female members of the royal family. Ladies-in-waiting were usually women from the most privileged backgrounds who took the position for the prestige of associating with royalty, or for the enhanced marriage prospects available to those who spent time at Royal court, court, but lady's companions usually took up their occupation because they needed to earn a living and have somewhere to live. A companion is not to be confused with lady's maid, a female personal attendant roughly equivalent to a "gentleman's gentleman" or valet. Status and duties Like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm, Count Brandenburg
Friedrich Wilhelm, Count of Brandenburg (24 January 1792 – 6 November 1850) was a morganatic son of King Frederick William II and politician, who served as Minister President of Prussia from 1848 until his death. Life Born in the Prussian capital Berlin, he was the son of King Frederick William II of Prussia (1744–1797) from his morganatic marriage with Sophie von Dönhoff (1768–1838). He and his younger sister Julie (1793–1848) received the comital title ''von Brandenburg'' in 1794, and were raised with the sons of ''Hofmarschall'' Valentin von Massow. His sister married Duke Frederick Ferdinand of Anhalt-Köthen in 1816. On 18 April 1806, Friedrich Wilhelm joined the Prussian Army by entering the ''Gardes du Corps'' regiment and from the next year participated in the Napoleonic War of the Fourth Coalition. In 1812 he achieved the rank of ''Rittmeister'' in the staff of Ludwig Yorck von Wartenburg, leading the Prussian auxiliary forces in support of the French invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1768 Births
Events January–March * January 9 – Philip Astley stages the first modern circus, with acrobats on galloping horses, in London. * February 11 – Samuel Adams's circular letter is issued by the Massachusetts House of Representatives, and sent to the other Thirteen Colonies. Refusal to revoke the letter will result in dissolution of the Massachusetts Assembly, and (from October) incur the institution of martial law to prevent civil unrest. * February 24 – With Russian troops occupying the nation, opposition legislators of the national legislature having been deported, the government of Poland signs a treaty virtually turning the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth into a protectorate of the Russian Empire. * February 27 – The first Secretary of State for the Colonies is appointed in Britain, the Earl of Hillsborough. * February 29 – Five days after the signing of the treaty, a group of the szlachta, Polish nobles, establishes the Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastel
A pastel () is an art medium in a variety of forms including a stick, a square a pebble or a pan of color; though other forms are possible; they consist of powdered pigment and a binder. The pigments used in pastels are similar to those used to produce some other colored visual arts media, such as oil paints; the binder is of a neutral hue and low saturation. The color effect of pastels is closer to the natural dry pigments than that of any other process. Pastels have been used by artists since the Renaissance, and gained considerable popularity in the 18th century, when a number of notable artists made pastel their primary medium. An artwork made using pastels is called a pastel (or a pastel drawing or pastel painting). ''Pastel'' used as a verb means to produce an artwork with pastels; as an adjective it means pale in color. Pastel media Pastel sticks or crayons consist of powdered pigment combined with a binder. The exact composition and characteristics of an individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therese Forster
Marie Therese Forster (10 August 1786 – 3 June 1862) was a German educator, writer, correspondent and editor. Born in Vilnius in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth to Georg Forster and his wife Therese Huber, Therese, she spent her early childhood in Mainz. Her father was active in the revolutionary Republic of Mainz, and she and her mother fled the city in late 1792. After her father's death, she was raised by her mother and stepfather Ludwig Ferdinand Huber. From 1801 to 1805, Forster lived with Dutch-Swiss writer Isabelle de Charrière and collaborated with her on an epistolary novel. Until 1826, she worked as a teacher and educator, first at Philipp Emanuel von Fellenberg's school in Hofwil and then for several upper-class families. After her mother's 1829 death, she lived with family and educated her nieces and nephews. From 1840, she collaborated with Georg Gottfried Gervinus on the first complete edition of her father's works, which were published by F. A. Brockhaus AG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
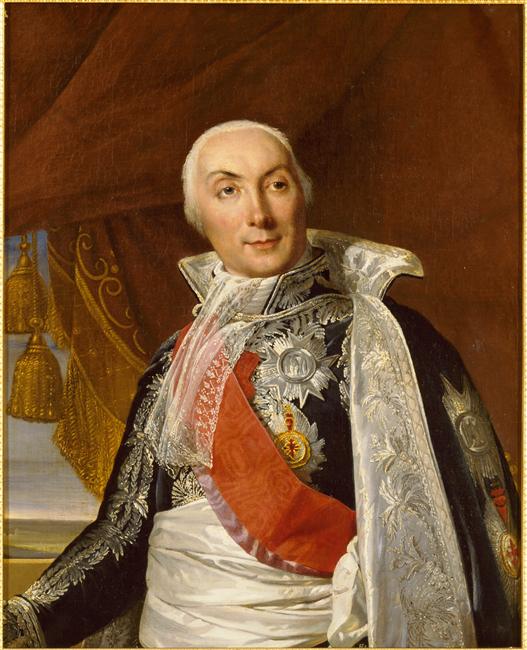
Louis Philippe, Comte De Ségur
Louis Philippe, comte de Ségur (10 December 175327 August 1830) was a French diplomat and historian. Biography Ségur was born in Paris, the son of Philippe Henri, marquis de Ségur and Louise Anne Madeleine de Vernon. He entered the army in 1769, served in the American War of Independence in 1781 as a colonel under Rochambeau. This cites: * Duc de Broglie, "Deux Français aux États-Unis" in ''Mélanges publiés par la Société des Bibliophiles français'' (2nd part, 1903) * A. Cornereau, "La Mission du comte de Ségur dans la xviiie division militaire," in the ''Mémoires de la Société bourguignonne de géographie et d'histoire'' (vol. 17, 1901) In 1784 he was sent as minister plenipotentiary to Saint Petersburg, where he was received into the intimacy of the empress Catherine II and wrote some comedies for her theatre. At Saint Petersburg he concluded (in January 1787) a commercial treaty which was exceedingly advantageous to France. The same year he accompanied Catherine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angermünde
Angermünde () is a town in the district of Uckermark in the state of Brandenburg, Germany. It is about northeast of Berlin, the capital of Germany. The population is about 14,000, but has been declining since its traditional industrial base, enamel-working, has declined. An administrative sub-centre of its district, it has several Protestant churches, a former Franciscan church, a number of schools of higher learning and a recently refurbished historic marketplace with an old town hall. Located in the game-filled forests of the Uckermark, with its many lakes, it now relies heavily on tourism and the sources of revenue linked to it. Since 2010, Angermünde is a federally declared resort town. Name The name Angermünde is an abbreviation of the older town of Tangermünde, for a while the town was named New-Tangermünde (''Neu-Tangermünde''), until it was changed to "Angermünde", with ''Anger'' being German for a central square in a town. Geography With an area of around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baar, Switzerland
Baar () is a municipality in the canton of Zug in Switzerland. History Baar is first mentioned in 1045 as ''Barra''. Geography Baar has an area, , of . Of this area, 51% is used for agricultural purposes, while 25% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 22.8% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (0.8%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains). The municipality is located in the northern portion of the flood plain of the Lorze river. It was originally a linear village along the road between Lake Zug and Lake Zurich. Since the 1960s it has grown rapidly. It consists of the village of Baar and the former hamlets of Allenwinden, Blickensdorf and Inwil, as well as the farm houses of Deinikon. Demographics Baar has a population (as of ) of . , 24.9% of the population was made up of foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years, the population has grown at a rate of 20.9%. Most of the population () speaks German (83.1%), with Italian being second most common ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
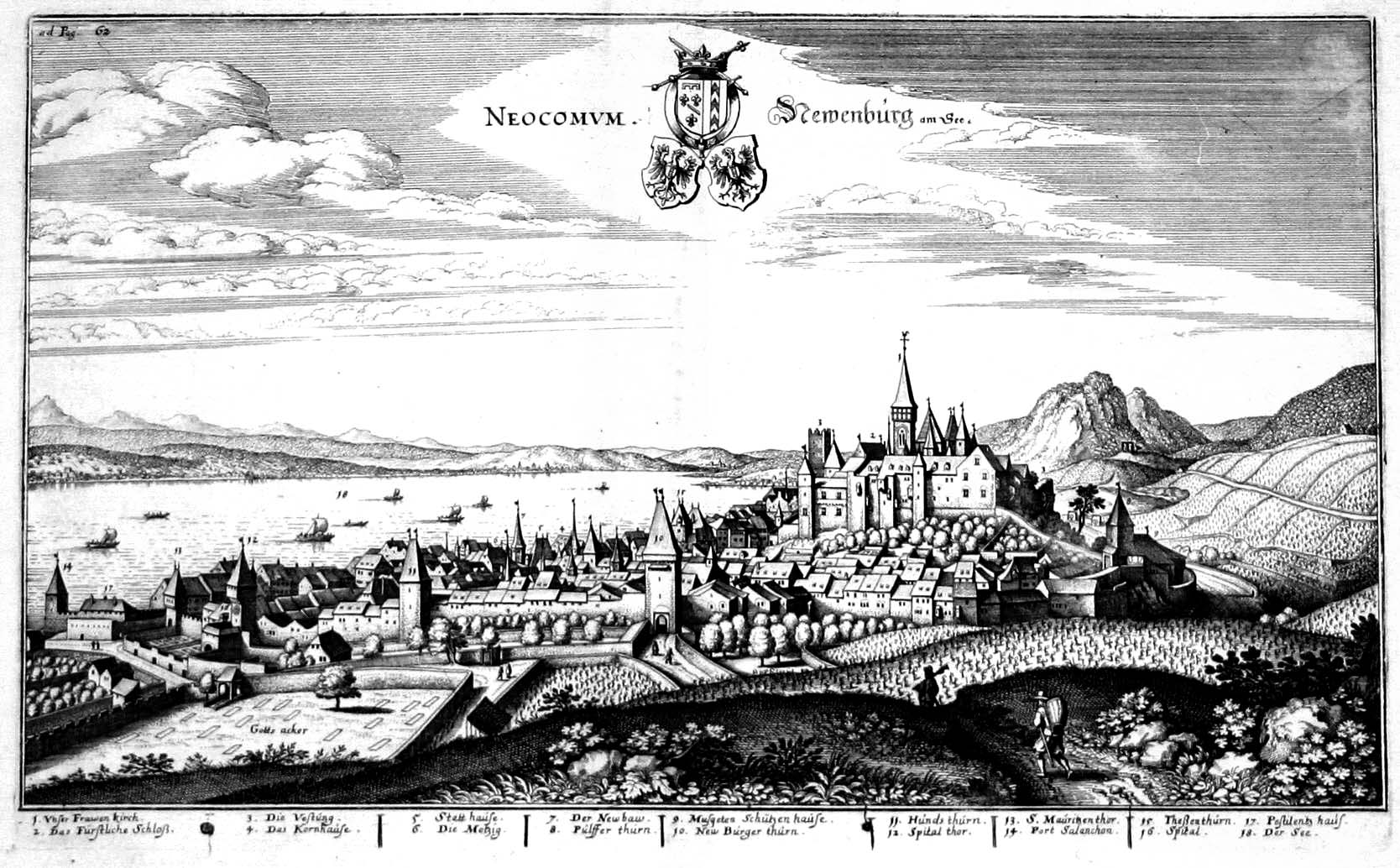
Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier , twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy) Neuchâtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel, situated on the shoreline of Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Neuch� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombier, Neuchâtel
Colombier () is a former municipality in the Boudry District in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland. The municipalities of Auvernier, Bôle and Colombier merged on 1 January 2013 into the new municipality of Milvignes.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 2 January 2013 History |
Canton Of Neuchâtel
The Republic and Canton of Neuchâtel (french: République et Canton de Neuchâtel); rm, Chantun Neuchâtel; it, Cantone di Neuchâtel is a French-speaking canton in western Switzerland. In 2007, its population was 169,782, of whom 39,654 (or 23.4%) were foreigners. The capital is Neuchâtel. History The only part of present-day Switzerland to enter the Confederation as a principality (on May 19, 1815), Neuchâtel has a unique history. Its first recorded ruler, Rudolph III of Burgundy, mentioned Neuchâtel in his will in 1032. The dynasty of Ulrich count of Fenis (Hasenburg) took over the town and its territories in 1034. The dynasty prospered and, by 1373, all the lands now part of the canton belonged to the count. In 1405, the cities of Bern and Neuchâtel entered a union. The lands of Neuchâtel had passed to the Zähringen lords of Freiburg in the late 14th century as inheritance from the childless Elisabeth, Countess of Neuchâtel, to her nephews, and then in 1458 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |