|
Hemichromis Letourneuxi
''Hemichromis letourneuxi'' is a species of cichlid which is native to West Africa and is popular in the aquarium hobby and it has been introduced to the Caribbean and the south-east United States where it is invasive. Description ''Hemichromis letourneuxi'' is a small species of fish that has quite a long, thin body and a rounded tail and which has 13–15 spines in the dorsal fin and 3 in the anal fin. It has a highly variable background colour to the body which may be green-yellow to red-brown or even almost black, this colouration is dependent on various factors such as the sex of the fish, the season, the nature of the fish's habitat and stress. Breeding males may develop red colouration over the gills and underside. Both sexes have a limited amount of small, brilliant blue iridescent spots on the head, body, and fins and these may be more obvious in breeding adults. It has a dark black spot situated above the lateral line on the flanks and smaller blotches on gill covers an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Émile Sauvage
Henri Émile Sauvage (22 September 1842 in Boulogne-sur-Mer – 3 January 1917 in Boulogne-sur-Mer) was a French paleontologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. He was a leading expert on Mesozoic fish and reptiles.Dinosaurs and Other Extinct Saurians: A Historical Perspective edited by Richard Moody He worked as a curator at the Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle in , and published extensively on |
Hemichromis Lifalili
''Hemichromis lifalili'', common name blood-red jewel cichlid, is a species of fish in the family Cichlidae. Description ''Hemichromis lifalili'' can grow up to long. They are red-orange or bright red with rows of small blue spots all over the body, the head and fins. Two dark spots are present on the sides, the first on the opercle, the second in the middle of the body, while they lack the dark spot at the base of the tail present in ''Hemichromis bimaculatus''. In the mating period almost the whole body is red. Outside the spawning season adult males and females can be distinguished mainly by their body shape. The females are much leaner and show a brighter red. The males are much stronger and have a more massive head than females. Diet These fishes mainly feeds on worms, crustaceans, insects, small fish, but also on vegetable matter. Reproduction This species, as the more common and congener ''Hemichromis bimaculatus The African jewelfish (''Hemichromis bimaculatus''), al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning "pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cichlidogyrus
''Cichlidogyrus'' is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Ancyrocephalidae. The type-species of the genus is '' Cichlidogyrus arthracanthus'' Paperna, 1960, by original designation. All the species of the genus are parasites on the gills of fish, namely African Cichlidae, Nandidae and Cyprinodontidae. Species of ''Cichlidogyrus'' are parasitic in many clichlid species in the Lake Tanganyika; a recent study (2016) has shown that species which are parasite on deep-water fish show reduced parasite-host specificity in comparison to species from littoral waters, probably an adaptation to low host availability. According to Antoine Pariselle and Louis Euzet, 71 species of ''Cichlidogyrus'' were known in 2009 - new species have been described since. Nikol Kmentová, Milan Gelnar, Stephan Koblmüller and Maarten P.M. Vanhove estimated that the number of species was more than 100 in 2016 and Chahrazed Rahmouni, Maarten P. M. Vanhove and Andrea Šimková ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenea
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.L.A. Tubbsa et al. (2005). "Effects of temperature on fecundity in vitro, egg hatching and reproductive development of ''Benedenia seriolae'' and ''Zeuxapta seriolae'' (Monogenea) parasitic on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi". ''International Journal for Parasitology''(35), 315–327. Some monogeneans are oviparous (egg-laying) and some are viviparous (live-bearing). Oviparous varieties release eggs into the water. Viviparous varieties release larvae, which immediately attach to another host. The genus ''Gyrodactylus'' is an example of a viviparous variety, while the genus ''Dactylogyrus'' is an example of an oviparous variety. Signs and symptoms Freshwater fish that become infected with this parasite become let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
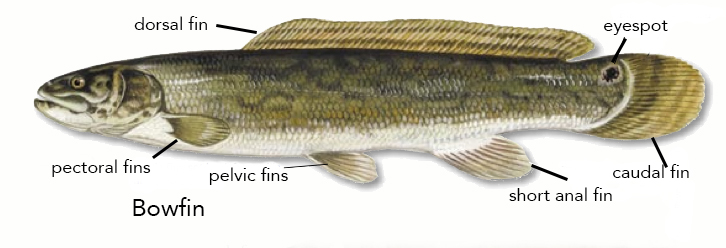
Bowfin
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being the sole surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "primitive fish" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Now, their range is limited to much of the eastern United States and adjacent southern Canada, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longnose Gar
The longnose gar (''Lepisosteus osseus''), also known as longnose garpike or billy gar, is a ray-finned fish in the family Lepisosteidae. The genus may have been present in North America for about 100 million years. References are made to gars being a primitive group of bony fish because they have retained some primitive features, such as a spiral valve intestine, but they are not primitive in the sense of not being fully developed. They have an olive brown to green, torpedo-shaped body armored with ganoid scales, elongated jaws that form a needle-like snout nearly three times the length of its head, and a row of numerous sharp, cone-shaped teeth on each side of the upper jaw. They typically inhabit freshwater lakes, brackish water near coastal areas, swamps, and sluggish backwaters of rivers and streams. They can breathe both air and water, which allows them to inhabit aquatic environments that are low in oxygen. Longnose gar are found along the east coasts of North and Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largemouth Bass
The largemouth bass (''Micropterus salmoides'') is a carnivorous freshwater gamefish in the Centrarchidae ( sunfish) family, a species of black bass native to the eastern and central United States, southeastern Canada and northern Mexico, but widely introduced elsewhere. It is known by a variety of regional names, such as the widemouth bass, bigmouth bass, black bass, bucketmouth, largies, Potter's fish, Florida bass, Florida largemouth, green bass, bucketmouth bass, Green trout, gilsdorf bass, Oswego bass, LMB, and southern largemouth and northern largemouth. The largemouth bass is the state fish of Georgia and Mississippi, and the state freshwater fish of Florida and Alabama. Taxonomy The largemouth bass was first formally described as ''Labrus salmoides'' in 1802 by the French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède with the type locality given as the Carolinas. Lacépède based his description on an illustration of a specimen collected by Louis Bosc near Charleston, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Gar
The Florida gar (''Lepisosteus platyrhincus'') is a species of gar found in the US from the Savannah River and Ochlockonee River watersheds of Georgia and throughout peninsular Florida. Florida gar can reach a length over 3 ft (91 cm). The young feed on zooplankton and insect larvae, as well as small fish. Adults mainly eat fish, shrimp, and crayfish. Although edible, they are not popular as food. The roe is highly toxic to many animals, including humans and birds. Appearance This is a mid-sized species of gar. It measures from long and typically weighs . According to the IGFA, the record weight for this species is . This species has irregular round, black spots on the top of its head and over the entire body including the anal fin. The distance of the eyes is less than two-thirds the length of the snout. Also, it has a shorter, broad snout with a single row of irregularly spaced sharp teeth on the upper and lower jaws. No bony scales are on the throat. Their color is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Snook
The common snook (''Centropomus undecimalis'') is a species of Seawater, marine fish in the family (biology), family Centropomidae of the order (biology), order Perciformes. The common snook is also known as the sergeant fish or robalo. It was originally assigned to the Sciaenidae, sciaenid genus ''Sciaena;'' ''Sciaena undecimradiatus'' and ''Centropomus undecimradiatus'' are obsolete synonyms for the species. One of the largest Centropomidae, snooks, ''C. undecimalis'' grows to a maximum overall length of , but the common length is . The IGFA world record is 24.32 kg (53 lb 10 oz) caught in Parismina Ranch, Costa Rica, by Rafael Montalvo. Of typical centropomid form, it possesses drab coloration except for a distinctive black lateral line. It can also have bright yellow pelvic and caudal fins, especially during spawn. General ecology Reproductive ecology The common snook is a protandric hermaphrodite fish species. Its spawning season appears to span from April to Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)