|
Heinrich II Von Rotteneck
Heinrich II von Rotteneck (died 7 August 1296) was prince-bishop of Regensburg from 1277 to 1296. Family Heinrich II von Rotteneck was the son of Count Meinard of Rotteneck and Beatrix, born Countess of Moosburg. His family gave their name to the town of Rottenegg, near Geisenfeld. He was the last of his line. His sister was the mother of Konrad II von Pfeffenhausen, Bishop of Eichstätt. Bishop Heinrich became bishop of Regensburg in 1277. The Regensburg Cathedral had been damaged in a great fire in 1273, and many of its treasures had been lost. On 21 August 1279 Heinrich von Rotteneck sold the Rottenegg castle and its possessions including the Mainburg castle to Duke Ludwig II of Bavaria to obtain funds for rebuilding his cathedral. As well as promoting construction of the new Gothic cathedral, Heinrich donated many devices and vestments. He introduced choral singing, and brought in two monks from Heilsbronn Abbey to give lessons in music. Heinrich and Gottfried, Bishop of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Regensburg
The Diocese of Regensburg ( la, Dioecesis Ratisbonensis) is a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical territory seated in Regensburg, Germany. Its district covers parts of northeastern Bavaria; it is subordinate to the archbishop of Munich and Freising. , the diocese had 1.20 million Catholics, constituting 70% of its total population. The current bishop is Rudolf Voderholzer. The main diocesan church is Saint Peter in Regensburg. The diocese is divided into eight regions and 33 deaneries with 769 parishes. It covers an area of 14,665 km². History The diocese was founded in 739 by Saint Boniface; it was originally subordinate to the archbishop of Salzburg. By the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803, the Bishopric was incorporated into the new Archbishopric of Regensburg. Ordinaries *Friedrich von Parsberg † (24 May 1437 Appointed – Nov 1449 Died) *Friedrich von Plankenfels † (23 Jan 1450 Appointed – 24 May 1457 Died) * Ruprecht Pfalzgraf von Rhein † (2 Sep 1457 Appo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry XIII, Duke Of Bavaria
Henry XIII (19 November 1235 – 3 February 1290 in Burghausen), member of the Wittelsbach dynasty, was Duke of Lower Bavaria. Family He was the younger son of Otto II and Agnes of Brunswick. Biography In 1254, he succeeded his father together with his brother Louis II in Bavaria and the Palatinate. The brothers divided their land in 1255 against the law. Henry received Lower Bavaria and Louis Upper Bavaria and the Palatinate. It was the first of many divisions of the duchy. Henry resided in Landshut and, in 1255, the work for the main castle of Burghausen Castle was begun. As the division of the duchy was against the law, it caused anger of the Bishops in Bavaria who allied with Ottokar II of Bohemia in 1257. In August 1257, Ottokar invaded Bavaria, but Henry and Louis managed to repulse the attack. It was one of the rare concerted and harmonious actions of both brothers who often argued. Henry was also later several times at war against the Archbishopric of Salzburg an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Roman Catholic Bishops In Bavaria
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1296 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antependium
An ''antependium'' (from Latin ''ante-'' and ''pendēre'' "to hang before"; pl: ''antependia''), also known as a ''parament'' or ''hanging'', or, when speaking specifically of the hanging for the altar, an altar frontal (Latin: ''pallium altaris''), is a decorative piece, usually of textile, but also metalwork, stone or other material that can adorn a Christian altar. Specifically, and as the etymology of the word suggests, an antependium hangs down in front of whatever it covers, and is to be distinguished from the altar linens which are used in the service of the Eucharist, and an altar cloth which covers the top of the altar table (''mensa''). Types of antependia Western Christianity "Antependium" is the word used for elaborate fixed altar frontals, which, in large churches and especially in the Ottonian art of the Early Medieval period, were sometimes of gold studded with gems, enamels and ivories, and in other periods and churches often carved stone, painted wood panel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
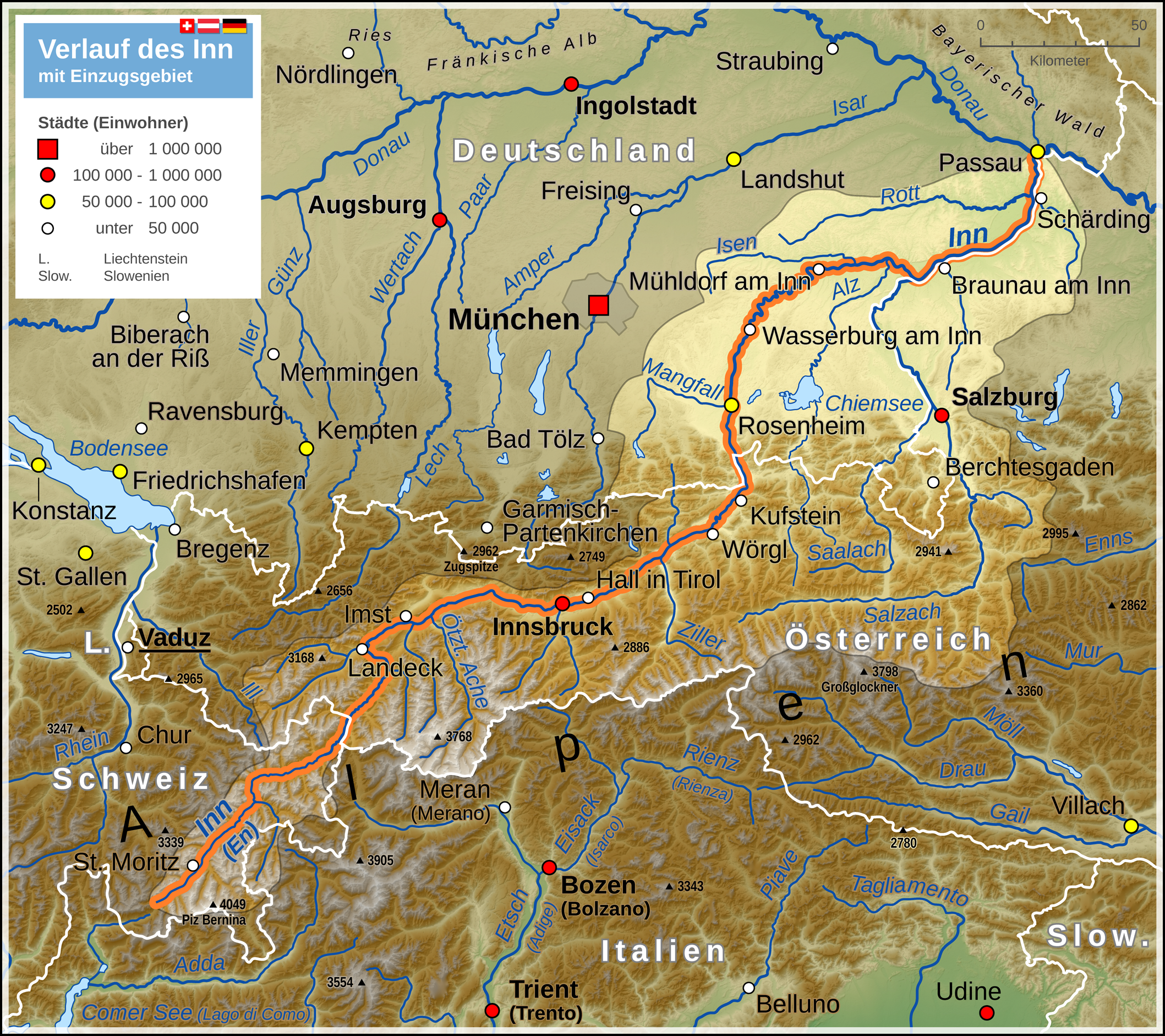
Inn (river)
, image = UnterinntalWest.JPG , image_caption = Lower Inn valley from Rattenberg castle , source1_location = Swiss Alps (Lägh dal Lunghin) , source1_elevation = , source1_coordinates= , mouth_location = Danube (Passau) , mouth_elevation = , mouth_coordinates = , progression = , subdivision_type1 = Countries , subdivision_name1 = , subdivision_type2 = Cities , subdivision_name2 = , length = , discharge1_location= mouth , discharge1_avg = , basin_size = The Inn ( la, Aenus; rm, En) is a river in Switzerland, Austria and Germany. The river is long. It is a right tributary of the Danube and it is the third largest tributary of the Danube by discharge. The highest point of its drainage basin is the summit of Piz Bernina at . The Engadine, the valley of the En, is the only Swiss valley whose waters end up in the Black Sea (via the Danube). Etymology The name Inn is derived from the old Celtic words ''en'' and ''enios'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Salzburg
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Salzburg ( la, Archidioecesis Salisburgensis) is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in Austria. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian archdioceses, serving alongside the Archdiocese of Vienna. The Archbishopric of Salzburg was a prince-bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire until 1803, when it was secularized as the Electorate of Salzburg. The archdiocese was reestablished in 1818 without temporal power. Suffragan dioceses * Feldkirch * Graz–Seckau * Gurk * Innsbruck Episcopal Ordinaries Abbot-Bishops of Iuvavum c. 300s – c. 482 * St. Maximus of Salzburg, died 476. ''Abandoned after c. 482'' Bishops of Iuvavum (from 755, Salzburg) *St. Ruprecht, born c. 543 ''or'' c. 698 – c. 718. *Vitalis *Erkenfried *Ansologus *Ottokar *Flobrigis *Johann I * St. Virgil, c. 745 ''or'' c. 767 – c. 784 Archbishops of Salzburg, 798–1213 * Arno 784–821 * Adalram 821–836 * Leutram 836–859 * Adalwin 859–873 * Adalber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I Of Germany
Albert I of Habsburg (german: Albrecht I.) (July 12551 May 1308) was a Duke of Austria and Styria from 1282 and King of Germany from 1298 until his assassination. He was the eldest son of King Rudolf I of Germany and his first wife Gertrude of Hohenberg. Sometimes referred to as 'Albert the One-eyed' because of a battle injury that left him with a hollow eye socket and a permanent snarl. Biography From 1273 Albert ruled as a landgrave over his father's Swabian (Further Austrian) possessions in Alsace. In 1282 his father, the first German monarch from the House of Habsburg, invested him and his younger brother Rudolf II with the duchies of Austria and Styria, which he had seized from late King Ottokar II of Bohemia and defended in the 1278 Battle on the Marchfeld. By the 1283 Treaty of Rheinfelden his father entrusted Albert with their sole government, while Rudolf II ought to be compensated by the Further Austrian Habsburg home territories – which, however, never happened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Passau
The Diocese of Passau is a Roman Catholic diocese in Germany that is a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Munich and Freising."Diocese of Passau" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016"Diocese of Passau" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 Though similar in name to the Prince-Bishopric of Passau—an ecclesiastical principality that existed for centuries until it was |
Moosburg
Moosburg an der Isar (Central Bavarian: ''Mooschbuag on da Isa'') is a town in the ''Landkreis'' Freising of Bavaria, Germany. The oldest town between Regensburg and Italy, it lies on the river Isar at an altitude of 421 m (1381 ft). It has 18,033 inhabitants (2016) and covers an area of 44 km2. It is easily reached by the A 92 autobahn and regional trains on the Munich–Regensburg line. Furthermore, it takes just 20 minutes to get to Munich Airport. Moosburg is popular with commuters who travel to Munich, Freising, and Munich Airport. There is considerable industry in the town consisting of chemical, electro-technical, food processing, and machine-building plants. History There was a Benedictine abbey in Moosburg in the 8th century: a cluster of dwellings and artisans sprang up around it. Duke Heinrich der Löwe started the construction of the Kastulus Minster (cathedral) in 1171, dedicated to Saint Castulus – whose supposed relics were brought to the cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heilsbronn Abbey
Heilsbronn Abbey was a Cistercian monastery at Heilsbronn in the district of Ansbach in Middle Franconia, Bavaria, Germany. It was part of the Diocese of Eichstätt. History It was founded in 1132–33 by Saint Otto of Bamberg and was settled by monks from Ebrach Abbey, under the first abbot Rapotho. It was one of the wealthiest monasteries of Germany, with possessions around Franconia as far as Regensburg and in Württemberg. These rich endowments were mostly made by the dukes of Abenberg and their heirs, the Hohenzollern Burgraves of Nuremberg. It was the hereditary burial-place of the Hohenzollern family and ten burgraves of Nuremberg, five margraves and three electors of Brandenburg, besides many other persons of note, were buried here. Reformation and dissolution Heilsbronn was a flourishing monastery until the time of the Reformation. In 1530 Abbot John Schopper (1529–1540) founded a monastic school here, which later became a Protestant school for princes, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (lit. French work); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was reconstructed between 1140 and 1144, draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)






.jpg)