|
Hawk-dove
The game of chicken, also known as the hawk–dove game or snowdrift game, is a model of conflict for two players in game theory. The principle of the game is that while the ideal outcome is for one player to yield (to avoid the worst outcome if neither yields), the individuals try to avoid it out of pride for not wanting to look like a "chicken". Each player taunts the other to increase the risk of shame in yielding. However, when one player yields, the conflict is avoided, and the game is for the most part over. The name "chicken" has its origins in a game in which two drivers drive toward each other on a collision course: one must swerve, or both may die in the crash, but if one driver swerves and the other does not, the one who swerved will be called a ":wikt:chicken, chicken", meaning a coward; this terminology is most prevalent in political science and economics. The name "hawk–dove" refers to a situation in which there is a competition for a shared resource and the conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of Attrition (game)
In game theory, the ''war of attrition'' is a dynamic timing game in which players choose a time to stop, and fundamentally trade off the strategic gains from outlasting other players and the real costs expended with the passage of time. Its precise opposite is the ''pre-emption game'', in which players elect a time to stop, and fundamentally trade off the strategic costs from outlasting other players and the real gains occasioned by the passage of time. The model was originally formulated by John Maynard Smith; a mixed evolutionarily stable strategy (ESS) was determined by Bishop & Cannings. An example is a second price ''all-pay'' auction, in which the prize goes to the player with the highest bid and each player pays the loser's low bid (making it an all-pay sealed-bid second-price auction). Examining the game To see how a war of attrition works, consider the all pay auction: Assume that each player makes a bid on an item, and the one who bids the highest wins a resource of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions among rational agents. Myerson, Roger B. (1991). ''Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict,'' Harvard University Press, p.&nbs1 Chapter-preview links, ppvii–xi It has applications in all fields of social science, as well as in logic, systems science and computer science. Originally, it addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which each participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by those of other participants. In the 21st century, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations; it is now an umbrella term for the science of logical decision making in humans, animals, as well as computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum game and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
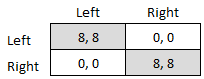
Coordination Game
A coordination game is a type of simultaneous game found in game theory. It describes the situation where a player will earn a higher payoff when they select the same course of action as another player. The game is not one of pure conflict, which results in multiple pure strategy Nash equilibria in which players choose matching strategies. Figure 1 shows a 2-player example. Both (Up, Left) and (Down, Right) are Nash equilibria. If the players expect (Up, Left) to be played, then player 1 thinks their payoff would fall from 2 to 1 if they deviated to Down, and player 2 thinks their payoff would fall from 4 to 3 if they chose Right. If the players expect (Down, Right), player 1 thinks their payoff would fall from 2 to 1 if they deviated to Up, and player 2 thinks their payoff would fall from 4 to 3 if they chose Left. A player's optimal move depends on what they expect the other player to do, and they both do better if they coordinate than if they played an off-equilibrium combinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick (; July 26, 1928 – March 7, 1999) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and photographer. Widely considered one of the greatest filmmakers of all time, his films, almost all of which are adaptations of novels or short stories, cover a wide range of genres and are noted for their innovative cinematography, Black comedy, dark humor, realistic attention to detail and extensive set designs. Kubrick was raised in the Bronx, New York City, and attended William Howard Taft High School (New York City), William Howard Taft High School from 1941 to 1945. He received average grades but displayed a keen interest in literature, photography, and film from a young age, and taught himself all aspects of film production and directing after graduating from high school. After working as a photographer for ''Look (American magazine), Look'' magazine in the late 1940s and early 1950s, he began making short films on shoestring budgets, and made his first major Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Holding Potential
In biology, resource holding potential (RHP) is the ability of an animal to win an all-out fight if one were to take place. The term was coined by Geoff Parker to disambiguate physical fighting ability from the motivation to persevere in a fight (Parker, 1974). Originally the term used was 'resource holding power', but 'resource holding potential' has come to be preferred. The latter emphasis on 'potential' serves as a reminder that the individual with greater RHP does not always prevail. An individual with more RHP may lose a fight if, for example, it is less motivated (has less to gain by winning) than its opponent. Mathematical models of RHP and motivation ( resource value or V) have traditionally been based on the hawk-dove game (e.g. Hammerstein, 1981) in which subjective resource value is represented by the variable 'V'. In addition to RHP and V, George Barlow (Barlow et al., 1986) proposed that a third variable, which he termed 'daring', played a role in determining figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawk-Dove Transforming Into Prisoner's Dilemma
The game of chicken, also known as the hawk–dove game or snowdrift game, is a model of conflict for two players in game theory. The principle of the game is that while the ideal outcome is for one player to yield (to avoid the worst outcome if neither yields), the individuals try to avoid it out of pride for not wanting to look like a "chicken". Each player taunts the other to increase the risk of shame in yielding. However, when one player yields, the conflict is avoided, and the game is for the most part over. The name "chicken" has its origins in a game in which two drivers drive toward each other on a collision course: one must swerve, or both may die in the crash, but if one driver swerves and the other does not, the one who swerved will be called a "chicken", meaning a coward; this terminology is most prevalent in political science and economics. The name "hawk–dove" refers to a situation in which there is a competition for a shared resource and the contestants can choo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner's Dilemma
The Prisoner's Dilemma is an example of a game analyzed in game theory. It is also a thought experiment that challenges two completely rational agents to a dilemma: cooperate with their partner for mutual reward, or betray their partner ("defect") for individual reward. This dilemma was originally framed by Merrill Flood and Melvin Dresher while working at RAND in 1950. Albert W. Tucker appropriated the game and formalized it by structuring the rewards in terms of prison sentences and named it "prisoner's dilemma". William Poundstone in his 1993 book ''Prisoner's Dilemma'' writes the following version:Two members of a criminal gang are arrested and imprisoned. Each prisoner is in solitary confinement with no means of speaking to or exchanging messages with the other. The police admit they don't have enough evidence to convict the pair on the principal charge. They plan to sentence both to two years in prison on a lesser charge. Simultaneously, the police offer each prisoner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George R
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith (6 January 1920 – 19 April 2004) was a British theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he took a second degree in genetics under the well-known biologist J. B. S. Haldane. Maynard Smith was instrumental in the application of game theory to evolution with George R. Price, and theorised on other problems such as the evolution of sex and signalling theory. Biography Early years John Maynard Smith was born in London, the son of the surgeon Sidney Maynard Smith, but following his father's death in 1928, the family moved to Exmoor, where he became interested in natural history. Quite unhappy with the lack of formal science education at Eton College, Maynard Smith took it upon himself to develop an interest in Darwinian evolutionary theory and mathematics, after having read the work of old Etonian J. B. S. Haldane, whose books were in the school's library despite the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Strategy
In game theory, a player's strategy is any of the options which they choose in a setting where the outcome depends ''not only'' on their own actions ''but'' on the actions of others. The discipline mainly concerns the action of a player in a game affecting the behavior or actions of other players. Some examples of "games" include chess, bridge, poker, monopoly, diplomacy or battleship. A player's strategy will determine the action which the player will take at any stage of the game. In studying game theory, economists enlist a more rational lens in analyzing decisions rather than the psychological or sociological perspectives taken when analyzing relationships between decisions of two or more parties in different disciplines. The strategy concept is sometimes (wrongly) confused with that of a move. A move is an action taken by a player at some point during the play of a game (e.g., in chess, moving white's Bishop a2 to b3). A strategy on the other hand is a complete algorithm for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nash Equilibrium
In game theory, the Nash equilibrium, named after the mathematician John Nash, is the most common way to define the solution of a non-cooperative game involving two or more players. In a Nash equilibrium, each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no one has anything to gain by changing only one's own strategy. The principle of Nash equilibrium dates back to the time of Cournot, who in 1838 applied it to competing firms choosing outputs. If each player has chosen a strategy an action plan based on what has happened so far in the game and no one can increase one's own expected payoff by changing one's strategy while the other players keep their's unchanged, then the current set of strategy choices constitutes a Nash equilibrium. If two players Alice and Bob choose strategies A and B, (A, B) is a Nash equilibrium if Alice has no other strategy available that does better than A at maximizing her payoff in response to Bob choosing B, and Bob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-excludable Good
In economics, a good, service or resource are broadly assigned two fundamental characteristics; a degree of excludability and a degree of rivalry. Excludability is defined as the degree to which a good, service or resource can be limited to only paying customers, or conversely, the degree to which a supplier, producer or other managing body (e.g. a government) can prevent "free" consumption of a good. Excludability was originally proposed in 1954 by American economist Paul Samuelson where he formalised the concept now known as public goods, i.e. goods that are both non-rivalrous and non-excludable. Samuelson additionally highlighted the market failure of the free-rider problem that can occur with non-excludable goods. Samuelson's theory of good classification was then further expanded upon by Richard Musgrave in 1959, Garret Hardin in 1968 who expanded upon another key market inefficiency of non-excludeable goods; the tragedy of the commons. Excludability is not an inherent chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

