|
Hassall's Corpuscles
Hassall's corpuscles (or thymic corpuscles (bodies)) are structures found in the medulla of the human thymus, formed from eosinophilic type VI epithelial reticular cells arranged concentrically. These concentric corpuscles are composed of a central mass, consisting of one or more granular cells, and of a capsule formed of epithelioid cells. They vary in size with diameters from 20 to more than 100μm, and tend to grow larger with age. They can be spherical or ovoid and their epithelial cells contain keratohyalin and bundles of cytoplasmic fibres. Later studies indicate that Hassall's corpuscles differentiate from medullary thymic epithelial cells after they lose autoimmune regulator (AIRE) expression. They are named for Arthur Hill Hassall, who discovered them in 1846. The function of Hassall's corpuscles is currently unclear, and the absence of this structure in the thymus of most murine species (except for the New Zealand White Mouse strain) has previously restricted mechanisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a micros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murine
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents. Description The Murinae are native to Africa, Europe, Asia, and Australia. They are terrestrial placental mammals. They have also been introduced to all continents except Antarctica, and are serious pest animals. This is particularly true in island communities where they have contributed to the endangerment and extinction of many native animals. Two prominent murine species have become vital laboratory animals: the brown rat and house mouse are both used as medical subjects. The murines have a distinctive molar pattern that involves three rows of cusps instead of two, the primitive pattern seen most fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis, is a chronic disease in which the body interprets the thyroid glands and its hormone products T3, T4 and TSH as threats, therefore producing special antibodies that target the thyroid's cells, thereby destroying it. It may present with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism and with or without a goiter. Signs and symptoms The symptoms may vary depending on the thyroid function, i.e. hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism can cause sweating, rapid heart rate, anxiety, tremors, fatigue, difficulty sleeping, sudden weight loss, and protruding eyes. Hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, fatigue, dry skin, hair loss, intolerance to cold, and constipation. The effects of this disease may be permanent but can sometimes be transient. Symptoms may come and go depending on whether the person receives treatment, and whether the treatment takes effect. Causes Thyroid autoimmunity is familial. The disease is said to be inherited as a dominant trait since i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetics, genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSLP
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a protein belonging to the cytokine family. It is known to play an important role in the maturation of T cell populations through activation of antigen-presenting cells. TSLP is produced mainly by non-hematopoietic cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial cells and different types of stromal or stromal-like cells. Gene ontology TSLP production has been observed in various species, including humans and mice. In humans TSLP is encoded by the ''TSLP'' gene. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants. Function It mainly impacts myeloid cells and induces the release of T cell-attracting chemokines from monocytes and enhances the maturation of myeloid (CD11c+) dendritic cells. TSLP has also been shown to activate the maturation of a specific subset of dendritic cells located within the epidermis, called Langerhans cells. Within the thymus TSLP activation of both myeloid and plasmacytoid (CD123+) dendritic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Hill Hassall
Arthur Hill Hassall (13 December 1817, Teddington – 9 April 1894, San Remo) was a British physician, chemist and microscopist who is primarily known for his work in public health and food safety. Biography Hassall was born in Middlesex as the youngest son of five children in a house of a surgeon. His father was Thomas Hassall (1771–1844) and his mother, née Ann Sherrock ( 1778–1817). He spent his school years in Richmond. He entered medicine through apprenticeship in 1834 to his uncle Sir James Murray (1788–1871), spending his early career in Dublin, where he also studied botany and the seashore. In 1846 he published a two-volume study, ''The Microscopic Anatomy of the Human Body in Health and Disease'', the first English textbook on the subject. After further studying botany at Kew and publishing on botanical topics, particularly freshwater algae, he came to public attention with his 1850 book ''A microscopical examination of the water supplied to the inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
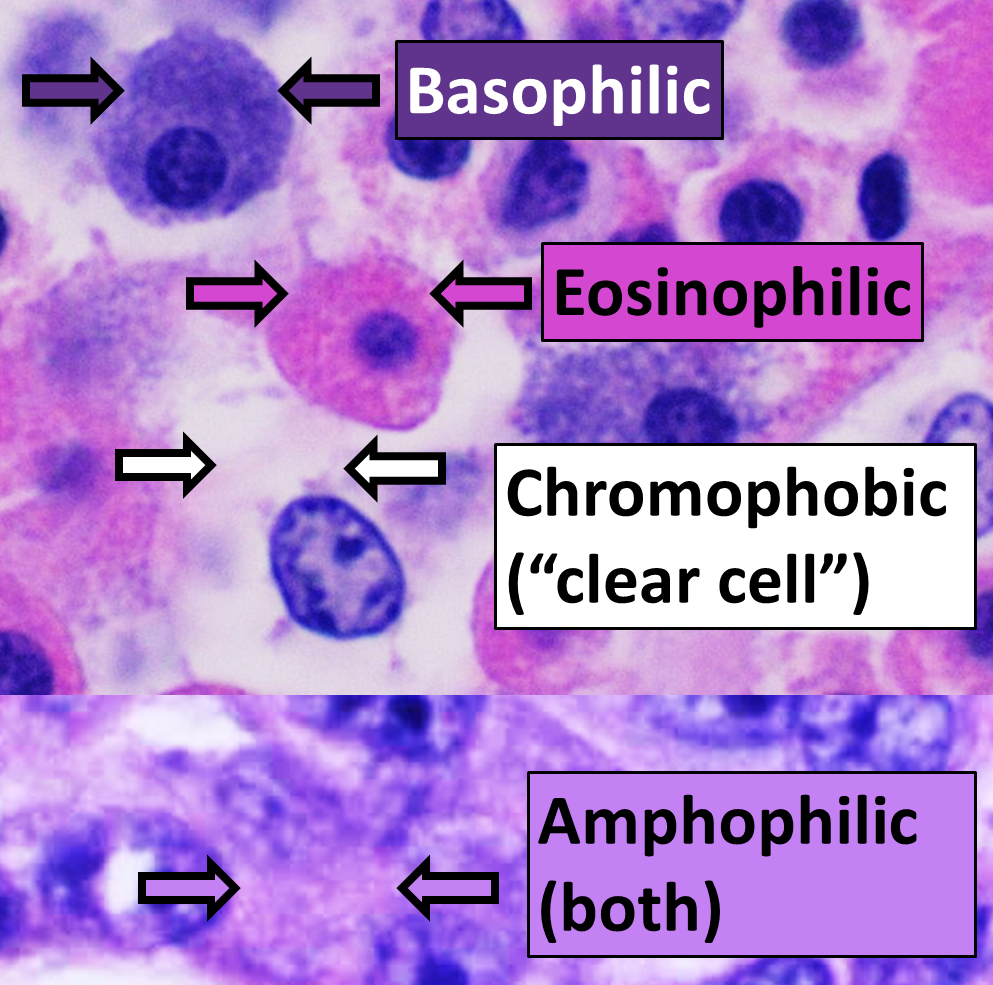
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Regulator
The autoimmune regulator (''AIRE'') is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AIRE'' gene. It is a 13kb gene on chromosome 21q22.3 that has 545 amino acids. AIRE is a transcription factor expressed in the medulla (inner part) of the thymus. It is part of the mechanism which eliminates self-reactive T cells that would cause autoimmune disease. It exposes T cells to normal, healthy proteins from all parts of the body, and T cells that react to those proteins are destroyed. Each T cell recognizes a specific antigen when it is presented in complex with a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule by an antigen presenting cell. This recognition is accomplished by the T cell receptors expressed on the cell surface. T cells receptors are generated by randomly shuffled gene segments which results in a highly diverse population of T cells - each with a unique antigen specificity. Subsequently, T cells with receptors that recognize the body's own proteins need to be elimin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |