|
Hardy Cross Method
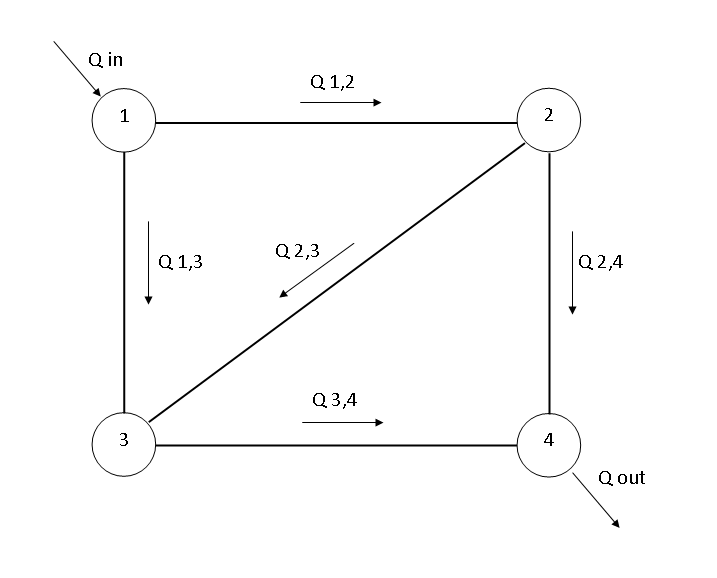
The Hardy Cross method is an iterative method for determining the flow in pipe network systems where the inputs and outputs are known, but the flow inside the network is unknown. The method was first published in November 1936 by its namesake, Hardy Cross, a structural engineering professor at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. The Hardy Cross method is an adaptation of the Moment distribution method, which was also developed by Hardy Cross as a way to determine the forces in statically indeterminate structures. The introduction of the Hardy Cross method for analyzing pipe flow networks revolutionized municipal water supply design. Before the method was introduced, solving complex pipe systems for distribution was extremely difficult due to the nonlinear relationship between head loss and flow. The method was later made obsolete by computer solving algorithms employing the Newton–Raphson method or other numerical methods that eliminate the need to solve nonlinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iterative Method
In computational mathematics, an iterative method is a Algorithm, mathematical procedure that uses an initial value to generate a sequence of improving approximate solutions for a class of problems, in which the ''n''-th approximation is derived from the previous ones. A specific implementation of an iterative method, including the Algorithm#Termination, termination criteria, is an algorithm of the iterative method. An iterative method is called convergent if the corresponding sequence converges for given initial approximations. A mathematically rigorous convergence analysis of an iterative method is usually performed; however, heuristic-based iterative methods are also common. In contrast, direct methods attempt to solve the problem by a finite sequence of operations. In the absence of rounding errors, direct methods would deliver an exact solution (for example, solving a linear system of equations A\mathbf=\mathbf by Gaussian elimination). Iterative methods are often the only cho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardy Cross
Hardy Cross (1885–1959) was an American structural engineer and the developer of the moment distribution method for structural analysis of statically indeterminate structures. The method was in general use from c. 1935 until c. 1960 when it was gradually superseded by other methods. Early life Cross was born in Nansemond County, Virginia, to Virginia planter Thomas Hardy Cross and his wife Eleanor Elizabeth Wright. He had an elder brother, Tom Peete Cross, who would later become a Celtic studies scholar. Both studied at Norfolk Academy. Then he attended Hampden-Sydney College where he earned both B.A. and B.S. degrees. He obtained a BS in civil engineering from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1908, and then joined the bridge department of the Missouri Pacific Railroad in St. Louis, where he remained for a year, after which he returned to Norfolk Academy in 1909. After a year of graduate study at Harvard he was awarded the MCE degree in 1911. Hardy Cross developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois At Urbana–Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the University of Illinois system and was founded in 1867. Enrolling over 56,000 undergraduate and graduate students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the country. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". In fiscal year 2019, research expenditures at Illinois totaled $652 million. The campus library system possesses the second-largest university library in the United States by holdings after Harvard University. The university also hosts the National Center for Supercomputing Applications and is home to the fastest supercomputer on a university campus. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Distribution Method
The moment distribution method is a structural analysis method for statically indeterminate beams and frames developed by Hardy Cross. It was published in 1930 in an ASCE journal. The method only accounts for flexural effects and ignores axial and shear effects. From the 1930s until computers began to be widely used in the design and analysis of structures, the moment distribution method was the most widely practiced method. Introduction In the moment distribution method, every joint of the structure to be analysed is fixed so as to develop the ''fixed-end moments''. Then each fixed joint is sequentially released and the fixed-end moments (which by the time of release are not in equilibrium) are distributed to adjacent members until equilibrium is achieved. The moment distribution method in mathematical terms can be demonstrated as the process of solving a set of simultaneous equations by means of iteration. The moment distribution method falls into the category of displaceme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Water Supply
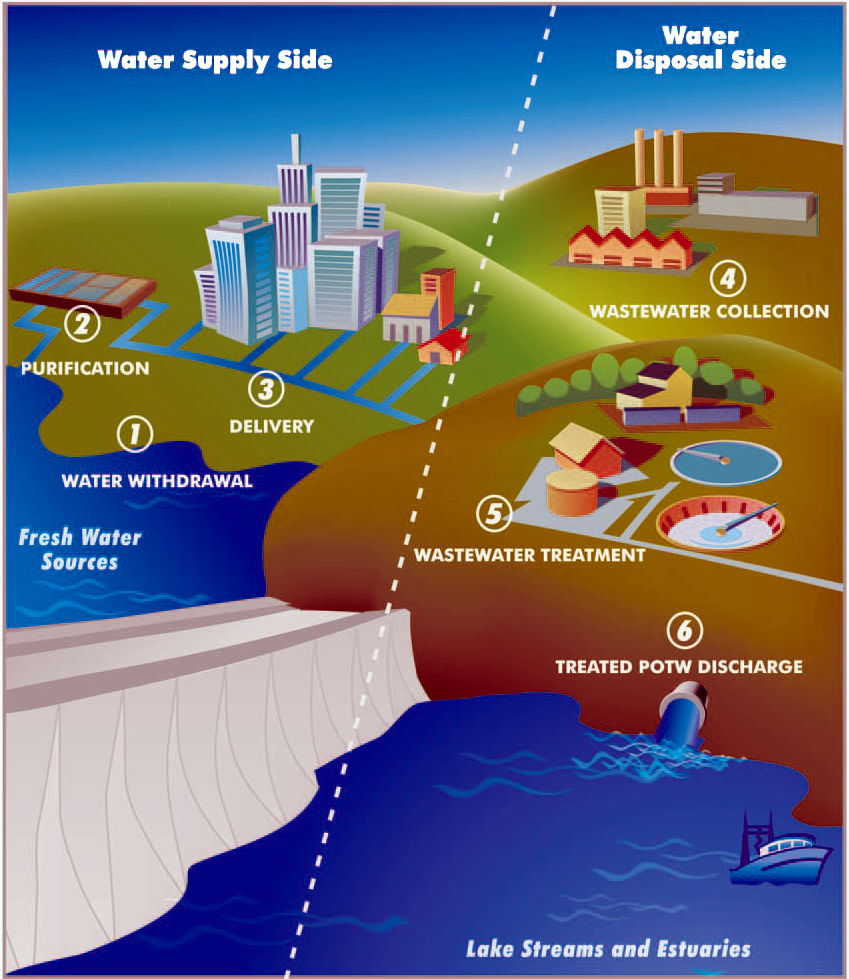
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following: # A drainage basin (see water purification – sources of drinking water) # A raw water collection point (above or below ground) where the water accumulates, such as a lake, a river, or groundwater from an underground aquifer. Raw water may be transferred using uncovered ground-level aqueducts, covered tunnels, or underground water pipes to water purification facilities. # Water purification facilities. Treated water is transferred using water pipes (usually underground). # Water storage facilities such as reservoirs, water tanks, or water towers. Smaller water systems may store the water in cisterns or pressure vessels. Tall buildings may also need to store water locally in pressure vessels in order for the water to reach the upper floors. # Additional water pressurizing components such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton–Raphson Method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method, also known as the Newton–Raphson method, named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a root-finding algorithm which produces successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. The most basic version starts with a single-variable function defined for a real variable , the function's derivative , and an initial guess for a root of . If the function satisfies sufficient assumptions and the initial guess is close, then :x_ = x_0 - \frac is a better approximation of the root than . Geometrically, is the intersection of the -axis and the tangent of the graph of at : that is, the improved guess is the unique root of the linear approximation at the initial point. The process is repeated as :x_ = x_n - \frac until a sufficiently precise value is reached. This algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method. The method can also be extended to complex functions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Distribution Method
The moment distribution method is a structural analysis method for statically indeterminate beams and frames developed by Hardy Cross. It was published in 1930 in an ASCE journal. The method only accounts for flexural effects and ignores axial and shear effects. From the 1930s until computers began to be widely used in the design and analysis of structures, the moment distribution method was the most widely practiced method. Introduction In the moment distribution method, every joint of the structure to be analysed is fixed so as to develop the ''fixed-end moments''. Then each fixed joint is sequentially released and the fixed-end moments (which by the time of release are not in equilibrium) are distributed to adjacent members until equilibrium is achieved. The moment distribution method in mathematical terms can be demonstrated as the process of solving a set of simultaneous equations by means of iteration. The moment distribution method falls into the category of displaceme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass cannot change, so quantity can neither be added nor be removed. Therefore, the quantity of mass is conserved over time. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form. For example, in chemical reactions, the mass of the chemical components before the reaction is equal to the mass of the components after the reaction. Thus, during any chemical reaction and low-energy thermodynamic processes in an isolated system, the total mass of the reactants, or starting materials, must be equal to the mass of the products. The concept of mass conservation is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, mechanics, and fluid dynamics. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be ''conserved'' over time. This law, first proposed and tested by Émilie du Châtelet, means that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, conservation of energy was distinct from conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to energy and vice versa by ''E = mc2'', and science now takes the view that mass-energy as a whole is conserved. Theoretically, this implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |