|
Half-speed Mastering
Half-speed mastering is a technique occasionally used when cutting the acetate lacquers from which phonograph records are produced. The cutting machine platter is run at half of the usual speed (16 rpm for 33 rpm records) while the signal to be recorded is fed to the cutting head at half of its regular playback speed. The reasons for using this technique vary but it is generally used for improving the high-frequency response of the finished record. By halving the speed during cutting, very high frequencies that are difficult to cut become much easier to cut since they are now mid-range frequencies. Mobile Fidelity Sound Lab Mobile Fidelity Sound Lab (MFSL or MoFi) is a record label specializing in the production of audiophile issues. The company produces reissued vinyl LP records, compact discs, and Super Audio CDs and other formats. History Recording engineer Br ... used half-speed mastering for its Original Master Recording LP's. References Audio storage {{Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonograph Records
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog signal, analog sound Recording medium, storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts near the periphery and ends near the center of the disc. At first, the discs were commonly made from shellac, with earlier records having a fine abrasive filler mixed in. Starting in the 1940s polyvinyl chloride became common, hence the name vinyl. The phonograph record was the primary medium used for music reproduction throughout the 20th century. It had co-existed with the phonograph cylinder from the late 1880s and had effectively superseded it by around 1912. Records retained the largest market share even when new formats such as the compact cassette were mass-marketed. By the 1980s, digital audio, digital media, in the form of the compact disc, had gained a larger market share, and the record left the main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
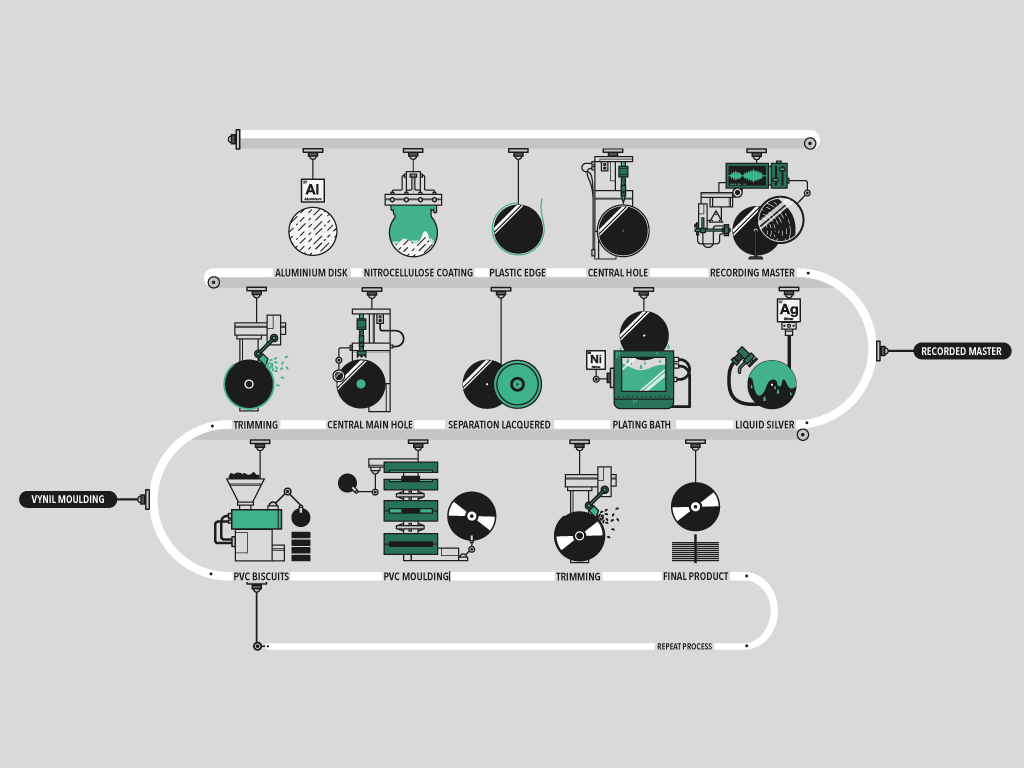
Production Of Phonograph Records
In the production of phonograph records – discs that were commonly made of shellac, and later, vinyl – sound was recorded directly onto a master disc (also called the matrix, sometimes just the master) at the recording studio. From about 1950 on (earlier for some large record companies, later for some small ones) it became usual to have the performance first recorded on audio tape, which could then be processed and/or edited, and then dubbed on to the master disc. Background The grooves are engraved into the master disc on a mastering lathe. Early versions of these master discs were soft wax, and later a harder lacquer was used. The mastering process was originally something of an art as the operator had to manually allow for the changes in sound which affected how wide the space for the groove needed to be on each rotation. Sometimes the engineer would sign his work, or leave humorous or cryptic comments in the lead-out groove area, where it was normal to scratch or stam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LP Record
The LP (from "long playing" or "long play") is an analog sound storage medium, a phonograph record format characterized by: a speed of rpm; a 12- or 10-inch (30- or 25-cm) diameter; use of the "microgroove" groove specification; and a vinyl (a copolymer of vinyl chloride acetate) composition disk. Introduced by Columbia in 1948, it was soon adopted as a new standard by the entire record industry. Apart from a few relatively minor refinements and the important later addition of stereophonic sound, it remained the standard format for record albums (during a period in popular music known as the album era) until its gradual replacement from the 1980s to the early 2000s, first by cassettes, then by compact discs, and finally by digital music distribution. Beginning in the late 2000s, the LP has experienced a resurgence in popularity. Format advantages At the time the LP was introduced, nearly all phonograph records for home use were made of an abrasive shellac compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Fidelity Sound Lab
Mobile Fidelity Sound Lab (MFSL or MoFi) is a record label specializing in the production of audiophile issues. The company produces reissued vinyl LP records, compact discs, and Super Audio CDs and other formats. History Recording engineer Brad Miller (1939–1998) released the first recordings on the Mobile Fidelity label in March 1958, a recording of a Southern Pacific steam locomotive. Later LPs included other steam trains, environmental sounds and orchestral music, and a few pop and orchestral recordings. In 1977 Mobile Fidelity Sound Labs was founded and began releasing Original Master Recording LPs, using a half-speed mastering process. In November 1999, Mobile Fidelity Sound Lab shut down after the bankruptcy of M. S. Distributing. In 2001 MFSL's assets were acquired by Jim Davis of Music Direct. Products LPs In 1977, Mobile Fidelity began to produce a line of records known as "Original Master Recording" vinyl LPs. These albums were previously released by other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |