|
Hairpin Ribozyme
The hairpin ribozyme is a small section of RNA that can act as a ribozyme. Like the hammerhead ribozyme it is found in RNA satellites of plant viruses. It was first identified in the minus strand of the tobacco ringspot virus (TRSV) satellite RNA where it catalyzes self-cleavage and joining (ligation) reactions to process the products of rolling circle virus replication into linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. The hairpin ribozyme is similar to the hammerhead ribozyme in that it does not require a metal ion for the reaction. Biological function The hairpin ribozyme is an RNA motif that catalyzes RNA processing reactions essential for replication of the satellite RNA molecules in which it is embedded. These reactions are self-processing, i.e. a molecule rearranging its own structure. Both cleavage and end joining reactions are mediated by the ribozyme motif, leading to a mixture of interconvertible linear and circular satellite RNA molecules. These reactions are imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function. There is no consensus in the literature on how much of non-coding transcription is functional. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional (sometimes referred to as "junk RNA"), spurious transcriptions. Others, however, disagree, arguing instead that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindbis Virus
''Sindbis virus'' (SINV) is a member of the ''Togaviridae'' family, in the ''Alphavirus'' genus. The virus was first isolated in 1952 in Cairo, Egypt. The virus is transmitted by mosquitoes (''Culex'' and Culiseta). SINV is linked to Pogosta diseaseKurkela S, Manni T, Vaheri A, Vapalahti OCausative agent of Pogosta disease isolated from blood and skin lesions Emerg Infect Dis erial on the Internet Published 2004 May. (accessed 2007-10-16) (Finland), Ockelbo disease ( Sweden) and Karelian fever (Russia). In humans, the symptoms include arthralgia, rash and malaise. Sindbis virus is widely and continuously found in insects and vertebrates in Eurasia, Africa, and Oceania. Clinical infection and disease in humans however has almost only been reported from Northern Europe (Finland, Sweden, Russian Karelia), where SINV is endemic and where large outbreaks occur intermittently. Cases are occasionally reported in Australia, China, and South Africa. SINV is an arbovirus, it is arthro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, dark urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey, a vulnerable West African primate. HIV-1 viruses can be further divided into groups M, N, O and P. The HIV-1 group M viruses predominate and are responsible for the AIDS pandemic. Group M can be further subdivided into subtypes based on genetic sequence data. Some of the subtypes are known to be more virulent or are resistant to different medications. Likewise, HIV-2 viruses are thought to be less virulent and transmissible than HIV-1 M group viruses, although HIV-2 is also known to cause AIDS. One of the obstacles to treatment of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is its high genetic variability. Major types HIV-1 HIV-1 is the most common and pathogenic strain of the virus. Over 2 million such infections occur annually. Scientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Cycle
In chemistry, a catalytic cycle is a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst. The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, materials science, etc. Since catalysts are regenerated, catalytic cycles are usually written as a sequence of chemical reactions in the form of a loop. In such loops, the initial step entails binding of one or more reactants by the catalyst, and the final step is the release of the product and regeneration of the catalyst. Articles on the Monsanto process, the Wacker process, and the Heck reaction show catalytic cycles. A catalytic cycle is not necessarily a full reaction mechanism. For example, it may be that the intermediates have been detected, but it is not known by which mechanisms the actual elementary reactions occur. Precatalysts Precatalysts are not catalysts but are ''precursors'' to catalysts. Precatalysts are converted in the react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides ( dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides ( A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA. To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crystalline materials. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
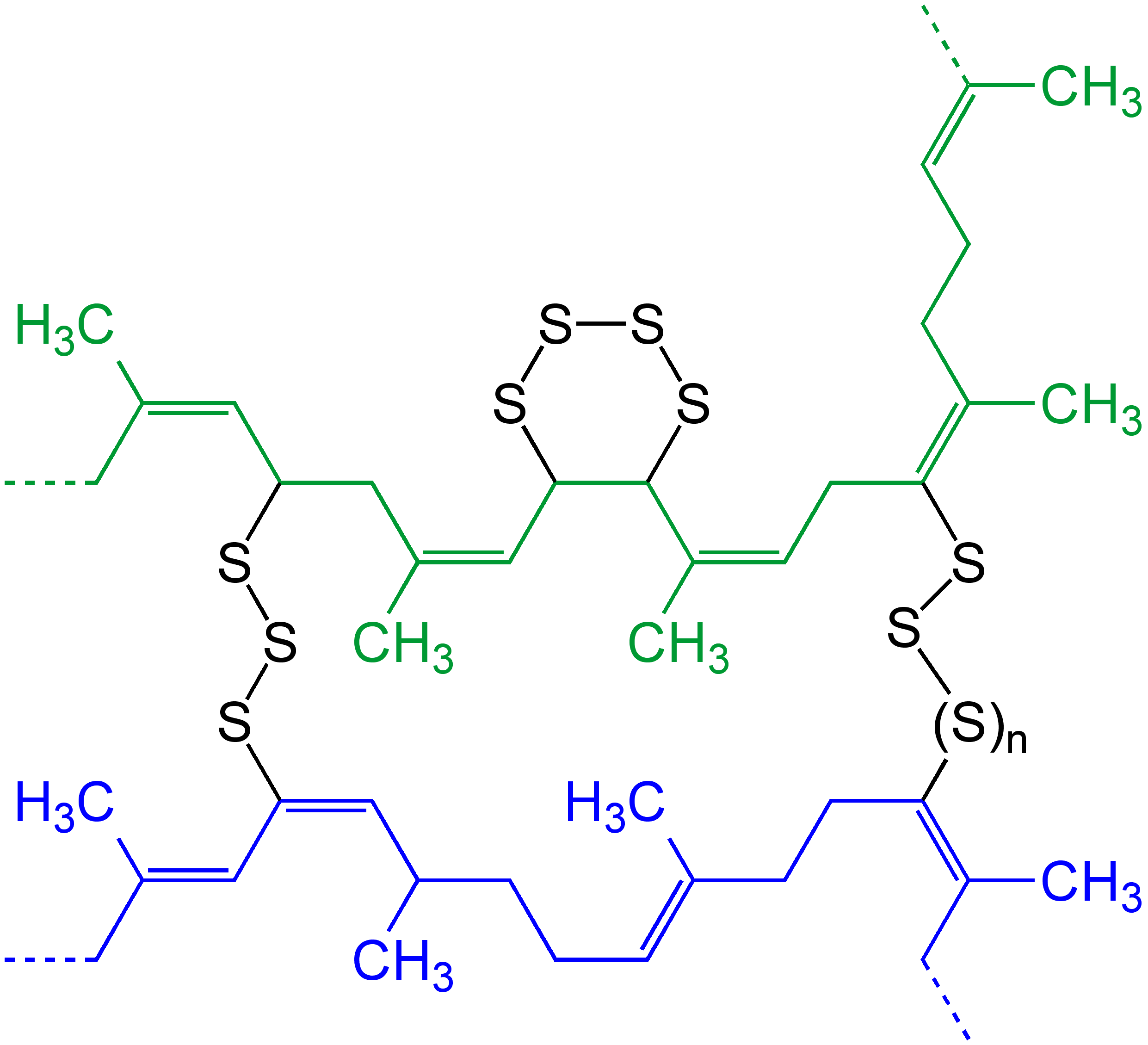
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy (also known as fluorimetry or spectrofluorometry) is a type of electromagnetic spectroscopy that analyzes fluorescence from a sample. It involves using a beam of light, usually ultraviolet light, that excites the electrons in molecules of certain compounds and causes them to emit light; typically, but not necessarily, visible light. A complementary technique is absorption spectroscopy. In the special case of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy, intensity fluctuations from the emitted light are measured from either single fluorophores, or pairs of fluorophores. Devices that measure fluorescence are called fluorometers. Theory Molecules have various states referred to as energy levels. Fluorescence spectroscopy is primarily concerned with electronic and vibrational states. Generally, the species being examined has a ground electronic state (a low energy state) of interest, and an excited electronic state of higher energy. Within each of these elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |