|
H-tree
In fractal geometry, the H tree is a fractal tree structure constructed from perpendicular line segments, each smaller by a factor of the square root of 2 from the next larger adjacent segment. It is so called because its repeating pattern resembles the letter "H". It has Hausdorff dimension 2, and comes arbitrarily close to every point in a rectangle. Its applications include VLSI design and microwave engineering. Construction An H tree can be constructed by starting with a line segment of arbitrary length, drawing two shorter segments at right angles to the first through its endpoints, and continuing in the same vein, reducing (dividing) the length of the line segments drawn at each stage by \sqrt2. A variant of this construction could also be defined in which the length at each iteration is multiplied by a ratio less than 1/\sqrt2, but for this variant the resulting shape covers only part of its bounding rectangle, with a fractal boundary. An alternative process that generate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
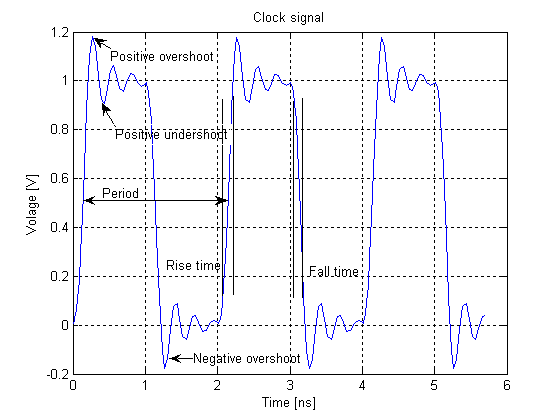
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review B
''Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics'' (also known as PRB) is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal, published by the American Physical Society (APS). The Lead Editor of PRB is Stephen E. Nagler and the Chief Editor is Sarma Kancharla. It is part of the '' Physical Review'' family of journals. About the Physical Review Journals The current Editor in Chief is Randall Kamien. PRB currently publishes over 5000 papers a year, making it one of the largest physics journals in the world. PRB ranked by the Eigenfactor, University of Washington, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membership group, reporting nearly 110,000 student and professional members . Its headquarters are in New York City. The ACM is an umbrella organization for academic and scholarly interests in computer science (informatics). Its motto is "Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession". History In 1947, a notice was sent to various people: On January 10, 1947, at the Symposium on Large-Scale Digital Calculating Machinery at the Harvard computation Laboratory, Professor Samuel H. Caldwell of Massachusetts Institute of Technology spoke of the need for an association of those interested in computing machinery, and of the need for communication between them. ..After making some inquiries during May and June, we believe there is ample interest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benoit Mandelbrot
Benoit B. Mandelbrot (20 November 1924 – 14 October 2010) was a Polish-born French-American mathematician and polymath with broad interests in the practical sciences, especially regarding what he labeled as "the art of roughness" of physical phenomena and "the uncontrolled element in life". He referred to himself as a "fractalist" and is recognized for his contribution to the field of fractal geometry, which included coining the word "fractal", as well as developing a theory of "roughness and self-similarity" in nature. In 1936, at the age of 11, Mandelbrot and his family emigrated from Warsaw, Poland, to France. After World War II ended, Mandelbrot studied mathematics, graduating from universities in Paris and in the United States and receiving a master's degree in aeronautics from the California Institute of Technology. He spent most of his career in both the United States and France, having dual French and American citizenship. In 1958, he began a 35-year career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a Set (mathematics), set whose complement (set theory), complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points. In a complete metric space, a closed set is a set which is Closure (mathematics), closed under the limit of a sequence, limit operation. This should not be confused with closed manifold. Sets that are both open and closed and are called clopen sets. Definition Given a topological space (X, \tau), the following statements are equivalent: # a set A \subseteq X is in X. # A^c = X \setminus A is an open subset of (X, \tau); that is, A^ \in \tau. # A is equal to its Closure (topology), closure in X. # A contains all of its limit points. # A contains all of its Boundary (topology), boundary points. An alternative characterization (mathematics), characterization of closed sets is available via sequences and Net (mathematics), net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendroid (topology)
In mathematics, a dendroid is a type of topological space, satisfying the properties that it is hereditarily unicoherent (meaning that every subcontinuum of ''X'' is unicoherent), arcwise connected, and forms a continuum. The term dendroid was introduced by Bronisław Knaster lecturing at the University of Wrocław,. although these spaces were studied earlier by Karol Borsuk and others.. proved that dendroids have the fixed-point property: Every continuous function from a dendroid to itself has a fixed point. proved that every dendroid is ''tree-like'', meaning that it has arbitrarily fine open covers whose nerve is a tree. The more general question of whether every tree-like continuum has the fixed-point property, posed by , was solved in the negative by David P. Bellamy, who gave an example of a tree-like continuum without the fixed-point property. In Knaster's original publication on dendroids, in 1961, he posed the problem of characterizing the dendroids which can be emb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Torsion (mechanics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a Set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of List of continuity-related mathematical topics, continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and Homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space-filling Curve
In mathematical analysis, a space-filling curve is a curve whose Range of a function, range reaches every point in a higher dimensional region, typically the unit square (or more generally an ''n''-dimensional unit hypercube). Because Giuseppe Peano (1858–1932) was the first to discover one, space-filling curves in the plane (mathematics), 2-dimensional plane are sometimes called ''Peano curves'', but that phrase also refers to the Peano curve, the specific example of a space-filling curve found by Peano. The closely related FASS curves (approximately space-Filling, self-Avoiding, Simple, and Self-similar curves) can be thought of as finite approximations of a certain type of space-filling curves. Definition Intuitively, a curve in two or three (or higher) dimensions can be thought of as the path of a continuously moving point. To eliminate the inherent vagueness of this notion, Camille Jordan, Jordan in 1887 introduced the following rigorous definition, which has since been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Canopy
In geometry, a fractal canopy, a type of fractal tree, is one of the easiest-to-create types of fractals. Each canopy is created by splitting a line segment into two smaller segments at the end (symmetric binary tree), and then splitting the two smaller segments as well, and so on, infinitely.Bello, Ignacio; Kaul, Anton; and Britton, Jack R. (2013). ''Topics in Contemporary Mathematics'', p.511. Cengage Learning. . Canopies are distinguished by the angle between concurrent adjacent segments and ratio between lengths of successive segments. A fractal canopy must have the following three properties: #The angle between any two neighboring line segments is the same throughout the fractal. #The ratio of lengths of any two consecutive line segments is constant. #Points all the way at the end of the smallest line segments are interconnected, which is to say the entire figure is a Graph (discrete mathematics)#Connected graph, connected graph. The pulmonary system used by humans to breath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Canopy1
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |