|
Gyorshadtest
The ''Gyorshadtest'' (variously translated "Rapid Corps", "Fast Corps" or "Mobile Corps") was the most modern and best-equipped mechanized unit of the Royal Hungarian Army (''Magyar KirûÀlyi Honvûˋdsûˋg'') at the beginning of World War II. However, the "Rapid Corps" name was something of a misnomer as it was only "mechanized" compared to other Hungarian units. The corps was not particularly mechanized when compared to similar units fielded by countries like Germany or the Soviet Union. Organization The mechanized corps of the "Carpathian Group" At the outset of the war, the Hungarian General Staff assembled a "strike force" consisting of VIII Corps, the 1st Mountain Brigade, the 8th Border Guard Brigade, and the "Rapid Corps" (''Gyorshadtest''). This 40,000-man strong elite "Rapid Corps" of two infantry brigades and the mechanized corps was collectively known as the "Carpathian Group" (''KûÀrpûÀt Csoport''). The commander of the "Carpathian Group" was Hungarian General ('' Vezû ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Third Army
The Hungarian Third Army ( hu, 3. magyar hadsereg) was a field army in the Royal Hungarian Army that saw action during World War II. Commanders * Lieutenant General Elemûˋr Gorondy-NovûÀk from 1 March 1940 to 1 November 1941 * Lieutenant General ZoltûÀn Decleva from 1 November 1941 to 1 December 1942 * Lieutenant General Lajos Csatay from 1 December 1942 to 12 June 1943 * Lieutenant General KûÀroly Beregfy from 12 June 1943 to 15 May 1944 * ''The Hungarian Third Army was disbanded May 1944 and reformed September 1944'' * Colonel General Jû°zsef Vitûˋz Heszlûˋnyi from 19 September 1944 to 8 May 1945 Order of Battle - Yugoslavia - April 1941 On 5 April 1941, the Hungarian Third Army was mobilized for the invasion of Yugoslavia. The invasion began with the bombing of Belgrade and the crossing of the border by the Germans on 6 April. The Third Army faced the Yugoslavian First Army. By the time the Hungarians crossed the border and finally attacked, the Germans had been attackin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Hungarian Army
The Royal Hungarian Army ( hu, Magyar KirûÀlyi Honvûˋdsûˋg, german: KûÑniglich Ungarische Armee) was the name given to the land forces of the Kingdom of Hungary in the period from 1922 to 1945. Its name was inherited from the Royal Hungarian Honvûˋd which went under the same Hungarian title of ''Magyar KirûÀlyi Honvûˋdsûˋg'' from 1867 to 1918. Initially restricted by the Treaty of Trianon to 35,000 men, the army was steadily upgraded during the 1930s and fought on the side of the Axis powers in the Second World War. History Background As a vanquished power in the First World War, Hungary had hardly grown at all in the immediate post-war years thanks to the territorial demands of its old and new neighbouring states, the Kingdom of Rumania, Czechoslovakia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. The Hungarian Red Army that was formed during the period of the Hungarian Soviet Republic, in which many world war veterans enlisted, was defeated by the allied armies in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Yugoslavia
The invasion of Yugoslavia, also known as the April War or Operation 25, or ''Projekt 25'' was a German-led attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II. The order for the invasion was put forward in " Fû¥hrer Directive No. 25", which Adolf Hitler issued on 27 March 1941, following a Yugoslav coup d'ûˋtat that overthrew the pro-Axis government. The invasion commenced with an overwhelming air attack on Belgrade and facilities of the Royal Yugoslav Air Force (VVKJ) by the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) and attacks by German land forces from southwestern Bulgaria. These attacks were followed by German thrusts from Romania, Hungary and the Ostmark (modern-day Austria, then part of Germany). Italian forces were limited to air and artillery attacks until 11 April, when the Italian army attacked towards Ljubljana (in modern-day Slovenia) and through Istria and Lika and down the Dalmatian coast. On the same day, Hungaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
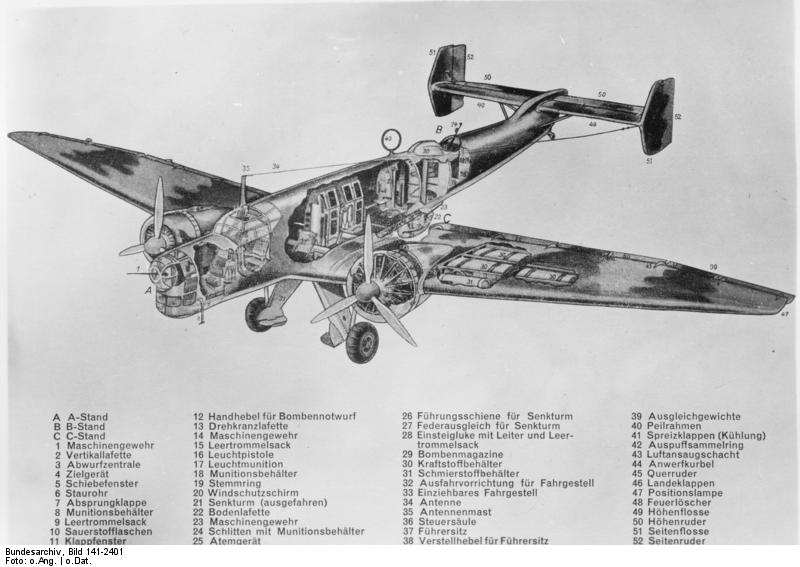
Junkers Ju 86
The Junkers Ju 86 was a German monoplane bomber and civilian airliner designed in the early 1930s, and employed by various air forces on both sides during World War II. The civilian model Ju 86B could carry ten passengers. Two were delivered to Swissair and five to Deutsche Luft Hansa. In addition a single civilian Ju 86Z was delivered to Sweden's AB Aerotransport. Design and development In 1934, a specification for a modern twin-engined aircraft, capable of operating both as a high-speed airliner for the German airline Luft Hansa and as a medium bomber for the nascent Luftwaffe, was issued to both Junkers and Heinkel. Five prototypes were ordered from each company; the Junkers Ju 86 and Heinkel He 111.Green and Swanborough 1982, p. 15. Junkers' design was a low-winged twin-engined monoplane, of all-metal stressed skin construction. Unlike most of Junkers' previous designs, it discarded the typical corrugated skinning in favour of smooth metal skinning which helped to reduce drag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Roundel WW2
Hungarian may refer to: * Hungary, a country in Central Europe * Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946 * Hungarians, ethnic groups in Hungary * Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the assignment problem * Hungarian language, a Finno-Ugric language spoken in Hungary and all neighbouring countries * Hungarian notation, a naming convention in computer programming * Hungarian cuisine Hungarian or Magyar cuisine is the cuisine characteristic of the nation of Hungary and its primary ethnic group, the Magyars. Traditional Hungarian dishes are primarily based on meats, seasonal vegetables, fruits, bread, and dairy products. ..., the cuisine of Hungary and the Hungarians See also * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferenc Bisza
Ferenc () is a given name of Hungarian origin. It is a cognate of Francis, Francisco, Francesco, FranûÏois, Frank and Franz. People with the name include: * Ferenc BatthyûÀny, Hungarian magnate and general * Ferenc Berûˋnyi, Hungarian artist * Ferenc Csik, Hungarian swimmer * Ferenc DeûÀk (politician), Hungarian statesman, Minister of Justice * Ferenc Erkel, Hungarian composer and conductor * Ferenc Farkas de Boldogfa (1713ã1770), Hungarian nobleman * Ferenc Farkas (Jesuit priest), Hungarian Jesuit priest * Ferenc Farkas (Zala county auditor), Hungarian nobleman * Ferenc Farkas, Hungarian composer * Ferenc Fricsay, Hungarian conductor * Ferenc GyurcsûÀny, Hungarian Prime Minister * Ferenc Karinthy, Hungarian writer and translator * Ferenc KûÑlcsey, Hungarian poet, literary critic, orator, politician * Ferenc Koncz, Hungarian politician * Ferenc Liszt (1811ã1886), Hungarian composer and conductor known as Franz Liszt * Ferenc MûÀdl, Hungarian legal scholar, politici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslavian First Army
The 1st Army was a Royal Yugoslav Army formation commanded by ''Armijski áeneral'' Milan Raáenkoviá during the German-led Axis invasion of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in April 1941 during World War II. It consisted of one infantry division, one horsed cavalry division, and two brigade-strength infantry detachments. It formed part of the 2nd Army Group, and was responsible for the defence of the section of the Yugoslav- Hungarian border between the Danube and the Tisza rivers. The 1st Army was not directly attacked during the first few days after the invasion commenced, but attacks on its flanks resulted in successive orders to withdraw to the lines of the Danube and then the Sava. The Hungarians then crossed the border in the sector for which the 1st Army had been responsible, but the Yugoslavs were already withdrawing and the Hungarians faced almost no resistance. This was followed by the German capture of Belgrade and the rear area units of 1st Army. Remnants of the 1st Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
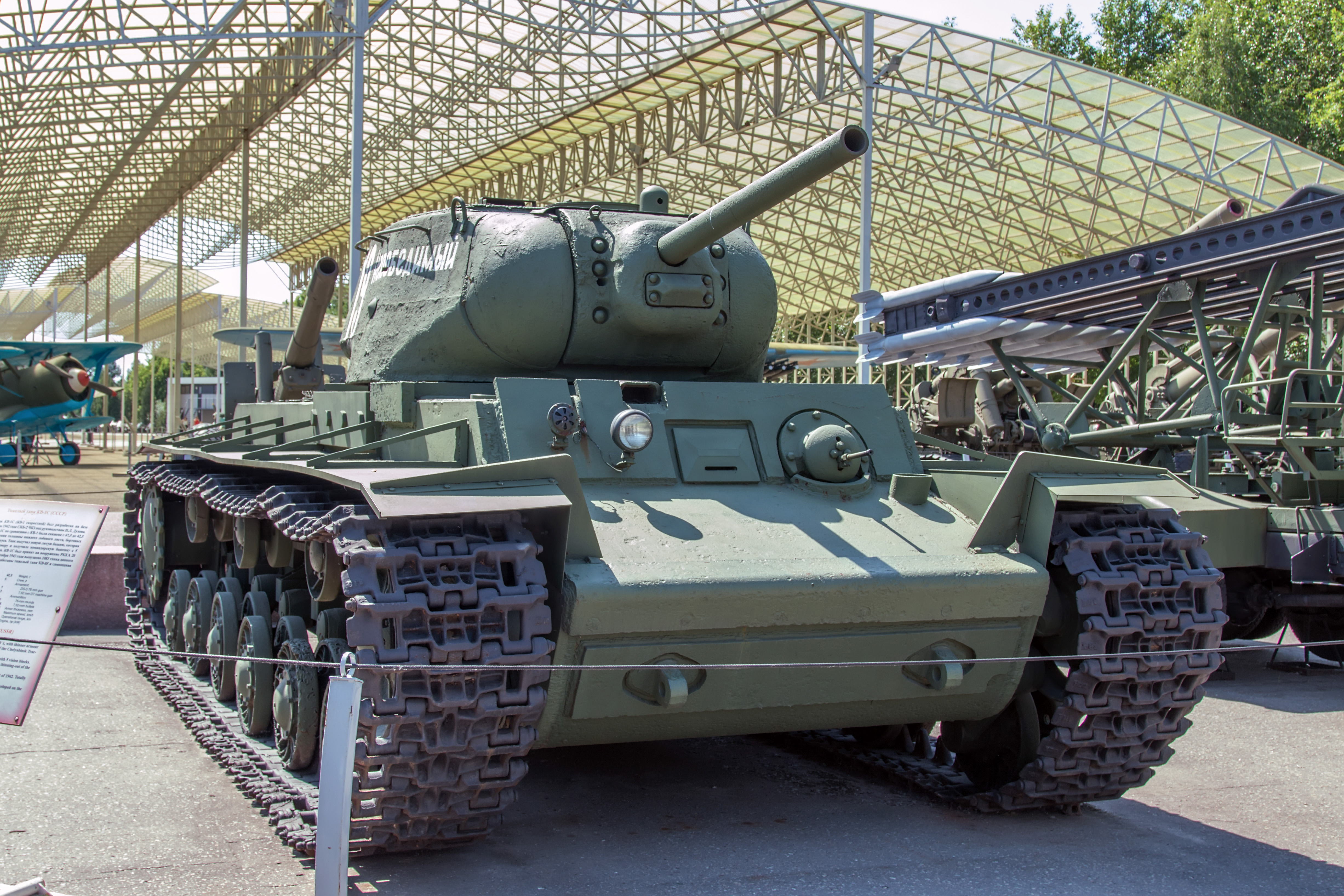
Kliment Voroshilov Tank
The Kliment Voroshilov (KV) tanks are a series of Soviet heavy tanks named after the Soviet defence commissar and politician Kliment Voroshilov who operated with the Red Army during World War II. The KV tanks were known for their heavy armour protection during the early stages of the war, especially during the first year of the German invasion of the Soviet Union. In certain situations, even a single KV-1 or KV-2 supported by infantry could halt German formations. The German ''Wehrmacht'' at that time rarely deployed its tanks against KVs, as their own armament was too poor to deal with the "''Russischer Koloss''" ã "Russian Colossus". The KV tanks were practically immune to the 3.7 cm KwK 36 and howitzer-like, short-barreled 7.5 cm KwK 37 guns mounted, respectively, on the early Panzer III and Panzer IV tanks fielded by the invading German forces. Until the Germans developed more effective guns, the KV-1 was invulnerable to almost any German weapon except the 8.8 cm Flak gun. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The Christie suspension was inherited from the design of American J. Walter Christie's M1928 tank, versions of which were sold turret-less to the Red Army and documented as "farm tractors", after being rejected by the U.S. Army. The T-34 had a profound effect on the conflict on the Eastern Front in the Second World War, and had a short lasting impact on tank design. After the Germans encountered the tank in 1941 during Operation Barbarossa, German general Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist called it "the finest tank in the world" and Heinz Guderian affirmed the T-34's "vast superiority" over German tanks. Alfred Jodl, chief of operations staff of the German armed forces noted in his war diary "the surprise at this new and thus unknown ''wunder''-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Tank
A light tank is a tank variant initially designed for rapid movements in and out of combat, to outmaneuver heavier tanks. It is smaller in size with thinner armor and a less powerful main gun, tailored for better tactical mobility and ease of transport and logistics. They are primarily employed in the screening, armored reconnaissance, skirmishing, artillery observation, and supplementing landing operations in a fire support role of expeditionary forces where larger, heavier tanks are unavailable or have difficulties operating safely or efficiently. The fast light tank was a major feature of the pre-World War II army buildup, where it was expected they would be used to exploit breakthroughs in enemy lines created by slower, heavier tanks, with the goal of disrupting communications and supply lines. Numerous small tank designs and " tankettes" were developed during this period and known under a variety of names, including the " combat car". Early light tank designs were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
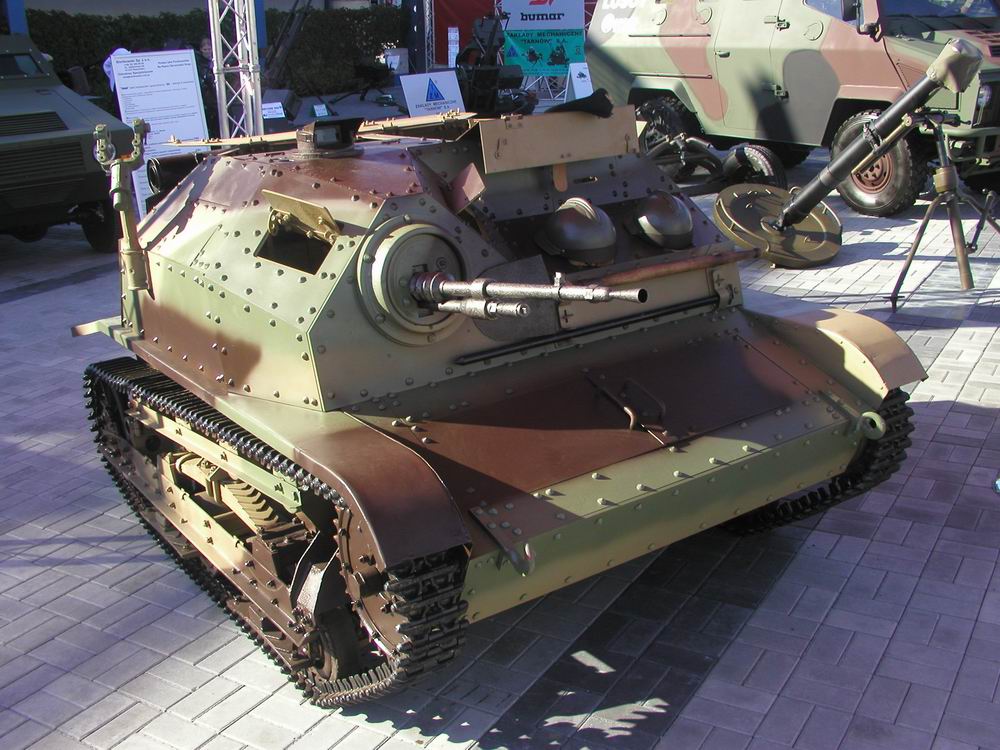
38M Toldi
The 38M Toldi was a Hungarian light tank, developed on the basis of the Swedish Landsverk L-60. It was named after the 14th century Hungarian knight Miklû°s Toldi. Development and production The Hungarian general staff wanted a modern light tank as soon as possible, after the domestically developed V-4 turned out to be too expensive by 1936 and work on it progressed slower than expected. Meanwhile, the Swedish AB Landsverk finished its recent development, the Landsverk L-60 in October, and was looking for a customer to cover the costs. After a series of trials in 1937 with the V-4 and the Panzer I, the MûVAG heavy industries decided to purchase the license of the L-60, with a prototype for further development. The turret of the vehicle was then modified, making space for the radio and other devices, with a cupola being placed on top (since the L-60 was still unfinished and lacked in many necessary features). The original main armament, the 20 mm Madsen was also repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tankette
A tankette is a tracked armoured fighting vehicle that resembles a small tank, roughly the size of a car. It is mainly intended for light infantry support and scouting.T-27 Tankette (from the 'battlefield.ru' website, with further references cited. Accessed 2008-02-21.) Colloquially it may also simply mean a small tank. Several countries built tankettes between the 1920s and 1940s, and some saw limited combat in the early phases of . The vulnerability of their light armour, however, eventually led armies to abandon the concept with some exceptions such as the more modern German Wiesel (Weasel) series. ...
|