|
Guy Halsall
Guy Halsall (born 1964) is an English historian and academic, specialising in Early Medieval Europe. He is currently based at the University of York, and has published a number of books, essays, and articles on the subject of early medieval history and archaeology. Halsall's current research focuses on western Europe in the important period of change around AD 600 and on the application of continental philosophy (especially the work of Jacques Derrida) to history. He taught at the University of Newcastle and Birkbeck, University of London, before moving to the University of York. Life Guy Halsall was born in North Ferriby in 1964 and raised in Worcestershire. He studied archaeology and history at the University of York, earning the first First-Class degree from York's archaeology department in 1986. He completed his D.Phil. at York in 1991 with a thesis on the "history and archaeology of the region of Metz in the Merovingian period" supervised by Edward James and examined by Stev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouse
''Nouse'' ( ; Ancient Greek: , meaning intellect, or common sense; also the local River Ouse; also a potential pun on the words 'No Use') is a student newspaper and website at the University of York. It is the oldest registered society of, and funded by, the University of York Students' Union. ''Nouse'' was founded in 1964 by student Nigel Fountain, some twenty years before its rival ''York Vision''. The newspaper is printed three times in each of the Autumn and Spring terms, and twice in the Summer term, with frequent website updates in between print runs. As of June 2022, ''Nouse'' has printed 500 editions. Unlike many other university newspapers, which have sabbatical editors, ''Nouse''′s staff is made up entirely of current students. It has changed dramatically in outlook and presentation over the years, being known at one point as the ''Nouse Co-operative'' or ''NouseCoop'', and presenting itself as a samizdat publication throughout the 1980s. The last edition of the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups that emerged af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anders Behring Breivik
Fjotolf Hansen (born 13 February 1979), better known by his birth name Anders Behring Breivik () and by his pseudonym Andrew Berwick, is a Norwegian far-right domestic terrorist, known for committing the 2011 Norway attacks on 22 July 2011. On that day, he killed eight people by detonating a van bomb at Regjeringskvartalet in Oslo, then killed 69 participants of a Workers' Youth League (AUF) summer camp in a mass shooting on the island of Utøya. Breivik's trial was held in 2012. After being found psychologically competent to stand trial, in July 2012, he was found guilty of mass murder, causing a fatal explosion, and terrorism. Breivik was sentenced to the maximum civilian criminal penalty in Norway, which is 21 years imprisonment in addition to preventive detention, which is the possibility of one or more extensions for as long as he is deemed a danger to society. Breivik must serve at least ten years imprisonment. Breivik announced that he did not recognize the legitimacy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blogspot
Blogger is an American online content management system founded in 1999 which enables multi-user blogs with time-stamped entries. Pyra Labs developed it before being acquired by Google in 2003. Google hosts the blogs, which can be accessed through a subdomain of blogspot.com. Blogs can also be accessed from a user-owned custom domain (such as www.example.com) by using DNS facilities to direct a domain to Google's servers. A user can have up to 100 blogs or websites per account. Google Blogger also enabled users to publish blogs and websites to their own web hosting server via FTP until May 1, 2010. All such blogs and websites had to be redirected to a blogspot.com subdomain or point their own domain to Google's servers via DNS. Google Blogger has a wide international user base and is available in more than 60 languages, despite its decline in popularity in the United States. History Pyra Labs launched Blogger on August 23, 1999. It is credited with popularizing the format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less civilized or orderly (such as a tribal society) but may also be part of a certain "primitive" culture, cultural group (such as nomads) or social class (such as bandits) both within and outside one's own nation. Alternatively, they may instead be admired and romanticised as noble savages. In idiomatic or figurative usage, a "barbarian" may also be an individual reference to a brutal, cruel, warlike, and insensitive person. The term originates from the el, βάρβαρος (''barbaros'' pl. βάρβαροι ''barbaroi''). In Ancient Greece, the Greeks used the term not only towards those who did not speak Greek and follow classical Greek customs, but also towards Greek populations on the fringe of the Greek world with peculiar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto School Of History
The Vienna School of History is an influential school of historical thinking based at the University of Vienna. It is closely associated with Reinhard Wenskus, Herwig Wolfram and Walter Pohl. Partly drawing upon ideas from sociology and critical theory, scholars of the Vienna School have utilized the concept of ethnogenesis to reassess the notion of ethnicity as it applies to historical groups of peoples such as the Germanic tribes. Focusing on Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, the Vienna School has a large publishing output, and has had a major influence on the modern analysis of barbarian identity. Theories The origins of the Vienna School of History can be traced to the works of the German historian Reinhard Wenskus. During the 1960s, there was as reaction against previous scholarship on Germanic tribes. Drawing upon studies on modern tribes, Wenskus posited that the Germanic tribes of antiquity did not constitute distinct ethnicities, but were rather diverse alliance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Goffart
Walter Goffart (born February 22, 1934) is a German-born American historian who specializes in Late Antiquity and the European Middle Ages. He taught for many years in the History Department and Centre for Medieval Studies of the University of Toronto (1960–1999), and is currently a senior research scholar at Yale University. He is the author of monographs on a ninth-century forgery (''Le Mans Forgeries''), late Roman taxation (''Caput and Colonate''), four "barbarian" historians, and historical atlases. Two controversial themes in his research concern the Roman policies used when settling barbarian soldiers in the West Roman Empire (''Barbarians and Romans'' and the sixth chapter of ''Barbarian Tides''), and his criticism of the old idea that there was a single Germanic people opposed to the empire in late antiquity, which he believes still influences academics studying the period. Early life Walter Goffart was born in Berlin on February 22, 1934, the son of Francis-Leo Goffar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
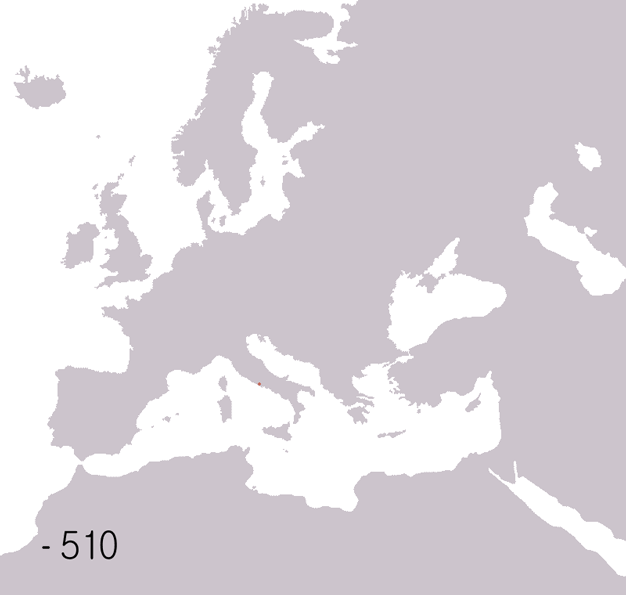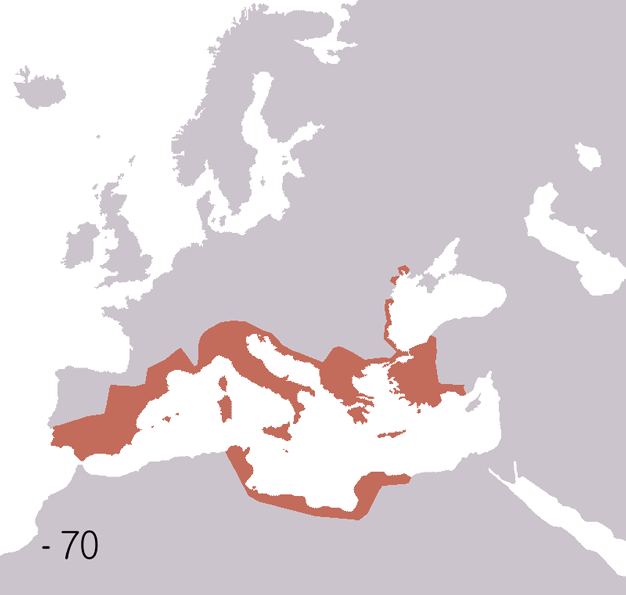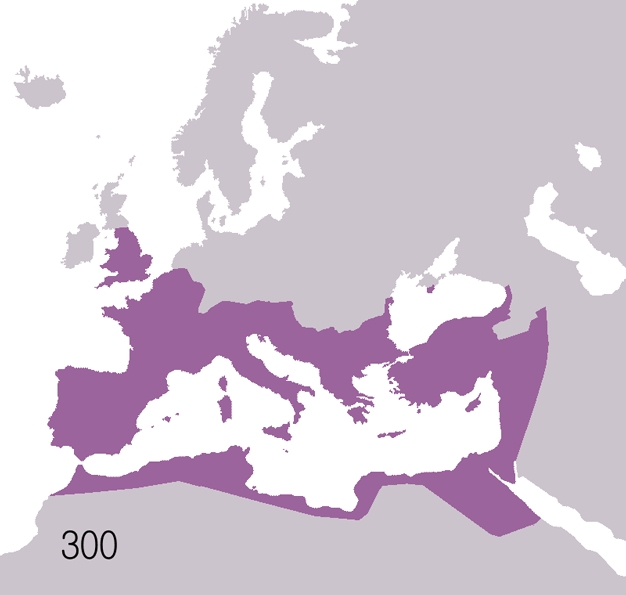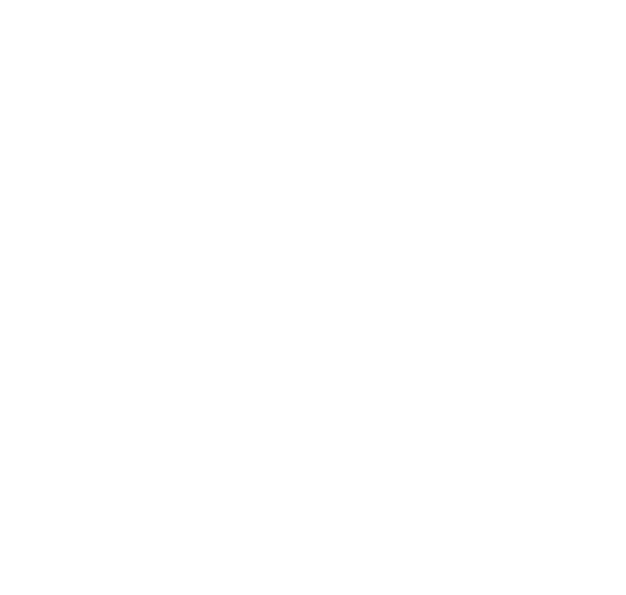
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor Polity, polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western Roman province, provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the Late Roman army, army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the Roman economy, economy, the competence of the Roman emperor, emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climate variability and change, Climatic changes and both Endemic (epide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived ''Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subject of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Heather
Peter John Heather (born 8 June 1960) is a British historian of late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Heather is Chair of the Medieval History Department and Professor of Medieval History at King's College London. He specialises in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Goths, on which he for decades has been considered the world's leading authority. Biography Heather was born in Northern Ireland on 8 June 1960. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, and received his M.A. and D.Phil. from New College, Oxford. Among his teachers at Oxford were John Matthews and James Howard-Johnston. Heather subsequently lectured at Worcester College, Oxford, Yale University and University College London. In January 2008, Heather was appointed chair of the Medieval History Department and professor of medieval history at King's College London. Research As a historian, Heather specialises in late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, especially the relationships between the Roman Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |