|
Gustaf Ising
Gustaf Adolf Ising (; 19 February 1883 - 5 February 1960) was a Swedish metrologist, geophysicist, and accelerator physicist. Biography Ising earned his first academic degree (''filosofie kandidat''/Bachelor of Arts) at Uppsala University in 1903 and continued studying at Stockholm University receiving his Ph.D. in 1919, and receiving an honorary professor title in 1934. He is best known for the invention of the linear accelerator concept in 1924, which is the progenitor of all modern accelerators based on oscillating electromagnetic fields. His article was then taken up and turned into practice by Rolf Widerøe, also starting the development of cyclic accelerator structures like the cyclotron. He was elected to the Swedish Academy of Sciences in 1935, being a member of the Nobel Committee for Physics from 1947 to 1953, together with former Nobel laureate and chairman Manne Siegbahn, Svante Arrhenius, Erik Hulthen, Axel Edvin Lindh, Ivar Waller Ivar Waller (11 June 1898 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finja
Finja is a locality situated in Hässleholm Municipality, Scania County, Sweden. Finja is located north of Lake Finjasjön, between Hässleholm and Tyringe. The village had a population of 535 inhabitants in 2010. Finja Church Finja Church is in the parish of Tyringe in the Diocese of Lund The Diocese of Lund ( sv, Lunds stift) is a diocese within the Church of Sweden which corresponds to the provinces of Blekinge and Skåne. There are 217 parishes within the diocese, the most significant number in any of the dioceses of the Chur .... The church was constructed in the beginning of the 12th century in a romanesque style, but has since then gone through several alterations and repairs. The church tower was constructed later in the same century, and in 1664 it was equipped with stairs. Inside the church there are fresco paintings from the 1140s. The baptismal font in sandstone with palmette motifs. The altar dates from the 16th century, with canopy and columns with wood carvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
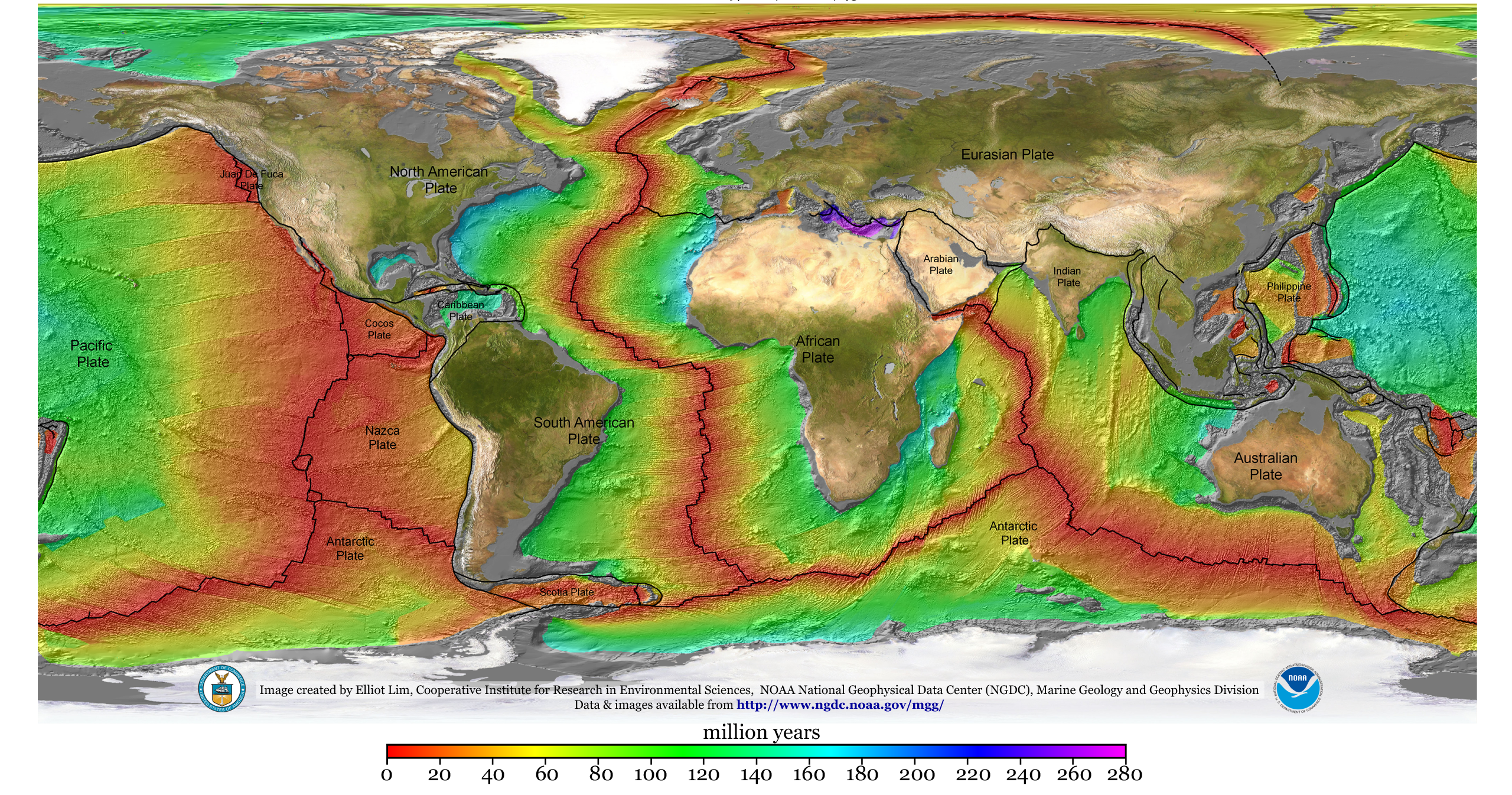
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physicists
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experiment, natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Physicists
Swedish or ' may refer to: Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically: * Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland ** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by the Swedish language * Swedish people or Swedes, persons with a Swedish ancestral or ethnic identity ** A national or citizen of Sweden, see demographics of Sweden ** Culture of Sweden * Swedish cuisine See also * * Swedish Church (other) * Swedish Institute (other) * Swedish invasion (other) * Swedish Open (other) Swedish Open is a tennis tournament. Swedish Open may also refer to: *Swedish Open (badminton) * Swedish Open (table tennis) *Swedish Open (squash) *Swedish Open (darts) The Swedish Open is a darts tournament established in 1969, held in Malm� ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivar Waller
Ivar Waller (11 June 1898 – 12 April 1991) was a Swedish professor of theoretical physics at Uppsala University. He developed the theory of X-ray scattering by lattice vibrations of a crystal, building upon the prior work of Peter Debye. The Debye–Waller factor, which he introduced in his doctoral thesis in 1925, is the definitive treatment of the effect of thermal vibrations in X-ray crystallography. He was a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences from 1945, and the Nobel Committee for Physics 1945-1972. One of his notable doctoral students was the quantum chemist Per-Olov Löwdin Per-Olov Löwdin (October 28, 1916 – October 6, 2000) was a Swedish physicist, professor at the University of Uppsala from 1960 to 1983, and in parallel at the University of Florida until 1993. A former graduate student under Ivar Waller, Löwd .... External links Obituary in Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1992 {{DEFAULTSORT:Waller, Ivar 1898 births 1991 deaths Swedish physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svante Arrhenius
Svante August Arrhenius ( , ; 19 February 1859 – 2 October 1927) was a Swedes, Swedish scientist. Originally a physicist, but often referred to as a chemist, Arrhenius was one of the founders of the science of physical chemistry. He received the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1903, becoming the first Sweden, Swedish Nobel laureate. In 1905, he became director of the Nobel Institute, where he remained until his death."Arrhenius, Svante August" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 635. Arrhenius was the first to use principles of physical chemistry to estimate the extent to which increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide are responsible for the Earth's increasing surface temperature. His work played an important role in the emergence of modern climate science. In the 1960s, Charles David Keeling demonstrated that the quantity of human-caused carbon dioxide emissions into the air is enough to cause global warming. The Arrhenius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manne Siegbahn
Karl Manne Georg Siegbahn FRS(For) HFRSE (3 December 1886 – 26 September 1978) was a Swedish physicist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1924 "for his discoveries and research in the field of X-ray spectroscopy". Biography Siegbahn was born in Örebro, Sweden, the son of Georg Siegbahn and his wife, Emma Zetterberg. He graduated in Stockholm 1906 and began his studies at Lund University in the same year. During his education he was secretarial assistant to Johannes Rydberg. In 1908 he studied at the University of Göttingen. He obtained his doctorate (PhD) at the Lund University in 1911, his thesis was titled ''Magnetische Feldmessungen'' (magnetic field measurements). He became acting professor for Rydberg when his (Rydberg's) health was failing, and succeeded him as full professor in 1920. However, in 1922 he left Lund for a professorship at Uppsala University. In 1937, Siegbahn was appointed Director of the Physics Department of the Nobel Institute of the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Academy Of Sciences
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences ( sv, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien) is one of the royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting natural sciences and mathematics and strengthening their influence in society, whilst endeavouring to promote the exchange of ideas between various disciplines. The goals of the academy are: * to be a forum where researchers meet across subject boundaries, * to offer a unique environment for research, * to provide support to younger researchers, * to reward outstanding research efforts, * to communicate internationally among scientists, * to advance the case for science within society and to influence research policy priorities * to stimulate interest in mathematics and science in school, and * to disseminate and popularize scientific information in various forms. Every year, the academy awards the Nobel Prizes in physics and chemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton accelerator and Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximum elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolf Widerøe
Rolf Widerøe (11 July 1902 – 11 October 1996) was a Norwegian accelerator physicist who was the originator of many particle acceleration concepts, including the ''resonance accelerator'' and the betatron accelerator. Early life Widerøe was born in Kristiania (now Oslo) in 1902 as a son of the mercantile agent Theodor Widerøe (1868–1947) and Carla Johanne Launer (1875–1971). He was a brother of the aviator and entrepreneur Viggo Widerøe who became the founder of the Norwegian airline Widerøe. After his A-level exams (Examen artium) in the summer of 1920 at the Halling School in Oslo, Widerøe left for Karlsruhe, Germany, to study electrical engineering. Betatron accelerator concept There he conceived the concept of electromagnetic induction to accelerate electrons, which became the basis of what would be known as betatron. This idea was to use a vortex field surrounding a magnetic field to accelerate electrons in a tube. Return to Germany In 1924, he returned to Norw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics (a quantum field theory). The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field can be identified ''as'' light) and interacts with charges and currents. Its quantum counterpart is one of the four fundamental forces of nature (the others are gravitation, weak interaction and strong interaction.) The field can be viewed as the combination of an electric field and a magnetic field. The electric field is produced by stationary charges, and the magnetic field by moving charges (currents); these two are often described as the sources of the field. The way in which charges and currents interact with the electromagnetic field is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |