|
Gurdwara Nanak Shahi
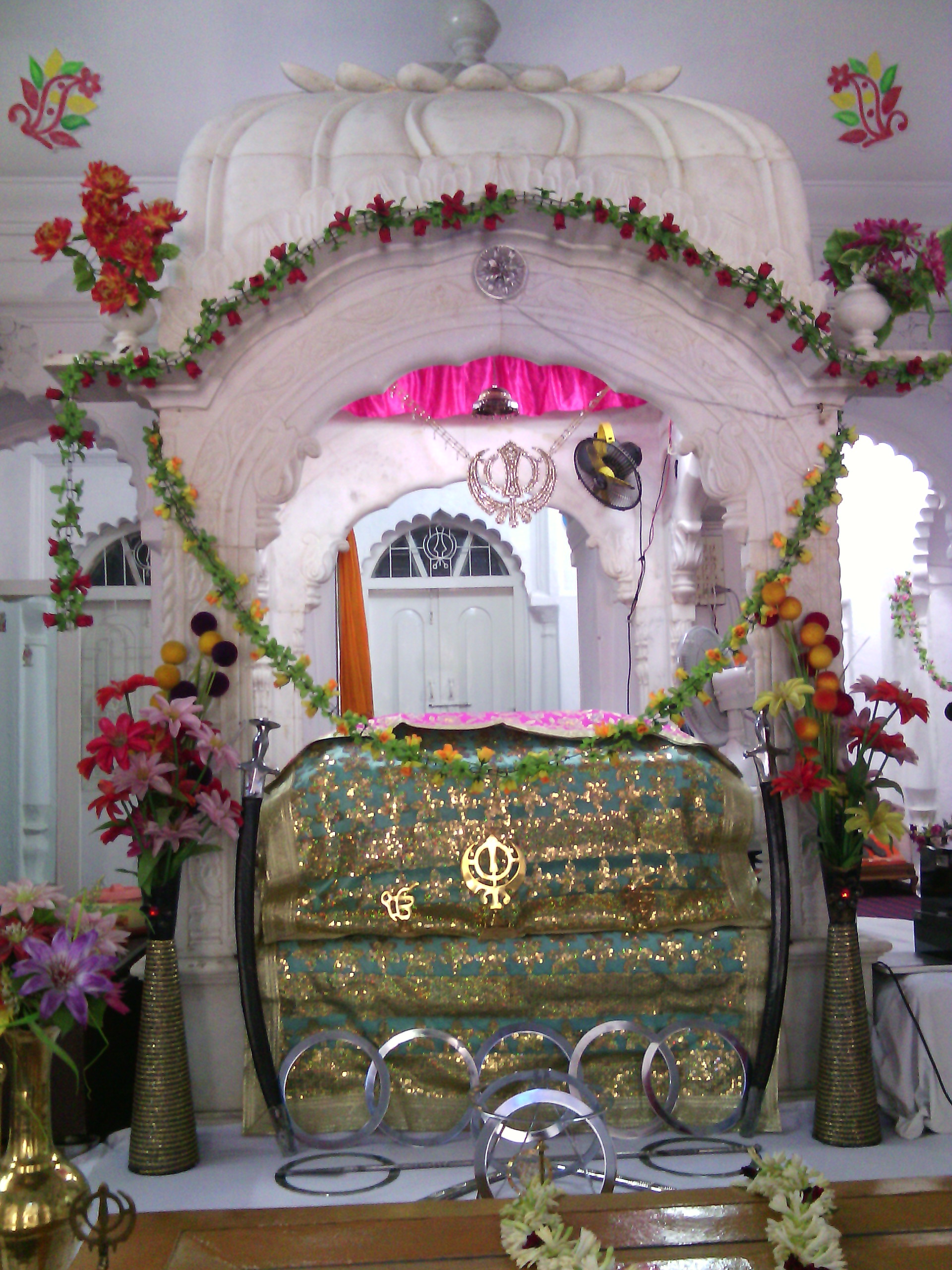
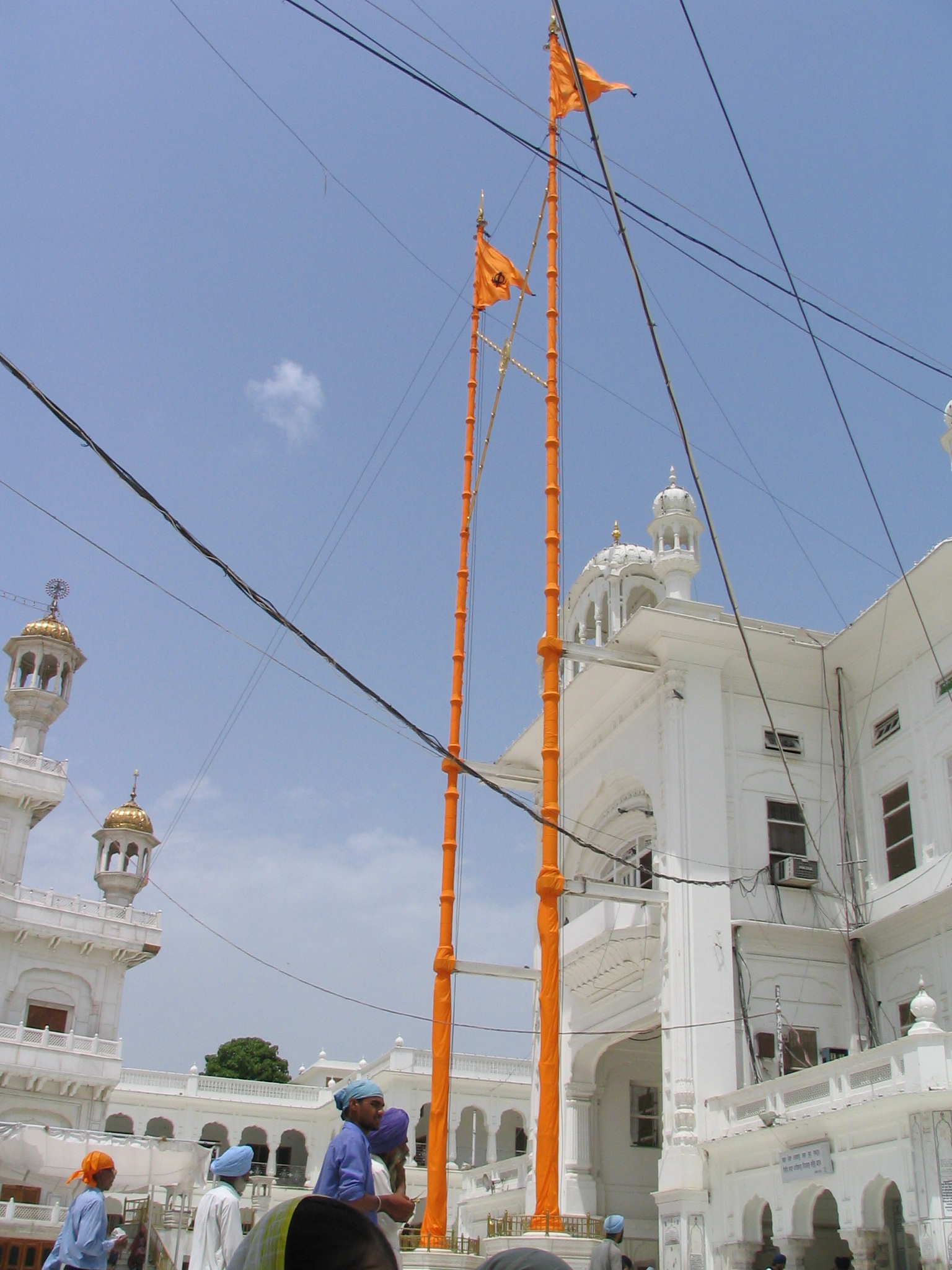
Gurdwara Nanak Shahi ( bn, গুরুদুয়ারা নানকশাহী, pa, ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ਨਾਨਕ ਸ਼ਾਹੀ) is the principal Sikh ''Gurdwara'' (prayer hall) in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is located at the campus of the University of Dhaka and considered to be the biggest of the 9 to 10 Gurdwaras in the country. The Gurudwara commemorates the visit of Guru Nanak (1506–1507). It is said to have been built in 1830. The present building of the Gurdwara was renovated in 1988–1989. The parkarma verandah had been constructed on all four sides of the original building to provide protection. History The Gurudwara was built originally by Bhai Natha ji, a missionary who came to Dhaka during the time of the sixth guru. The building was completed in 1830. This Gurudwara commemorates the stay of Sri Guru Nanak Dev Ji (1469–1539). In 1988 to 1989 the building was renovated and the outside verandah was constructed for its protection and preservation wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurdwara NanakShahi Dhaka By Ragib Hasan
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Sikh gurus, Guru") is a place of assembly and place of worship, worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths are welcomed in gurdwaras. Each gurdwara has a ''Darbar Sahib Hall, Darbar Sahib'' where the current and everlasting guru of the Sikhs, the scripture Guru Granth Sahib, is placed on a (an elevated throne) in a prominent central position. Any congregant (sometimes with specialized training, in which case they can be known by the term granthi) may recite, sing, and explain the verses from the Guru Granth Sahib, in the presence of the rest of the congregation. All gurdwaras have a hall, where people can eat free vegetarian food served by volunteers at the gurdwara. They may also have a medical facility room, library, nursery, classroom, meeting rooms, playground, sports ground, a gift shop, and finally a repair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurudwara Nanak Shahi,Dhaka
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths are welcomed in gurdwaras. Each gurdwara has a '' Darbar Sahib'' where the current and everlasting guru of the Sikhs, the scripture Guru Granth Sahib, is placed on a (an elevated throne) in a prominent central position. Any congregant (sometimes with specialized training, in which case they can be known by the term granthi) may recite, sing, and explain the verses from the Guru Granth Sahib, in the presence of the rest of the congregation. All gurdwaras have a hall, where people can eat free vegetarian food served by volunteers at the gurdwara. They may also have a medical facility room, library, nursery, classroom, meeting rooms, playground, sports ground, a gift shop, and finally a repair shop. A gurdwara can be identified from a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Buildings And Structures In Dhaka
Religion is usually defined as a social-cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Religions have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurdwaras In Bangladesh
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Sikh gurus, Guru") is a place of assembly and place of worship, worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths are welcomed in gurdwaras. Each gurdwara has a ''Darbar Sahib Hall, Darbar Sahib'' where the current and everlasting guru of the Sikhs, the scripture Guru Granth Sahib, is placed on a (an elevated throne) in a prominent central position. Any congregant (sometimes with specialized training, in which case they can be known by the term granthi) may recite, sing, and explain the verses from the Guru Granth Sahib, in the presence of the rest of the congregation. All gurdwaras have a hall, where people can eat free vegetarian food served by volunteers at the gurdwara. They may also have a medical facility room, library, nursery, classroom, meeting rooms, playground, sports ground, a gift shop, and finally a repair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langar (Sikhism)
In Sikhism, a langar ( pa, ਲੰਗਰ, 'kitchen'Pashaura Singh, Louis E. Fenech, 2014The Oxford Handbook of Sikh Studies/ref>) is the community kitchen of a gurdwara, which serves meals to all free of charge, regardless of religion, caste, gender, economic status, or ethnicity. People sit on the floor and eat together, and the kitchen is maintained and serviced by Sikh community volunteers. The meals served at a langar are always lacto-vegetarian. Etymology ''Langar'' is a Persian word that was eventually incorporated into the Punjabi language and lexicon. Origins Concept of charity and providing cooked meals or uncooked raw material to ascetics and wandering yogis has been known in eastern cultures for over 2000 years. However, in spite of institutional support from several kings and emperors of the Delhi sultanate (up to the Mughal empire), it could not be institutionalized into a sustainable community kitchen, but continued as volunteer-run free food opportunities. Suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirtan
Kirtana ( sa, कीर्तन; ), also rendered as Kirtan, is a Sanskrit word that means "narrating, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts, connoting a musical form of narration or shared recitation, particularly of spiritual or religious ideas, native to the Indian subcontinent. With roots in the Vedic ''anukirtana'' tradition, a kirtan is a call-and-response style song or chant, set to music, wherein multiple singers recite or describe a legend, or express loving devotion to a deity, or discuss spiritual ideas. It may include dancing or direct expression of ''bhavas'' (emotive states) by the singer. Many kirtan performances are structured to engage the audience where they either repeat the chant,Sara Brown (2012), ''Every Word Is a Song, Every Step Is a Dance'', PhD Thesis, Florida State University (Advisor: Michael Bakan), pages 25-26, 87-88, 277 or reply to the call of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib ( pa, ਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru following the lineage of the ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth ( pa, ਆਦਿ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ), its first rendition, was compiled by the fifth guru, Guru Arjan (1564–1606). Its compilation was completed on 29 August 1604 and first installed inside Golden Temple in Amritsar on 1 September 1604. Baba Buddha was appointed the first Granthi of the Golden Temple. Shortly afterwards Guru Hargobind added Ramkali Ki Vaar. Later, Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru, added hymns of Guru Tegh Bahadur to the Adi Granth and affirmed the text as his successor. This second rendition became known as the Guru Granth Sahib and is also sometimes referred to as the Adi Granth. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib ( pa, ਗੁਰੂ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ) is the central holy religious scripture of Sikhism, regarded by Sikhs as the final, sovereign and Guru Maneyo Granth, eternal Guru following the lineage of the Sikh gurus, ten human gurus of the religion. The Adi Granth ( pa, ਆਦਿ ਗ੍ਰੰਥ), its first rendition, was compiled by the fifth guru, Guru Arjan (1564–1606). Its compilation was completed on 29 August 1604 and first installed inside Golden Temple in Amritsar on 1 September 1604. Baba Buddha was appointed the first Granthi of the Golden Temple. Shortly afterwards Guru Hargobind added Ramkali Ki Vaar. Later, Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh guru, added hymns of Guru Tegh Bahadur to the Adi Granth and affirmed the text as his successor. This second rendition became known as the Guru Granth Sahib and is also sometimes referred to as the Adi Granth. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recension
Recension is the practice of editing or revising a text based on critical analysis. When referring to manuscripts, this may be a revision by another author. The term is derived from Latin ''recensio'' ("review, analysis"). In textual criticism (as is the case with Biblical scholarship) the count noun ''recension'' is a family of manuscripts sharing similar traits; for example, the Alexandrian text-type may be referred to as the "Alexandrian recension". The term ''recension'' may also refer to the process of collecting and analyzing source texts in order to establish a tree structure leading backward to a hypothetical original text. See also *Biblical manuscript *Categories of New Testament manuscripts *Critical apparatus A critical apparatus ( la, apparatus criticus) in textual criticism of primary source material, is an organized system of notations to represent, in a single text, the complex history of that text in a concise form useful to diligent readers and ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanak Dev Ji
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated worldwide as Guru Nanak Gurpurab on '' Katak Pooranmashi'' ('full-moon of Kattak'), i.e. October–November. Nanak is said to have travelled far and wide across Asia teaching people the message of '' ik onkar'' (), who dwells in every one of his creations and constitutes the eternal Truth. With this concept, he would set up a unique spiritual, social, and political platform based on equality, fraternal love, goodness, and virtue. Nanak's words are registered in the form of 974 poetic hymns, or '' shabda'', in the holy text of Sikhism, the Guru Granth Sahib, with some of the major prayers being the '' Japji Sahib'' (; ''ji'' and ''sahib'' are suffixes signifying respect); the '' Asa di Var'' ('ballad of hope'); and the '' Sidh Gosht'' ('di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes from the Sanskrit root ' meaning "disciple", or ' meaning "instruction". Singh, Khushwant. 2006. ''The Illustrated History of the Sikhs''. Oxford University Press. . p. 15.Kosh, Gur Shabad Ratnakar Mahan. https://web.archive.org/web/20050318143533/http://www.ik13.com/online_library.htm is an Indian religion that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent,"Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikh originated in India." around the end of the 15th century CE. It is the most recently founded major organized faith and stands at fifth-largest worldwide, with about 25–30 million adherents (known as Sikhs) .McLeod, William Hewat. 2019 998 Sikhism developed from the spiritual teachings of Guru Nanak (1469–1539), the faith's first gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verandah
A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure. Although the form ''verandah'' is correct and very common, some authorities prefer the version without an "h" (the ''Concise Oxford English Dictionary'' gives the "h" version as a variant and '' The Guardian Style Guide'' says "veranda not verandah"). Australia's ''Macquarie Dictionary'' prefers ''verandah''. Architecture styles notable for verandas Australia The veranda has featured quite prominently in Australian vernacular architecture and first became widespread in colonial buildings during the 1850s. The Victorian Filigree architecture style is used by residential (particularly terraced houses in Australia and New Zealand) and commercial buildings (particularly hotels) across Australia and features decorative screens of wrought iron, cast iron "lace" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |