|
Gundis
Gundis or comb rats (family Ctenodactylidae) are a group of small, stocky rodents found in Africa. They live in rocky deserts across the northern parts of the continent. The family comprises four living genera and five species ( Speke's gundi, Felou gundi, Val's or desert gundi, common or North African gundi and Mzab gundi), as well as numerous extinct genera and species. They are in the superfamily Ctenodactyloidea. Local people in northern Africa have always known about gundis, however they first came to the notice of western naturalists in Tripoli in 1774, and were given the name ''gundi mice''. While they are not regarded as pests, some people hunt gundis for food. Description Gundis are from 17 to 18 cm in body length, with compact bodies covered in soft fur, short legs, and large eyes. They have only four toes on all feet and the middle toes of the hind feet carry comb-like bristles, which earned them the name "comb rat". Gundis have short tails, which in some spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gundi (Ctenodactylidae)
Gundis or comb rats (family Ctenodactylidae) are a group of small, stocky rodents found in Africa. They live in rocky deserts across the northern parts of the continent. The family comprises four living genera and five species ( Speke's gundi, Felou gundi, Val's or desert gundi, common or North African gundi and Mzab gundi), as well as numerous extinct genera and species. They are in the superfamily Ctenodactyloidea. Local people in northern Africa have always known about gundis, however they first came to the notice of western naturalists in Tripoli in 1774, and were given the name ''gundi mice''. While they are not regarded as pests, some people hunt gundis for food. Description Gundis are from 17 to 18 cm in body length, with compact bodies covered in soft fur, short legs, and large eyes. They have only four toes on all feet and the middle toes of the hind feet carry comb-like bristles, which earned them the name "comb rat". Gundis have short tails, which in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
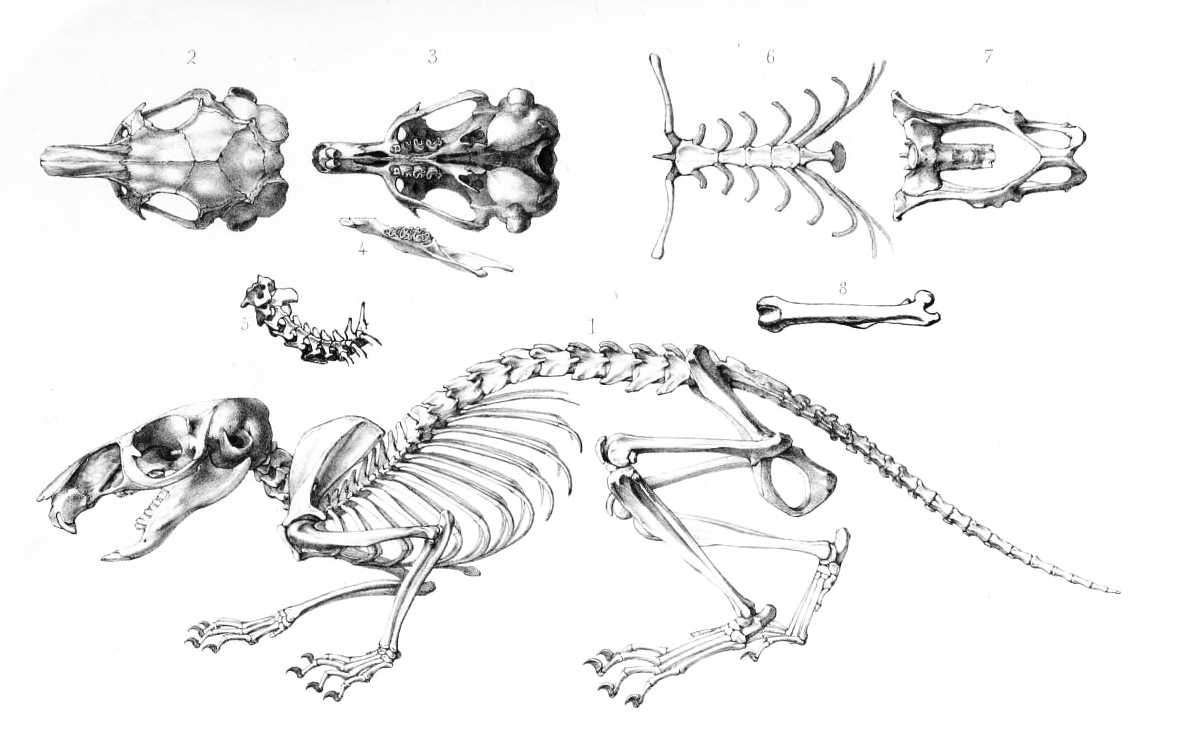
Common Gundi
The common gundi (''Ctenodactylus gundi'') is a species of rodent in the family Ctenodactylidae. It is found in Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia. The parasitic organism ''Toxoplasma gondii'' was first described in 1908 in Tunis by Charles Nicolle and Louis Manceaux within the tissues of the gundi. Description The common gundi grows to a length of between , having a stumpy tail of . A gundi weighs about . It resembles a guinea pig in appearance, having big eyes, flat ears and short limbs. Each foot has four digits and sharp, dark claws; the two hind feet have comblike bristles between the claws. Gundi's teeth are rootless. Distribution This gundi is found in northern Africa on the south side of the Atlas Mountains at altitudes up to about . Its range extends from western Libya through Tunisia and Algeria to eastern Morocco. Ecology and biology Gundis are Diurnality, diurnal and Herbivore, herbivorous. It lives in rocky, arid places, making its home in crevices and under bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Gundi
The common gundi (''Ctenodactylus gundi'') is a species of rodent in the family Ctenodactylidae. It is found in Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia. The parasitic organism ''Toxoplasma gondii'' was first described in 1908 in Tunis by Charles Nicolle and Louis Manceaux within the tissues of the gundi. Description The common gundi grows to a length of between , having a stumpy tail of . A gundi weighs about . It resembles a guinea pig in appearance, having big eyes, flat ears and short limbs. Each foot has four digits and sharp, dark claws; the two hind feet have comblike bristles between the claws. Gundi's teeth are rootless. Distribution This gundi is found in northern Africa on the south side of the Atlas Mountains at altitudes up to about . Its range extends from western Libya through Tunisia and Algeria to eastern Morocco. Ecology and biology Gundis are Diurnality, diurnal and Herbivore, herbivorous. It lives in rocky, arid places, making its home in crevices and under bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speke's Pectinator
Speke's pectinator (''Pectinator spekei'') or Speke's gundi, is a species of rodent in the family Ctenodactylidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Pectinator''.Dieterlen, F. 2005. Family Ctenodactylidae pp. 1536-1537 ''in'' D. E. Wilson and M. A. Reeder, eds. ''Mammal Species of the World'', 3rd edition, p. 1536. It is found in Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ..., and rocky areas. References * Coetzee, N. & Grubb, P. 2004''Pectinator spekei'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midday
Noon (or midday) is 12 12-hour clock, o'clock in the daytime. It is written as 12 noon, 12:00 m. (for 12-hour clock, meridiem, literally 12:00 noon), 12 p.m. (for 12-hour clock, post meridiem, literally "after noon"), 12 pm, or 12:00 (using a 24-hour clock) or 1200 (24-hour_clock, military time). Solar noon is the Sun transit time, time when the Sun appears to culmination, contact the local celestial meridian (astronomy), meridian. This is when the Sun reaches its apparent solar zenith angle, highest point in the sky, at 12 noon apparent solar time and can be observed using a sundial. The time zone, local or clock time of solar noon depends on the longitude and date, with Daylight Savings Time tending to place solar noon closer to 1:00pm. Etymology The word ''noon'' is derived from Latin ''nona hora'', the ninth Liturgy of the Hours#Canonical hours, canonical hour of the day, in reference to the Western Christian liturgical term None (liturgy)#Origin of None, none, one of the fix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenodactylus
''Ctenodactylus'' is a genus of rodent in the family Ctenodactylidae (comb rats or gundis). It encompasses the common gundi (''C. gundi'') and the closely related species Val's gundi Val's gundi (''Ctenodactylus vali'') is a species of rodent in the family Ctenodactylidae. It is known from two widely separated areas of North Africa. Description Val's gundi is very similar to the other species of gundi, especially the common ... (''C. vali''). References * Dieterlen, F. 2005. Family Ctenodactylidae pp. 1536-1537 ''in'' D. E. Wilson and M. A. Reeder, eds. ''Mammal Species of the World'', 3rd edition, p. 1536. Rodent genera Mammals described in 1830 Taxa named by John Edward Gray Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{rodent-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaning
Weaning is the process of gradually introducing an infant human or another mammal to what will be its adult diet while withdrawing the supply of its mother's milk. The process takes place only in mammals, as only mammals produce milk. The infant is considered to be fully weaned once it is no longer fed by any breast milk (or bottled substitute). Humans In some cultures, weaning progresses with the introduction of feeding the child food that has been prechewed by the parent along with continued breastfeeding, a practice known as premastication. The practice was important throughout human history in that it naturally gave a child a greatly improved protein source in addition to preventing iron deficiency. However, premasticated food from caregivers of lower socioeconomic status in areas of endemic diseases can result in the passing of the disease to the child. How and when to wean a human infant is controversial. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends feeding a baby on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies that strengthen the immune system, and thus reduces the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose. As an agricultural product, dairy milk is Milking, collected from farm animals. In 2011, Dairy farming, dairy farms produced around of milk from 260 million dairy cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand for dairy products within India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New Zealand, Germany and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time, for example in a multiple birth. The time interval of a gestation is called the '' gestation period''. In obstetrics, ''gestational age'' refers to the time since the onset of the last menses, which on average is fertilization age plus two weeks. Mammals In mammals, pregnancy begins when a zygote (fertilized ovum) implants in the female's uterus and ends once the fetus leaves the uterus during labor or an abortion (whether induced or spontaneous). Humans In humans, pregnancy can be defined clinically or biochemically. Clinically, pregnancy starts from first day of the mother's last period. Biochemically, pregnancy starts when a woman's human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as ''diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)

