|
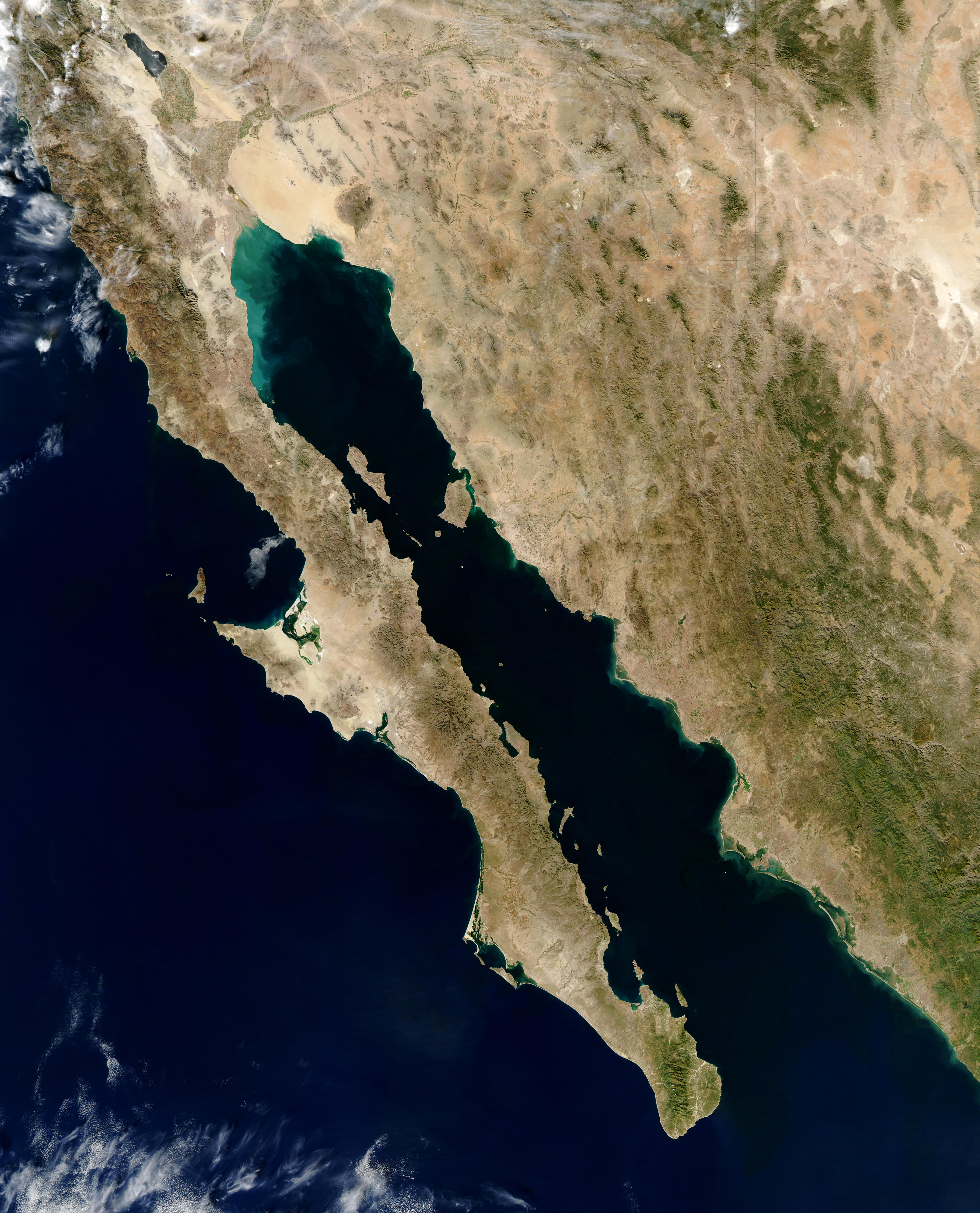
Gulf Of California Xeric Scrub
The Gulf of California xeric scrub ( es, Matorral xerófilo del Golfo de California) is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of Mexico's Baja California Peninsula. Geography The Gulf of California xeric scrub covers an area of , lying on the eastern side of the peninsula along the Gulf of California. The Peninsular Ranges, including the Sierra de San Francisco and Sierra de la Giganta, run the length of the peninsula, separate the Gulf of California xeric scrub from the Baja California Desert on Baja California's Pacific slope. The ecoregion extends from the gulf shore to the crest of the mountains, and includes several of the islands in the gulf, the largest of which are Isla Ángel de la Guarda, Isla del Carmen, and Isla San José. To the north, the Gulf of California xeric scrub transitions to the Sonoran Desert. At the southern end of the peninsula, the Gulf of California xeric scrub transitions to the San Lucan xeric scrub. Flora Most of the ecoregion is covered in dry shrubland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isla Ángel De La Guarda
Isla Ángel de la Guarda, (Guardian Angel Island) also called Archangel Island, is a large island in the Gulf of California (Sea of Cortez) east of Bahía de los Ángeles in northwestern Mexico, separated from the Baja California Peninsula by the Canal de Ballenas (Whales Channel). It is the second largest of the eleven Midriff Islands or Islas Grandes. It is part of the state of Baja California, located northwest of Tiburón Island. It is a biological reserve called Isla Angel de la Guarda National Park. The island is part of the Mexicali municipality. The geologically active Ballenas Fault runs along the seabed of the linear Canal de Ballenas. A 6.9 magnitude earthquake occurred on this fault in 2009. Geography The island is extremely dry, with no sources of freshwater other than washes following rainfall. It has an area of and a chain of mountains runs along its 69 km length, reaching a maximum of above sea level. It runs northwest to southeast. The west coast is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites Communis
''Phragmites australis'', known as the common reed, is a species of plant. It is a broadly distributed wetland grass that can grow up to tall. Description ''Phragmites australis'' commonly forms extensive stands (known as reed beds), which may be as much as or more in extent. Where conditions are suitable it can also spread at or more per year by horizontal runners, which put down roots at regular intervals. It can grow in damp ground, in standing water up to or so deep, or even as a floating mat. The erect stems grow to tall, with the tallest plants growing in areas with hot summers and fertile growing conditions. The leaves are long and broad. The flowers are produced in late summer in a dense, dark purple panicle, about long. Later the numerous long, narrow, sharp pointed spikelets appear greyer due to the growth of long, silky hairs. These eventually help disperse the minute seeds. Taxonomy Recent studies have characterized morphological distinctions between the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typha Domingensis
''Typha domingensis'', known commonly as southern cattail or cumbungi, is a perennial herbaceous plant of the genus '' Typha''. Distribution and habitat It is found throughout temperate and tropical regions worldwide. It is sometimes found as a subdominant associate in mangrove ecosystems such as the Petenes mangroves ecoregion of Yucatán. Uses In the Mesopotamian Marshes of southern Iraq, Khirret is a dessert made from the pollen of this plant. In Turkish folk medicine the female inflorescences of this plant and other ''Typha'' are used externally to treat wounds such as burns. Extracts of ''T. domingensis'' have been demonstrated to have wound healing properties in rat models. Water extracts of the fruit, female flower and male flower of ''Typha domingensis'' exhibit iron chelating activity as well as superoxide and nitric oxide scavenging activities. By contrast, only the fruit and female flower extracts were found to have alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity. A part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
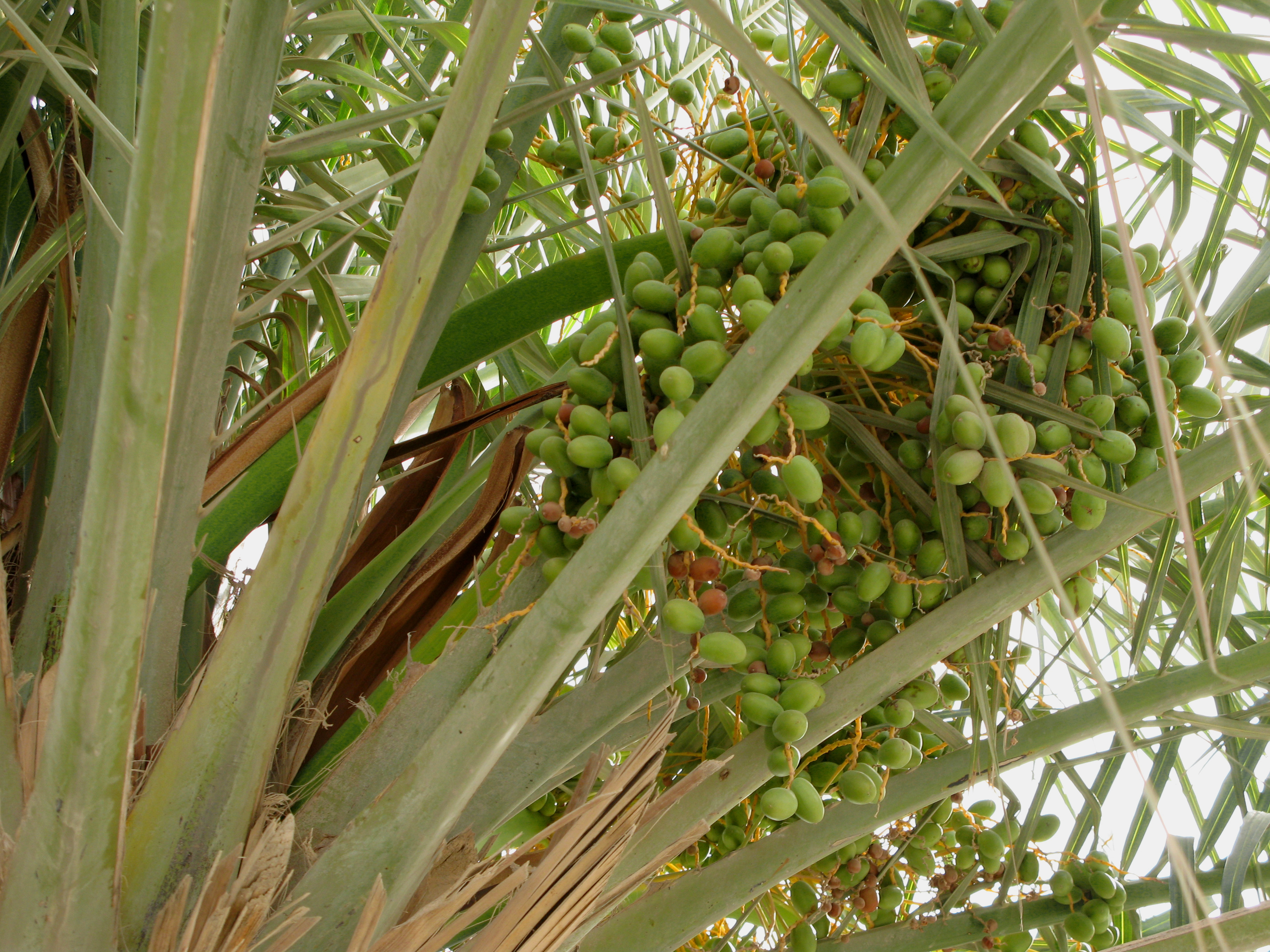
Date Palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia, and is naturalized in many tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. ''P. dactylifera'' is the type species of genus ''Phoenix'', which contains 12–19 species of wild date palms. Date trees reach up to in height, growing singly or forming a clump with several stems from a single root system. Slow-growing, they can reach over 100 years of age when maintained properly. Date fruits (dates) are oval-cylindrical, long, and about in diameter, with colour ranging from dark brown to bright red or yellow, depending on variety. Containing 61–68 percent sugar by mass when dried, dates are very sweet and are enjoyed as desserts on their own or within confections. Dates have been cultivated in the Middle East and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washingtonia Robusta
''Washingtonia robusta'', known by common name as the Mexican fan palm, Mexican washingtonia, or skyduster is a palm tree native to the Baja California peninsula and a small part of Sonora in northwestern Mexico. Despite its limited native distribution, ''W. robusta'' one of the most widely cultivated subtropical palms in the world. It is naturalized in Florida, California, Hawaii, Texas, parts of the Canary Islands, France, Italy, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Qatar, Spain, Réunion, and Morocco. Description ''W. robusta'' grows to tall, rarely up to . The leaves have a petiole up to long, and a palmate fan of leaflets up to long. The inflorescence is up to long, with numerous small, pale orange-pink flowers. The fruit is a spherical, blue-black drupe, diameter; it is edible, though thin-fleshed. Taxonomy It is one of two species in the genus ''Washingtonia''. The other is the close relative ''Washingtonia filifera,'' which occupies a more northerly distribution. Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pithecellobium Undulatum
''Pithecellobium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. The generic name is derived from the Greek words πίθηκος (''pithêkos''), meaning "ape" or "monkey," and ἐλλόβιον (''ellobion''), meaning "earring," which refers to the coiled shape of the fruit pods. Plants of the genus are known generally as blackbeads. Species There are about 75 species in the genus: The Plant List. * '''' Britton & Rose * '''' Northr. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercidium Floridum
''Parkinsonia florida'', the blue palo verde ( syn. ''Cercidium floridum''), is a species of palo verde native to the Sonoran Deserts in the Southwestern United States and Northwestern Mexico.Calflora Database: ''Parkinsonia florida'' accessed 4.1.2013 Its name means "green pole or stick" in Spanish, referring to the green trunk and branches, that perform . Description ''Parkinsonia florida'' grows to heights of . It is a rapidly growing large shrub or small , and rarely survives to 100 years. Compared to ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Brandegeana
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus name is New Latin, borrowed from the Greek (), a term used by Dioscorides for a preparation extracted from the leaves and fruit pods of ''Vachellia nilotica'', the original type of the genus. In his ''Pinax'' (1623), Gaspard Bauhin mentioned the Greek from Dioscorides as the origin of the Latin name. In the early 2000s it had become evident that the genus as it stood was not monophyletic and that several divergent lineages needed to be placed in separate genera. It turned out that one lineage comprising over 900 species mainly native to Australia, New Guinea, and Indonesia was not closely related to the much smaller group of African lineage that contained ''A. nilotica''—the type species. This meant that the Australasian lineage (by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olneya Tesota
''Olneya tesota'' is a perennial flowering tree of the family Fabaceae, legumes (peas, beans, etc.), which is commonly known as ironwood, desert ironwood, or palo fierro in Spanish. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Olneya''. This tree is part of the western Sonoran Desert complex in the Southwestern United States. Description The desert ironwood grows as a bush or tree, reaching heights of about and average trunk diameters of about . Exceptionally, in larger protected washes it can reach greater height and a more massive trunk. In younger trees, the bark is gray, shiny, and smooth; in older trees the bark is broken open. The tree is evergreen, but can lose its leaves if temperatures fall below . In continual drought conditions the leaves will be lost. The leaves are bluish-green and pinnately compound. They are arranged on a petiole, long, with 6–9 leaflets (or variously up to 15, with 7 opposite and one terminal), each measuring . At the base of each pinna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jatropha Cinerea
''Jatropha'' is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. The name is derived from the Greek words ἰατρός (''iatros''), meaning "physician", and τροφή (''trophe''), meaning "nutrition", hence the common name physic nut. Another common name is nettlespurge. It contains approximately 170 species of succulent plants, shrubs and trees (some are deciduous, like ''Jatropha curcas''). Most of these are native to the Americas, with 66 species found in the Old World. Plants produce separate male and female flowers. As with many members of the family Euphorbiaceae, ''Jatropha'' contains compounds that are highly toxic. ''Jatropha'' species have traditionally been used in basketmaking, tanning and dye production. In the 2000s, one species, ''Jatropha curcas'', generated interest as an oil crop for biodiesel production and also medicinal importance when used as lamp oil; native Mexicans in the Veracruz area developed by selective breeding a ''Jatropha cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrosia Dumosa
''Ambrosia dumosa'', the burro-weed or white bursage, a North American species of plants in the family Asteraceae. It is a common constituent of the creosote-bush scrub community throughout the Mojave desert of California, Nevada, and Utah and the Sonoran Desert of Arizona and northwestern Mexico (Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, Chihuahua). ''Ambrosia dumosa'' has been studied to determine allelopathic interactions with creosote bush, ''Larrea tridentata'', which produces a chemical that inhibits the growth of ''A. dumosa.'' Other studies have suggested that ''A. dumosa'' roots produce a chemical that causes them to grow away from conspecific roots, preventing competition for water resources. In addition to burro-weed, ''A. dumosa'' is also commonly called white bursage, and burrobush. Description ''Ambrosia dumosa'', a form of ragweed, is a highly branched shrub 20 to 90 cm in height. The younger stems are covered with soft gray-white hairs. Approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |