|
Guite
Guite is the progenitor clan of Mizo people He is also said to be the Older Brother of Thadou progenitor of the Thadou people. Mostly the Guite clan speak mizo language . Some known as Zomi and few also as kuki in India and as Zogam in Myanmar (Burma). Depending on local pronunciation, the clan was also called differently such as Nguite, Vuite, and was also recorded even as Gwete, Gwite, Nwite. In accord with the claim of their solar origin, the Guite clan has been called ''nampi'', meaning noble or major or even dominant people, of the region in local dialect in the past. Adoption of the name The name Guite is a direct derivation of the name of the progenitor of the family, known as Guite the Great (see, following genealogical charts), whose mysterious birth was, according to oral tradition, related to the Sun. Therefore, in order to reflect this solar relationship (i.e., "ni gui" meaning the ray of the Sun), the name "Guite" is said given at his birth by his father, Songthu(a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vangteh
Vangte or Vangteh is a large village in southern Tedim Township, Falam District, Chin State, in Myanmar. Vangteh is also the name of the village tract where Vangte lies. Name It is sometimes spelled as Wunkathe, probably a mispronunciation by Burmese guides when the British came to the land for the first time, and also recorded as Vangte by contemporary writers as can be seen in the information provided by such as ''the Satellite Views'', ''the Falling Rain Genomics, Inc.'', ''the Travel Post'', and such. In the local area, Vangteh is still known as a "khua-pi", in the language of the natives, "khua" generally means any human abode, big or small, and "pi" is a suffix meaning "large" in extent or "great" in character or "big" in size. Hence maybe a reference to former greatness despite its very discouraging geographical situation in the mountainous Chin Hills, where elevations vary from 1500 and 2700 meters. In common poetic expression, Vangteh is also addressed as "Khum''h''nua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciimnuai
Ciimnuai was the legendary city-state of Zomi, who are mostly referred to as Chins in Myanmar, Mizo, Kuki in India, and Bawmzo in Bangladesh. Being their birthplace, Ciimnuai bears many accounts of myths and legends of Zomi. Carey and Tuck even called the city "Eden of the Chins". According to tradition, it is located about two and half miles southwest from present Tedim and is in the precinct of present Saizang village. Traditions ascribe the founding of the city to Guite family, the then ruling house. Some of its remainings can still be collected at the site. However, some contemporary local historians contend that this current site might not be the only Ciimnuai that bears such numerous myths and stories, proposing that there might still be other ''Ciimnuai''s outside of present Chin Hills.Sing Khaw Khai, ''Zo People and Their Culture: a historical, cultural study and critical analysis of Zo and its ethnic tribes'' (New Lamka, Manipur: Khampu Hatzaw, 1995), 21. If it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciimnuai Generation
Ciimnuai was the legendary city-state of Zomi, who are mostly referred to as Chins in Myanmar, Mizo, Kuki in India, and Bawmzo in Bangladesh. Being their birthplace, Ciimnuai bears many accounts of myths and legends of Zomi. Carey and Tuck even called the city "Eden of the Chins". According to tradition, it is located about two and half miles southwest from present Tedim and is in the precinct of present Saizang village. Traditions ascribe the founding of the city to Guite family, the then ruling house. Some of its remainings can still be collected at the site. However, some contemporary local historians contend that this current site might not be the only Ciimnuai that bears such numerous myths and stories, proposing that there might still be other ''Ciimnuai''s outside of present Chin Hills.Sing Khaw Khai, ''Zo People and Their Culture: a historical, cultural study and critical analysis of Zo and its ethnic tribes'' (New Lamka, Manipur: Khampu Hatzaw, 1995), 21. If it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gokhothang
Goukhothang, Raja (–1872) was a prince from the Guite people, Guite family of Zo people, Zomi also known as Tedim Chin in Myanmar (Burma) and Paite language, Paite in India. He was known as the then leader of all Zo people as Carey and Tuck also noted him as the Yo (correct Zo people) Chief of Mwelpi (correct Mualpi) he was later capture by meetei Maharaj Chandrakirti and died in Imphal jail unconditionally. According to his documentary video presentation released in 2006, he was born in Tedim-Lamzang of present Chin State (Myanmar-Burma), one of the then political centers of the Guite dynasty. He succeeded his father, his lordship Prince Mang Suum II, in 1855, and moved the capital to fortified city of Mualpi of present Tonzang township of Chin State. In commemoration of his lordship, a football tournament is bi-annually held in Lamka (Churachandpur) by Ropiang Foundation Trust.More pages on Raja Gokhothang can be read in a recent publication on the Guite family history in Ngu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chin People
The Chin people (, ) are a Southeast Asian people native to Chin State and its neighbouring states of Myanmar.Head, JonathanBurma's 'abused Chin need help' ''BBC News'', Jan 28, 2009, accessed Jan 28, 2009 The Chin are one of the founding groups (Chin, Kachin, Shan and Bamar) of the Union of Burma. The Chin speak a variety of related languages, share elements of cultures and traditions. According to the British state media BBC News, "The Chin people... are one of the most persecuted minority groups in Burma." These people predominantly live in the Chin State, Bago Division, Ayeyarwady Division, Magwe Division, Rakhine State and Sagaing Region of Myanmar, but are also spread throughout Burma, Bangladesh and India. In the 2014 Burmese ethnic census, the Chin ethnicity was again dismissed by the people of the Chin State. It is to be noted that the Mizo people in Mizoram, India and the Chin are both Chin-Kuki-Mizo people, who share the same history with each other. The difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
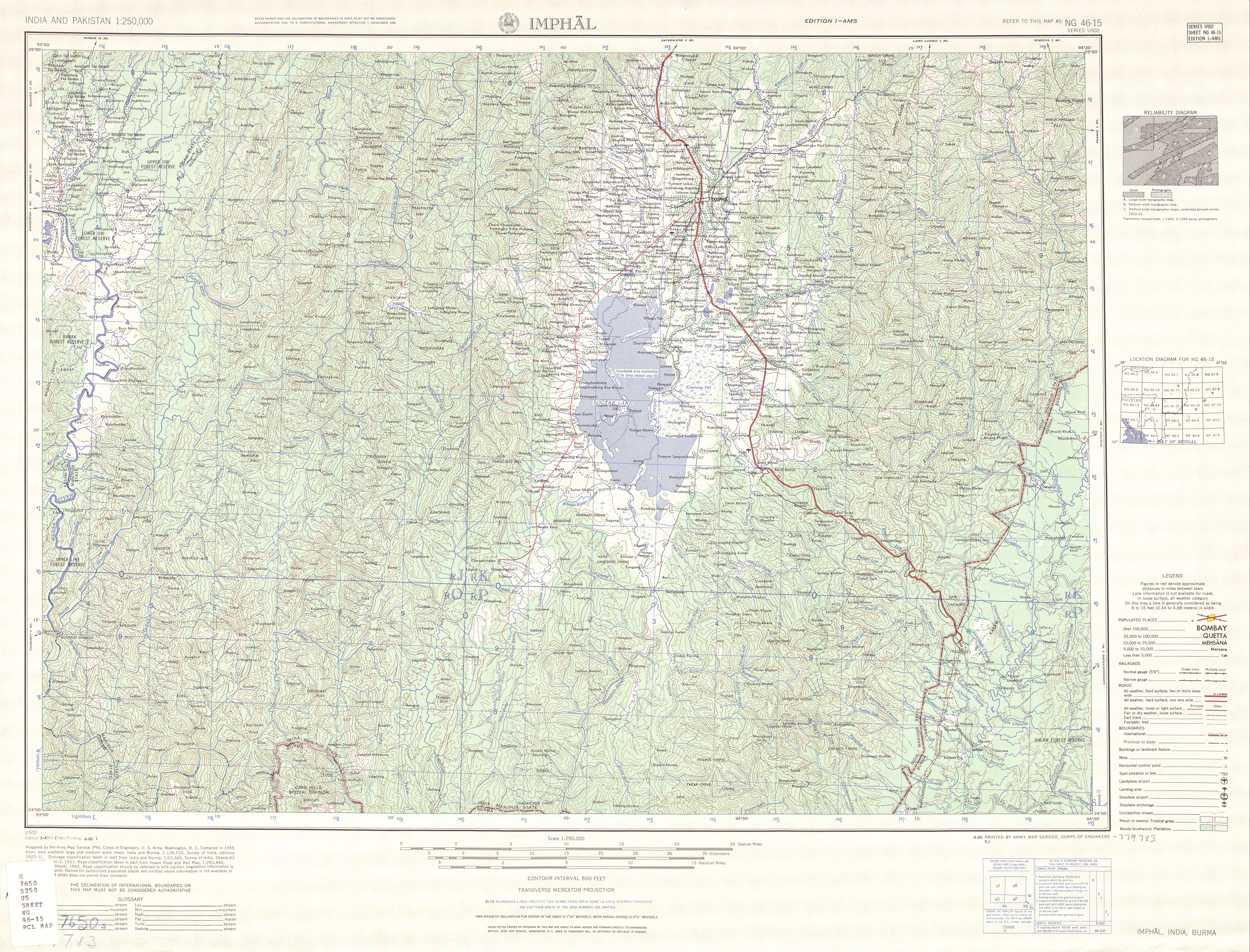
Tedim
Tedim (, , ( Zo: ''Tedim Khawpi'', pronounced ; is a town in and the administrative seat of Tedim Township, Chin State, in the north-western part of Burma. It is the second largest town in Chin State. The town's four major boroughs (''vengte'') are: Sakollam, Myoma, Lawibual and Leilum. The population is primarily Zomi. History The name "Tedim" was derived from a pool in the hills that used to twinkle in the sunlight. Therefore it was called ''te-dim'' (twinkling, shiny) in the local Zomi language. As the Zomi lacked a formal writing system in the past, the story of Tedim mostly depends on oral tradition Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication wherein knowledge, art, ideas and cultural material is received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another. Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985 .... Establishment of Tedim is ascribed to Gui Mang II, a powerful prince from the then ruling Guite family in the region (c. 1600 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
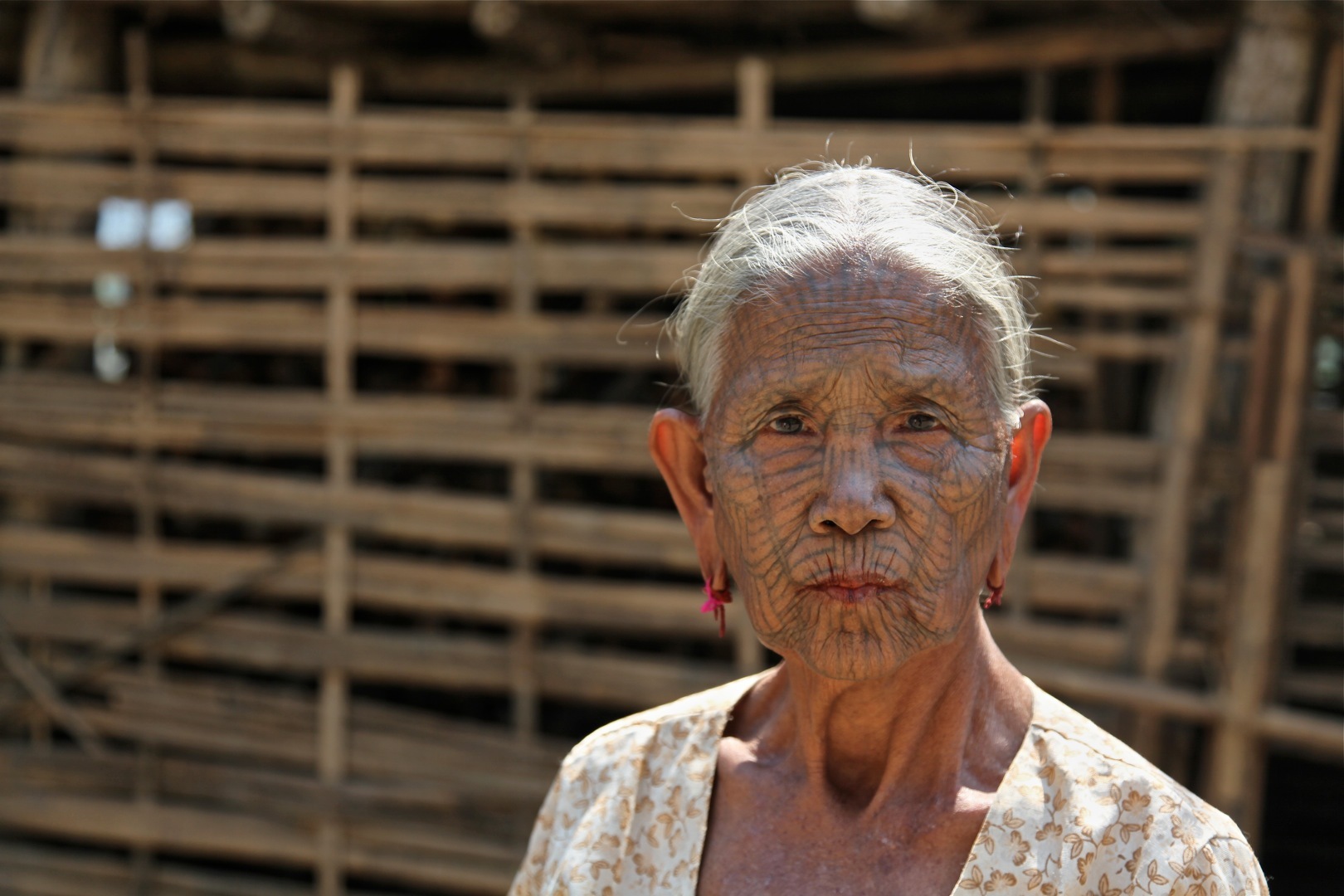
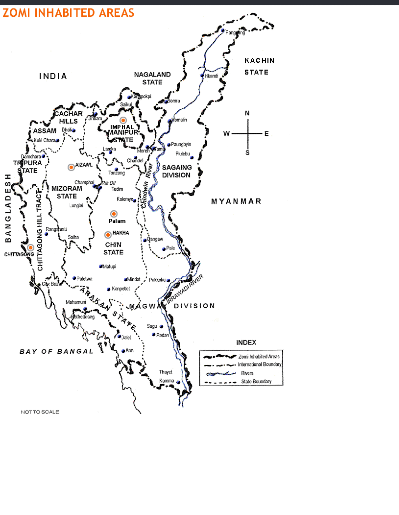
Zomi
The Zomi are an ethnic group which can be found in India, Myanmar and in Chittagong hill tracks of Bangladesh. The word Zomi is used to describe an ethnic group, which is also known as the Chin people, Chin, the Mizo people, Mizo, the Kuki people, Kuki, or a number of other names based on geographic distribution, that is a member of a large group of related Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman peoples spread throughout the Northeast India, northeastern states of India, northwestern Myanmar (Burma) and the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. In northeastern India, they are present in Chin State, Nagaland, Mizoram, Manipur and Assam. The dispersal across international borders resulted from a British Raj, British colonial policy that drew borders on political, rather than ethnic, grounds. They speak more than fifty dialects. Names Various names have been used for the Zomi peoples, but the individual groups generally acknowledge descent from ancestral Chin-Kuki. Among the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thadou People
Thadou people are an indigenous ethnic group of Chin-Kuki inhabiting North-east India. Thadou is a dialect of the Tibeto-Burman family. They are the second largest in terms of population in Manipur, next to Meetei according to Manipur census 2011. Thadou population have been reported only in India, some small population have settled in Nagaland, Assam, Tripura, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Delhi. Thadous share a common culture with all the Chin-Kuki-Mizo community. Religion A great majority of the Thadou people are Christians. Christianity among the Thadous can be traced back to an Anglican named William Pettigrew who worked in Manipur as a missionary from 1894. The 100th anniversary of the Thadou people embracing Christianity was held at Motbung, Sadar Hills, Manipur, India on 13 December 2008 under the aegis of the Thadou Baptist Association. History The Thadou people believed that Chongthu, a great Chief of the Thadous, emerged out from a cave called "Chinlung or Shinlung or Khul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabaw Valley
The Kabaw Valley also known as Kubo valley is a highland valley in Myanmar's western Sagaing division, close to the border with India's Manipur. The valley is located between Heerok or Yoma ranges of mountains, which constitute the present day border of Manipur, and the Chindwin River (also called the Ningthi River). The valley is home to a number of ethnic groups including the Meitei (Kathe and Paona), the Maring tribe, the Thadou people, Kuki people, the Mizo, the Kadu and the Kanan. During the First Anglo-Burmese War, the Manipuri prince Gambhir Singh conquered the Kabaw valley from Burma. It remained under Manipur control for several years. But the Burmans were able to prove to the British Resident, Major Burney, that the valley had been ceded to Burma by the former Manipur King Marjit Singh in 1813. The British were persuaded to hand the valley back to Burma in 1834. The British compensated Manipur for the loss of territory by annual subsidy. Lai (Hakha) History Kaba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningthou
Ningthou was a title used for the King of Manipur. The Ningthou was used to refer to the King after the reign of Pakhangba and was a title used until King Pamheiba. The subsequent Sanskritization undertaken by Pamheiba and Shantidas Adhikari changed the title of the King to Maharaja or Raja though the native name was still used for some Kings (ex. Ching-Thang Khomba, Ningthou Ching-Thang Khomba) See also *List of Meitei royals *Manipur (princely state) References External links * * Ningthou, Meitei royalty {{India-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subedar
Subedar is a rank of junior commissioned officer in the Indian Army; a senior non-commissioned officer in the Pakistan Army, and formerly a Viceroy's commissioned officer in the British Indian Army. History ''Subedar'' or ''subadar'' was the second-highest rank of Indian officer in the military forces of British India, ranking below "British Commissioned Officers" and above "Local Non-Commissioned Officers". Indian officers were promoted to this rank on the basis of both lengths of service and individual merit. Under British rule, a Risaldar was the cavalry equivalent of a Subedar. A Subedar / Risaldar was ranked senior to a Jemadar and junior to a Subedar Major / Risaldar Major in an infantry / cavalry regiment of the Indian Army. Both Subedars and Risaldars wore two stars as rank insignia. The rank was introduced in the East India Company's presidency armies (the Bengal Army, the Madras Army and the Bombay Army) to make it easier for British officers to communicate with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |