|
Großer Kranichsee
The ( cz, Velké jeřábí jezero) is one of the most important raised bogs (') under nature conservation in the Ore Mountains of Central Europe. Location The raised bog is located at an elevation of 950 metres above sea level (NN) in a high forest clearing southwest of Carlsfeld. The border between Germany and the Czech Republic runs through the reserve. West of the Kranichsee is the "black pond" ('). Name The name of the bog is related to the Slavic word ''granica'', which means border. Significance It is a watershed and krummholz bog that is drained to the northwest by the Große Pyra and to the southwest by the Rolava. To the east is the Kleiner Kranichsee, where the heart of the bog, unlike the Großer Kranichsee, lies on the German side of the border. Vegetation *Mountain pine (''Pinus mugo'') *Hare's-tail cotton-grass (''Eriophorum vaginatum'') *Black crowberry (''Empetrum nigrum'') *Bog bilberry (''Vaccinium uliginosum'') *Bog rosemary (''Andromeda polifolia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raised Bog
Raised bogs, also called ombrotrophic bogs, are acidic, wet habitats that are poor in mineral salts and are home to flora and fauna that can cope with such extreme conditions. Raised bogs, unlike fens, are exclusively fed by precipitation ( ombrotrophy) and from mineral salts introduced from the air. They thus represent a special type of bog, hydrologically, ecologically and in terms of their development history, in which the growth of peat mosses over centuries or millennia plays a decisive role. They also differ in character from blanket bogs which are much thinner and occur in wetter, cloudier climatic zones. Raised bogs are very threatened by peat cutting and pollution by mineral salts from the surrounding land (due to agriculture and industry). The last great raised bog regions are found in western Siberia and Canada. Terminology The term raised bog derives from the fact that this type of bog rises in height over time as a result of peat formation. They are like sponges o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Mugo
''Pinus mugo'', known as bog pine, creeping pine, dwarf mountain pine, mugo pine, mountain pine, scrub mountain pine, or Swiss mountain pine, is a species of conifer, native to high elevation habitats from southwestern to Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Description The tree has dark green leaves ("needles") in pairs, long. The cones are nut-brown, long. Custura Bucurei.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'', Romania Pinus mugo uncinata trees.jpg, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' Swiss National Park 007.JPG, ''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''rotundata'', Swiss National Park Бор кривул 01.JPG, On Jakupica mountain, Republic of North Macedonia Taxonomy There are three subspecies: *''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''mugo'' — in the east and south of the range (southern & eastern Alps, Balkan Peninsula), a low, shrubby, often multi-stemmed plant to tall with matte-textured symmetrical cones, which are thin-scaled. *''Pinus mugo'' subsp. ''uncinata'' — in the west and north o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogs Of Saxony
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; alkaline mires are called fens. A baygall is another type of bog found in the forest of the Gulf Coast states in the United States.Watson, Geraldine Ellis (2000) ''Big Thicket Plant Ecology: An Introduction'', Third Edition (Temple Big Thicket Series #5). University of North Texas Press. Denton, Texas. 152 pp. Texas Parks and Wildlife. Ecological Mapping systems of Texas: West Gulf Coastal Plain Seepage Swamp and Baygall'. Retrieved 7 July 2020 They are often covered in heath or heather shrubs rooted in the sphagnum moss and peat. The gradual accumulation of decayed plant material in a bog functions as a carbon sink. Bogs occur where the water at the ground surface is acidic and low in nutrients. In contrast to fens, they derive most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reserves In Saxony
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant " birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word '' physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
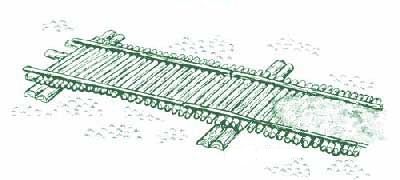
Corduroy Road
A corduroy road or log road is a type of road or timber trackway made by placing logs, perpendicular to the direction of the road over a low or swampy area. The result is an improvement over impassable mud or dirt roads, yet rough in the best of conditions and a hazard to horses due to shifting loose logs. Corduroy roads can also be built as a foundation for other surfacing. If the logs are buried in wet, acidic, anaerobic soils such as peat or muskeg, they decay very slowly. A few corduroy road foundations that date back to the early 20th century still exist in North America. One example is the Alaska Highway between Burwash Landing and Koidern, Yukon, Canada, which was rebuilt in 1943, less than a year after the original route was graded on thin soil and vegetation over permafrost, by using corduroy, then building a gravel road on top. During the 1980s, the gravel was covered with a chip-seal. The late 1990s saw replacement of this road with modern road construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ore Mountain Club
The Ore Mountain Club (german: Erzgebirgsverein) is one of the oldest and most tradition-steeped local history, mountain and hiking clubs in Germany. The club was founded in 1878. After the Second World War the club and its many branches were banned by the East German authorities, but it was refounded in West Germany in Frankfurt am Main in 1955. Only after the political events of ''Die Wende'' in 1990 was it newly founded in the Ore Mountains. At the end of 2008 the club had over 3,859 members in 61 branches. Before 1945 there were more than 25,000 members. In 1929 the Ore Mountain Club even had over 28,000 members in 156 branches and managed several accommodation houses on the Fichtelberg near Oberwiesenthal and the Schwartenberg between Seiffen and Neuhausen/Erzgeb. Today the Ore Mountain Club has 12 woodcarving and 30 bobbin lacemaking groups (''Schnitzgruppen'' and ''Klöppelgruppen''). In 2008 its members did 220,000 hours of voluntary work. The club's trail rangers l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviparous Lizard
The viviparous lizard, or common lizard, (''Zootoca vivipara'', formerly ''Lacerta vivipara''), is a Eurasian lizard. It lives farther north than any other species of non-marine reptile, and is named for the fact that it is viviparous, meaning it not only lays eggs, but also gives birth to live young. Both "''Zootoca''" and "''vivipara''" mean "live birth," in Greek and Latin respectively. It was called ''Lacerta vivipara'' until the genus ''Lacerta'' was split into nine genera in 2007 by Arnold, Arribas & Carranza. Male and female ''Zootoca vivipara'' are equally likely to contract blood parasites. Additionally, larger males have been shown to reproduce more times in a given reproductive season than smaller ones. The lizard is also unique as it is exclusively carnivorous, eating only flies, spiders, and insects. Studies show that the more carnivorous an individual is (the more insects they eat), the less diverse the population of parasitic helminths that infest the lizards. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
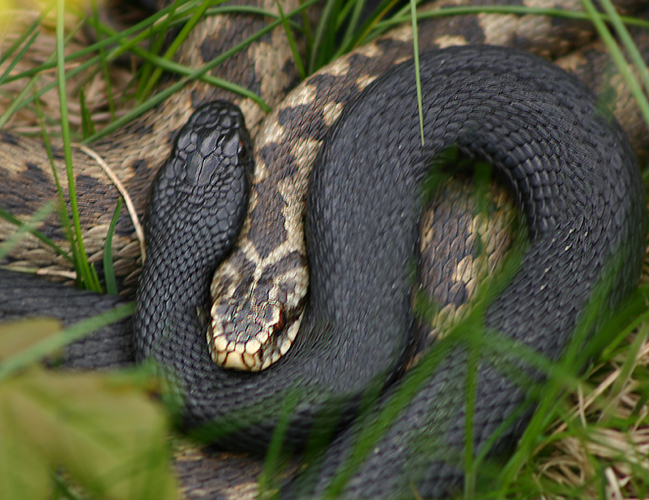
Vipera Berus
''Vipera berus'', the common European adderMallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. (2003). ''True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers''. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. . or common European viper,Stidworthy J. (1974). ''Snakes of the World''. New York: Grosset & Dunlap Inc. 160 pp. . is a venomous snake that is extremely widespread and can be found throughout most of central and eastern Europe and as far as East Asia. Known by a host of common names including common adder and common viper, adders have been the subject of much folklore in Britain and other European countries. They are not regarded as especially dangerous; the snake is not aggressive and usually bites only when really provoked, stepped on, or picked up. Bites can be very painful, but are seldom fatal. The specific name, ''berus'', is New Latin and was at one time used to refer to a snake, possibly the grass snake, ''Natrix natrix''.Gotch AF. (1986). ''Reptiles: Their Latin Names Explaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Polifolia
''Andromeda polifolia'', common name bog-rosemary, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae, native to northern parts of the Northern Hemisphere. It is the only member of the genus ''Andromeda'', and is only found in bogs in cold peat-accumulating areas. Description It is a small shrub growing to (rarely to ) tall with slender stems. The leaves are evergreen, alternately arranged, lanceolate, long and broad, dark green above (purplish in winter) and white beneath with the leaf margins curled under. The flowers are bell-shaped, white to pink, long; flowering is in late spring to early summer. The fruit is a small capsule containing numerous seeds. There are two varieties, treated as distinct species by some botanists: *''Andromeda polifolia'' var. ''polifolia''. Northern Europe and Asia, northwestern North America. *''Andromeda polifolia'' var. ''latifolia'' Aiton 789/small>. Northeastern North America ( syn. ''A. glaucophylla'' Link 821/small>, ''A. po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinium Uliginosum
''Vaccinium uliginosum'' (bog bilberry, bog blueberry, northern bilberry or western blueberry) is a Eurasian and North American flowering plant in the genus ''Vaccinium'' within the heath family. Distribution ''Vaccinium uliginosum'' is native to cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, at low altitudes in the Arctic, and at high altitudes south to the Pyrenees, the Alps, and the Caucasus in Europe, the mountains of Mongolia, northern China, the Korean Peninsula and central Japan in Asia, and the Sierra Nevada in California and the Rocky Mountains in Utah in North America. It grows on wet acidic soils on heathland, moorland, tundra, and in the understory of coniferous forests, from sea level in the Arctic, up to altitude in the south of the range. Description ''Vaccinium uliginosum'' is a small deciduous shrub growing to tall, rarely tall, with brown stems (unlike the green stems of the closely related bilberry). The leaves are oval, long and wide, blue-green wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empetrum Nigrum
''Empetrum nigrum'', crowberry, black crowberry, or, in western Alaska, blackberry, is a flowering plant species in the heather family Ericaceae with a near circumboreal distribution in the Northern Hemisphere. It is usually dioecious, but there is a bisexual tetraploid subspecies, ''Empetrum nigrum'' subsp. ''hermaphroditum'', which occurs in more northerly locations and at higher altitude. Description ''Empetrum nigrum'' is a low growing, evergreen shrub with a creeping habit. The leaves are long, arranged alternately along the stem. The stems are red when young and then fade to brown. It blooms between May and June. The flowers are small and not very noticeable, with greenish-pink sepals that turn reddish purple. The round fruits are drupes, wide, usually black or purplish-black but occasionally red. The metabolism and photosynthetic parameters of ''Empetrum'' can be altered in winter-warming experiments. Subspecies * ''Empetrum nigrum'' subsp. ''asiaticum'' (Nakai ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriophorum Vaginatum
''Eriophorum'' (cottongrass, cotton-grass or cottonsedge) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cyperaceae, the sedge family. They are found throughout the arctic, subarctic, and temperate portions of the Northern Hemisphere in acid bog habitats, being particularly abundant in Arctic tundra regions.Flora Europaea''Eriophorum''/ref> They are herbaceous perennial plants with slender, grass-like leaves. The seed heads are covered in a fluffy mass of cotton-like fibers which are carried on the wind to aid dispersal. The cotton grass also maintains a height of 12 inches and around 2 inches in water. In cold Arctic regions, these masses of translucent fibres also serve as 'down' – increasing the temperature of the reproductive organs during the Arctic summer by trapping solar radiation. Paper and the wicks of candles have been made of its fiber, and pillows stuffed with the same material. The leaves were formerly used in treating diarrhea, and the spongy pith of the stem for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
_in_the_Aamsveen%2C_The_Netherlands.jpg)

