|
Growth Curve (other) .
{{disambiguation ...
Growth curve can refer to: *Growth curve (statistics), an empirical model of the evolution of a quantity over time. *Growth curve (biology), a statistical growth curve used to model a biological quantity. * Curve of growth (astronomy), the relation between the equivalent width and the optical depth In physics, optical depth or optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to ''transmitted'' radiant power through a material. Thus, the larger the optical depth, the smaller the amount of transmitted radiant power throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Curve (statistics)
The growth curve model in statistics is a specific multivariate linear model, also known as GMANOVA (Generalized Multivariate Analysis-Of-Variance). It generalizes MANOVA by allowing post-matrices, as seen in the definition. Definition Growth curve model: Let X be a ''p''×''n'' random matrix corresponding to the observations, A a ''p''×''q'' within design matrix with ''q'' ≤ ''p'', B a ''q''×''k'' parameter matrix, C a ''k''×''n'' between individual design matrix with rank(''C'') + ''p'' ≤ ''n'' and let Σ be a positive-definite ''p''×''p'' matrix. Then : X=ABC+\Sigma^E defines the growth curve model, where A and C are known, B and Σ are unknown, and E is a random matrix distributed as ''N''''p'',''n''(0,''I''''p'',''n''). This differs from standard MANOVA by the addition of C, a "postmatrix". History Many writers have considered the growth curve analysis, among them Wishart (1938), Box (1950) and Rao (1958). Potthoff and Roy in 1964 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Curve (biology)
A growth curve is an empirical model of the evolution of a quantity over time. Growth curves are widely used in biology for quantities such as population size or biomass (in population ecology and demography, for population growth analysis), individual body height or biomass (in physiology, for growth analysis of individuals). Values for the measured property can be plotted on a graph as a function of time; see Figure 1 for an example... Bacterial growth In this example (Figure 1, see Lac operon for details) the number of bacteria present in a nutrient-containing broth was measured during the course of an 8-hour cell growth experiment. The observed pattern of bacterial growth is bi-phasic because two different sugars were present, glucose and lactose. The bacteria prefer to consume glucose (Phase I) and only use the lactose (Phase II) after the glucose has been depleted. Analysis of the molecular basis for this bi-phasic growth curve led to the discovery of the basic mechanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve Of Growth
In astronomy, the curve of growth describes the equivalent width of a spectral line as a function of the column density The area density (also known as areal density, surface density, superficial density, areic density, mass thickness, column density, or density thickness) of a two-dimensional object is calculated as the mass per unit area. The SI derived unit is ... of the material from which the spectral line is observed. References {{astronomy-stub Spectroscopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
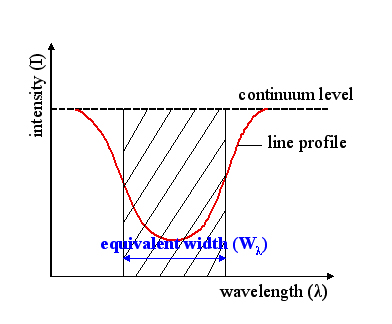
Equivalent Width
The equivalent width of a spectral line is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity versus wavelength in relation to underlying continuum level. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission, and finding the width such that the area of the rectangle is equal to the area in the spectral line. It is a measure of the strength of spectral features that is primarily used in astronomy. Definition Formally, the equivalent width is given by the equation W_\lambda = \int d\lambda = \int (1 - F_s / F_c) d\lambda. Here, F_c(\lambda) represents the underlying continuum intensity, while F_s(\lambda) represents the intensity of the actual spectrum (the line and continuum). Then W_\lambda represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |