|
Growth Curve (biology)
A growth curve is an empirical model of the evolution of a quantity over time. Growth curves are widely used in biology for quantities such as population size or biomass (in population ecology and demography, for population growth analysis), individual body height or biomass (in physiology, for growth analysis of individuals). Values for the measured property can be plotted on a graph as a function of time; see Figure 1 for an example... Bacterial growth In this example (Figure 1, see Lac operon for details) the number of bacteria present in a nutrient-containing broth was measured during the course of an 8-hour cell growth experiment. The observed pattern of bacterial growth is bi-phasic because two different sugars were present, glucose and lactose. The bacteria prefer to consume glucose (Phase I) and only use the lactose (Phase II) after the glucose has been depleted. Analysis of the molecular basis for this bi-phasic growth curve led to the discovery of the basic mechanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Growth Monod
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Curve
A sigmoid function is a mathematical function having a characteristic "S"-shaped curve or sigmoid curve. A common example of a sigmoid function is the logistic function shown in the first figure and defined by the formula: :S(x) = \frac = \frac=1-S(-x). Other standard sigmoid functions are given in the Examples section. In some fields, most notably in the context of artificial neural networks, the term "sigmoid function" is used as an alias for the logistic function. Special cases of the sigmoid function include the Gompertz curve (used in modeling systems that saturate at large values of x) and the ogee curve (used in the spillway of some dams). Sigmoid functions have domain of all real numbers, with return (response) value commonly monotonically increasing but could be decreasing. Sigmoid functions most often show a return value (y axis) in the range 0 to 1. Another commonly used range is from −1 to 1. A wide variety of sigmoid functions including the logistic and hype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
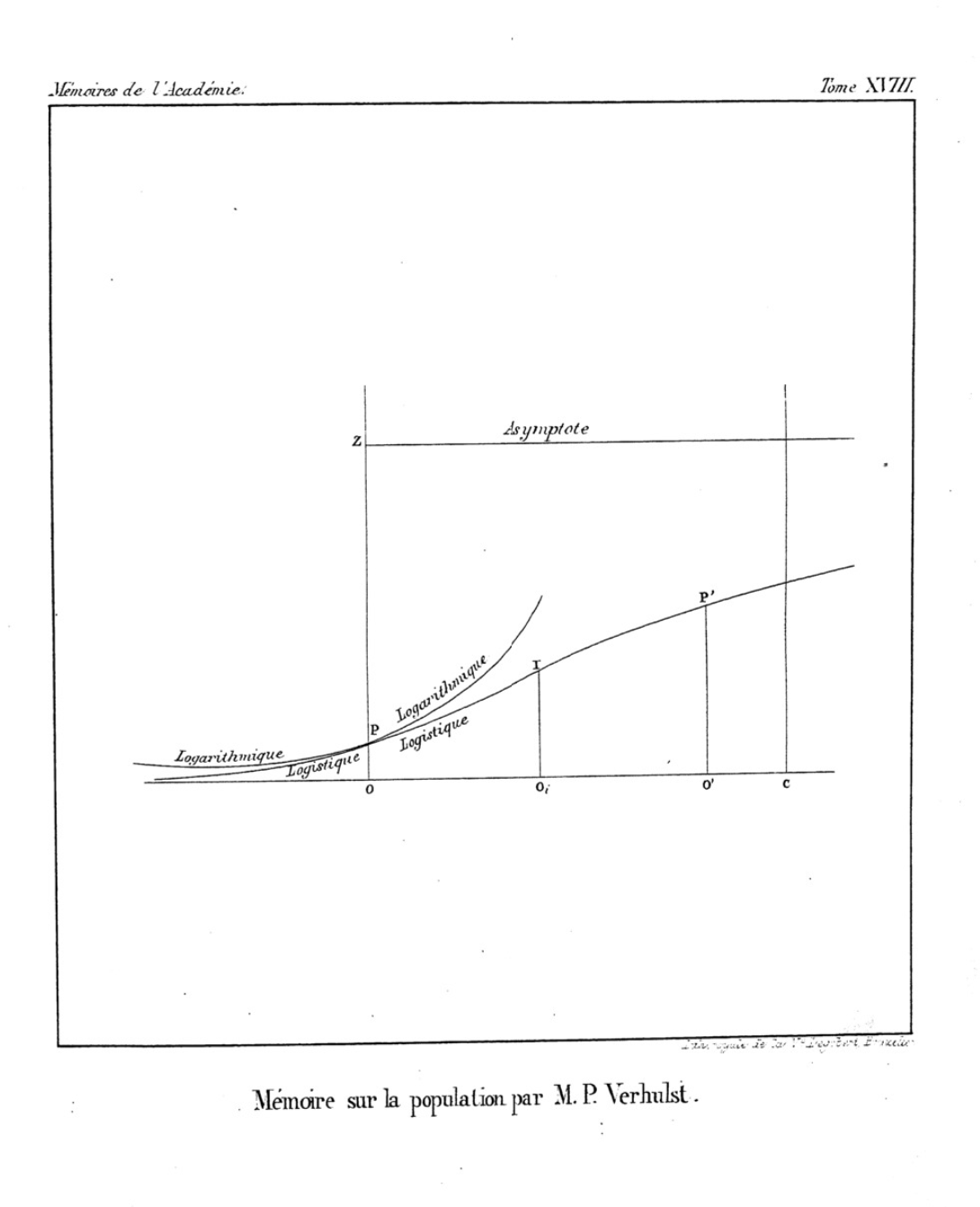
Logistic Curve
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve (sigmoid function, sigmoid curve) with equation f(x) = \frac, where For values of x in the domain of real numbers from -\infty to +\infty, the S-curve shown on the right is obtained, with the graph of f approaching L as x approaches +\infty and approaching zero as x approaches -\infty. The logistic function finds applications in a range of fields, including biology (especially ecology), biomathematics, chemistry, demography, economics, geoscience, mathematical psychology, probability, sociology, political science, linguistics, statistics, and artificial neural networks. A generalization of the logistic function is the hyperbolastic functions, hyperbolastic function of type I. The standard logistic function, where L=1,k=1,x_0=0, is sometimes simply called ''the sigmoid''. It is also sometimes called the ''expit'', being the inverse of the logit. History The logistic function was introduced in a series of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J-curve
A J curve is any of a variety of J-shaped diagrams where a curve initially falls, then steeply rises above the starting point. Political economy Balance of trade model In economics, the "J curve" is the time path of a country’s trade balance following a devaluation or depreciation of its currency, under a certain set of assumptions. A devalued currency means imports are more expensive, and on the assumption that the volumes of imports and exports change little at first, this causes a fall in the current account (a bigger deficit or smaller surplus). After some time, though, the volume of exports starts to rise because of their lower price to foreign buyers, and domestic consumers buy fewer imports, which have become more expensive for them. Eventually the trade balance moves to a smaller deficit or larger surplus compared to what it was before the devaluation. Likewise, if there is a currency revaluation or appreciation the same reasoning may be applied and will lead t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Curve
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). If the constant of proportionality is negative, then the quantity decreases over time, and is said to be undergoing exponential decay instead. In the case of a discrete domain of definition with equal intervals, it is also called geometric growth or geometric decay since the function values form a geometric progression. The formula for exponential growth of a variable at the growth rate , as time goes on in discrete intervals (that is, at integer times 0, 1, 2, 3, ...), is x_t = x_0(1+r)^t where is the value of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gompertz Function
The Gompertz curve or Gompertz function is a type of mathematical model for a time series, named after Benjamin Gompertz (1779–1865). It is a sigmoid function which describes growth as being slowest at the start and end of a given time period. The right-side or future value asymptote of the function is approached much more gradually by the curve than the left-side or lower valued asymptote. This is in contrast to the simple logistic function in which both asymptotes are approached by the curve symmetrically. It is a special case of the generalised logistic function. The function was originally designed to describe human mortality, but since has been modified to be applied in biology, with regard to detailing populations. History Benjamin Gompertz (1779–1865) was an actuary in London who was privately educated. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in 1819. The function was first presented in his June 16, 1825 paper at the bottom of page 518. The Gompertz function r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). If the constant of proportionality is negative, then the quantity decreases over time, and is said to be undergoing exponential decay instead. In the case of a discrete domain of definition with equal intervals, it is also called geometric growth or geometric decay since the function values form a geometric progression. The formula for exponential growth of a variable at the growth rate , as time goes on in discrete intervals (that is, at integer times 0, 1, 2, 3, ...), is x_t = x_0(1+r)^t where is the value of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or human growth hormone deficiency, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density. GHD can be present at birth or develop later in life. Causes may include genetics, trauma, infections, tumors, or radiation therapy. Genes that may be involved include GH1, GHRHR, or BTK. In a third of cases no cause is apparent. The underlying mechanism generally involves problems with the pituitary gland. Some cases are associated with a lack of other pituitary hormones, in which case it is known as combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure growth hormone levels. Treatment is by growth hormone replacement using synthetic human growth hormone. The frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Height
Human height or stature is the distance from the bottom of the feet to the top of the head in a human body, standing erect. It is measured using a stadiometer, in centimetres when using the metric system or SI system, or feet and inches when using United States customary units or the imperial system. In the early phase of anthropometric research history, questions about height techniques for measuring nutritional status often concerned genetic differences. Height is also important because it is closely correlated with other health components, such as life expectancy. Studies show that there is a correlation between small stature and a longer life expectancy. Individuals of small stature are also more likely to have lower blood pressure and are less likely to acquire cancer. The University of Hawaii has found that the "longevity gene" FOXO3 that reduces the effects of aging is more commonly found in individuals of small body size. Short stature decreases the risk of venous i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |