|
Group III Intron
Group III intron is a class of introns found in mRNA genes of chloroplasts in euglenid protists. They have a conventional group II-type dVI with a bulged adenosine, a streamlined dI, no dII-dV, and a relaxed splice site consensus. Splicing is done with two transesterification reactions with a dVI bulged adenosine as initiating nucleophile; the intron is excised as a lariat. Not much is known about how they work, although an isolated chloroplast transformation system has been constructed. Discovery and identification In 1984, Montandon and Stutz reported examples of a novel type of introns in Euglena chloroplast. In 1989, David A. Christopher and Richard B. Hallick found a few more examples and proposed the name "Group III introns" to identify this new class with the following characteristics: * Group III introns are much shorter than other self-splicing intron classes, ranging from 95 to 110 nucleotides amongst those known to Christopher and Hallick, and identified in chloroplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenid
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical of that group. They are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group consisting of the mixotrophic Rapaza viridis (1 species) and the two groups Eutreptiales (24 species) and Euglenales (983 species) have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon. Euglenids split from other Euglenozoa more than a billion years ago. The plastids in all extant photosynthetic species is the result from secondary endosymbiosis between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. Structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group II Intron
Group II introns are a large class of self-catalytic ribozymes and mobile genetic elements found within the genes of all three domains of life. Ribozyme activity (e.g., self- splicing) can occur under high-salt conditions ''in vitro''. However, assistance from proteins is required for ''in vivo'' splicing. In contrast to group I introns, intron excision occurs in the absence of GTP and involves the formation of a lariat, with an A-residue branchpoint strongly resembling that found in lariats formed during splicing of nuclear pre-mRNA. It is hypothesized that pre-mRNA splicing (see spliceosome) may have evolved from group II introns, due to the similar catalytic mechanism as well as the structural similarity of the Group II Domain V substructure to the U6/U2 extended snRNA. Finally, their ability to site-specifically insert into DNA sites has been exploited as a tool for biotechnology. For example, group II introns can be modified to make site-specific genome insertions and del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transesterification
In organic chemistry, transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases (one example is the lipase E.C.3.1.1.3). Strong acids catalyse the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile, whereas bases catalyse the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. If the alcohol produced by the reaction can be separated from the reactants by distillation this will drive the equilibrium toward the products, this means that esters with larger alkoxy groups can be made from methyl or ethyl esters in high purity by heating the mixture of ester, acid/base, and large alcohol. Mechanism In the transesterification mechanism, the carbonyl carbon of the starting e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cationoid' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Splicing
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and ''splicing'' back together exons (coding regions). For nuclear-encoded genes, splicing occurs in the nucleus either during or immediately after transcription. For those eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually needed to create an mRNA molecule that can be translated into protein. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing occurs in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). There exist self-splicing introns, that is, ribozymes that can catalyze their own excision from their parent RNA molecule. The process of transcription, splicing and translation is called gene expression, the central dogma of molecular biology. Splicing pathways Several methods of RNA splici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
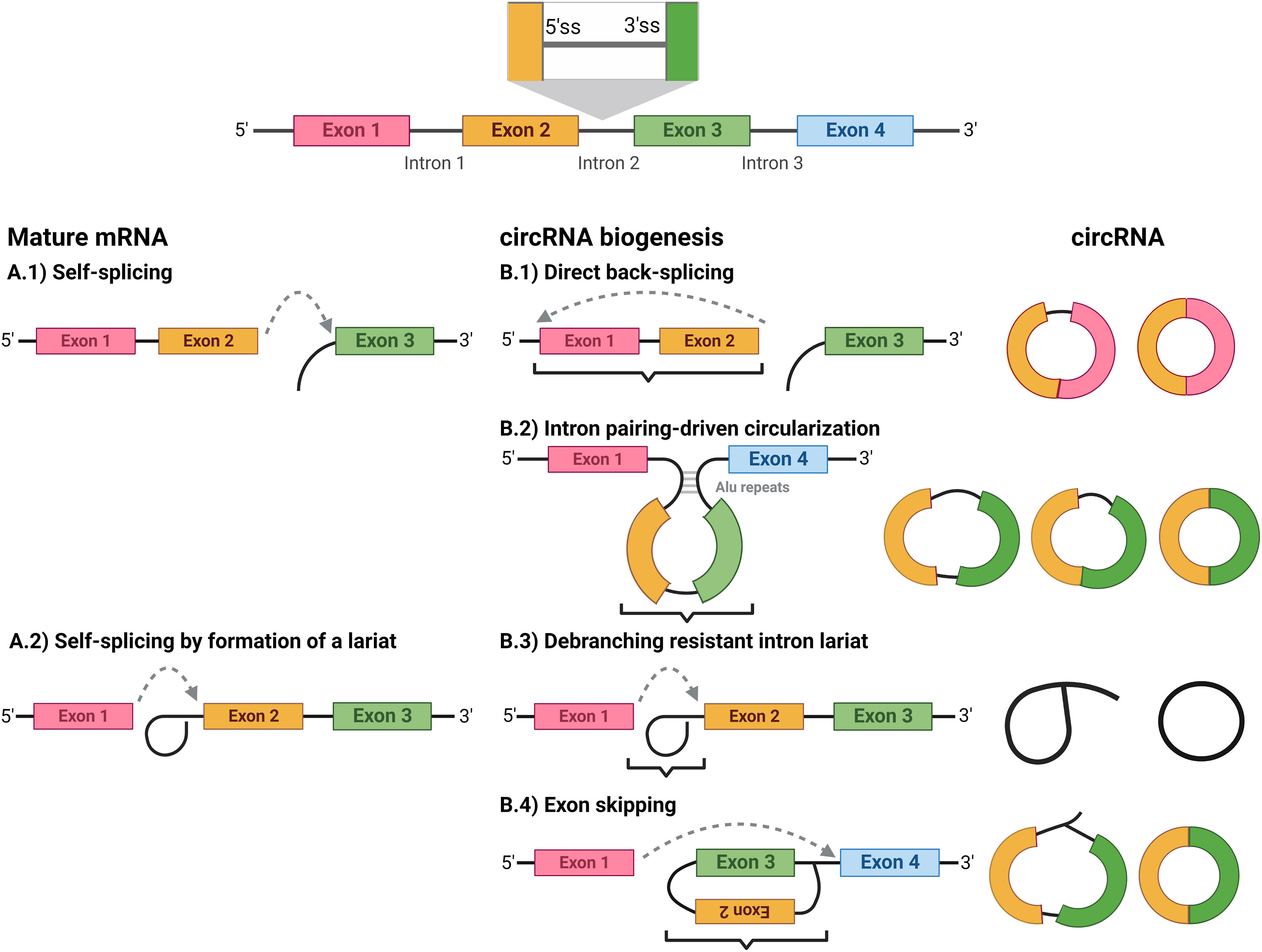
Circular RNA
Circular RNA (or circRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA which, unlike linear RNA, forms a covalently closed continuous loop. In circular RNA, the 3' and 5' ends normally present in an RNA molecule have been joined together. This feature confers numerous properties to circular RNA, many of which have only recently been identified. Many types of circular RNA arise from otherwise protein-coding genes. Some circular RNA has been shown to code for proteins. Some types of circular RNA have also recently shown potential as gene regulators. The biological function of most circular RNA is unclear. Because circular RNA does not have 5' or 3' ends, it is resistant to exonuclease-mediated degradation and is presumably more stable than most linear RNA in cells. Circular RNA has been linked to some diseases such as cancer. RNA splicing In contrast to genes in bacteria, eukaryotic genes are split by non-coding sequences called introns. In eukaryotes, as a gene is transcribed from DNA int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twintron
In molecular biology, a twintron is an intron-within-intron excised by sequential splicing reactions. A twintron is presumably formed by the insertion of a mobile intron into an existing intron. Discovery Twintrons were discovered by Donald W. Copertino and Richard B. Hallick as a group II intron within another group II intron in ''Euglena'' chloroplast genome. They found that splicing of both the internal and external introns occurs via lariat intermediates. Additionally, twintron splicing was found to proceed by a sequential pathway, the internal intron being removed prior to the excision of the external intron. Since the original discovery, there have been other reports of Group III twintrons and GroupII/III twintrons in the chloroplast of '' Euglena gracilis''. In 1993 a new type of complex twintron composed of four individual group III introns has been characterized. The external intron was interrupted by an internal intron containing two additional introns. In 1995 scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Ontology
The Gene Ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and gene product attributes; 2) annotate genes and gene products, and assimilate and disseminate annotation data; and 3) provide tools for easy access to all aspects of the data provided by the project, and to enable functional interpretation of experimental data using the GO, for example via enrichment analysis. GO is part of a larger classification effort, the Open Biomedical Ontologies, being one of the Initial Candidate Members of the OBO Foundry. Whereas gene nomenclature focuses on gene and gene products, the Gene Ontology focuses on the function of the genes and gene products. The GO also extends the effort by using markup language to make the data (not only of the genes and their products but also of curated attributes) machine read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribozymes
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or in vitro-evolved ribozymes are the cleavage or ligation of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. For example, the smallest ribozyme known (GUGGC-3') can aminoacylate a GCCU-3' sequence in the presence of PheAMP. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during protein synthesis. They also participate in a variety of RNA processing reactions, including RNA splicing, viral replication, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |