|
Grotta Regina Del Carso
Grotta Regina del Carso ("Queen of Karst cave", sl, Jama Kraljica Krasa) is a Karst cave in the village of ''San Michele del Carso'' ( Slovene: ''Vrh'') in the municipality of Savogna d'Isonzo (Gorizia, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Italy). The cave is not open to public, and the access is managed by ''Talpe del Carso/Kraški Krti'' speleological group, headquartered in the vicinity of the entrance. Morphology Grotta Regina opens above sea level. Overall, it is long and deep. The cave contains two main rooms, called respectively the ''Hall of the Council'' (Italian: ''Sala delle Riunioni''), due to the presence of a number of stalagmites that seem to be the members of a municipality council, and the ''Hall of San Michele'' (Italian: ''Sala del San Michele''), named after the main upland in the area. Two galleries connect the entrance with the Hall of the Council and this room with the Hall of San Michele. Rooms and galleries are full of cave formations (stalactites, stalagmites, co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savogna D'Isonzo
Savogna d'Isonzo ( sl, Sovodnje ob Soči; fur, Savogne di Gurize) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Italian region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, located about northwest of Trieste and about southwest of Gorizia, on the border with Slovenia. The name of the village comes from the Slovene word ''sovodnje'', which means confluence. Near Savogna, in fact, the Vipava river flows into the Isonzo at the conjunction of the Karst Plateau and the Vipava Valley. Ethnic composition 92% of the population was of Slovene ethnicity according to the Italian census of 1971.Thomas, Lee; Lokar A. (1977)Socioeconomic structure of the Slovene population in Italy Slovene Studies, Chicago, Illinois, p.28. Main sights *Church of San Martino, at Savogna *Castle of Rubbia *Church of San Nicolò, at Gabria *Small square of Gabria *Grotta Regina del Carso Twin towns * Škofja Loka, Slovenia References See also *Julian March *Gorizia and Gradisca *Slovene Lands The Slovene lands or Slovenian land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
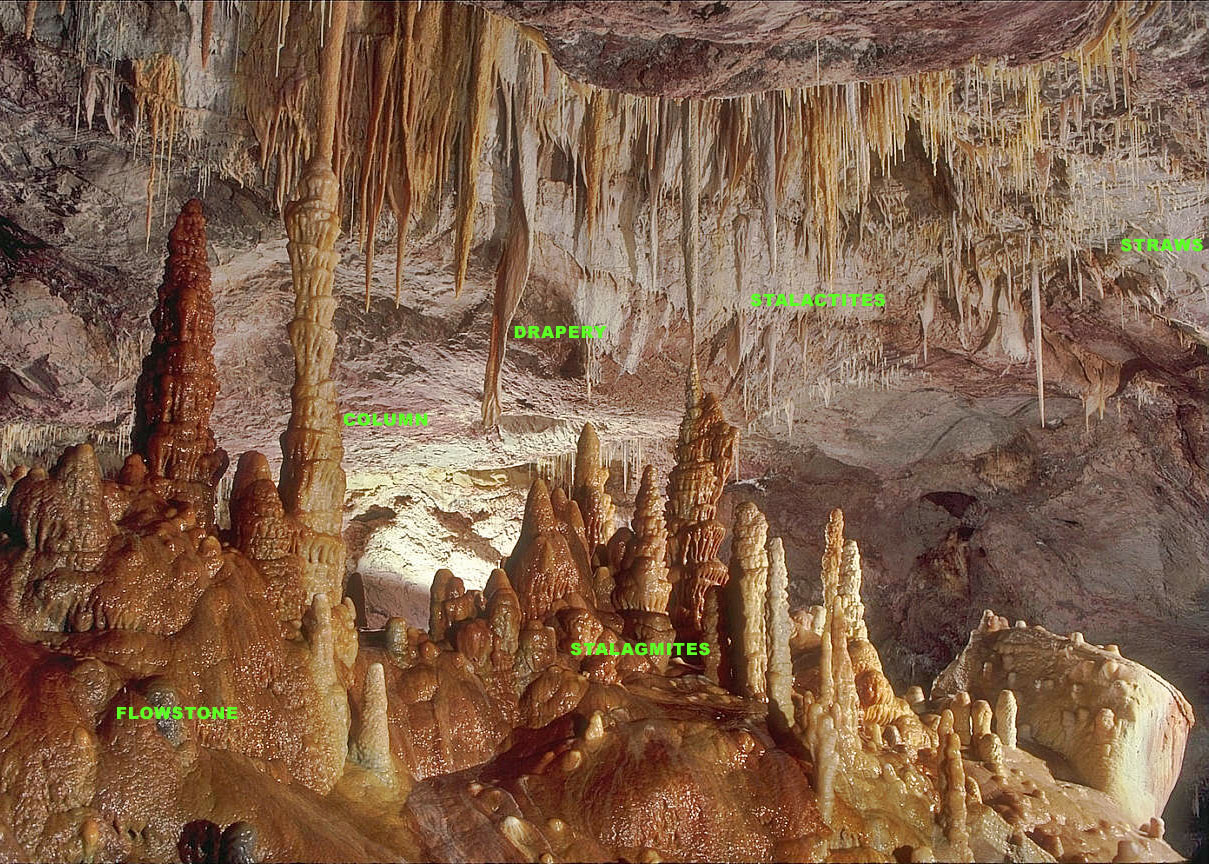
Stalagnate
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subterranean Fauna
The endemic of Dinaric Alps. Subterranean fauna refers to Animal, animal species that are adaptation, adapted to live in an underground Natural environment, environment. Troglofauna and stygofauna are the two types of subterranean fauna. Both are associated with hypogean habitats – troglofauna is associated with terrestrial subterranean environment (caves and underground spaces above the water table), and stygofauna with all kind of subterranean waters (groundwater, aquifers, subterranean rivers, dripping bowls, gours, etc.). Environment Subterranean fauna is found worldwide and includes representatives of many animal groups, mostly arthropods and other invertebrates. However, there is a number of vertebrates (such as cavefishes and cave salamanders), although they are less common. Because of the complexity in exploring underground environments, many subterranean species are yet to be discovered and described. Peculiarities of underground habitat make it an extreme environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually specialize in a particular branch (e.g., molecular biology, zoology, and evolutionary biology) of biology and have a specific research focus (e.g., studying malaria or cancer). Biologists who are involved in basic research have the aim of advancing knowledge about the natural world. They conduct their research using the scientific method, which is an empirical method for testing hypotheses. Their discoveries may have applications for some specific purpose such as in biotechnology, which has the goal of developing medically useful products for humans. In modern times, most biologists have one or more academic degrees such as a bachelor's degree plus an advanced degree like a master's degree or a doctorate. Like other scientists, biologists can be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research (field work) is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors searching for natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, precious and base metals. They are also in the forefront of preventing and mitigating damage from natural hazards and disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Their studies are used to warn the general public of the occurrence of these events. Geologists are also important contributors to climate ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 Friuli Earthquake
Events January * January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force. * January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea. * January 11 – The 1976 Philadelphia Flyers–Red Army game results in a 4–1 victory for the National Hockey League's Philadelphia Flyers over HC CSKA Moscow of the Soviet Union. * January 16 – The trial against jailed members of the Red Army Faction (the West German extreme-left militant Baader–Meinhof Group) begins in Stuttgart. * January 18 ** Full diplomatic relations are established between Bangladesh and Pakistan 5 years after the Bangladesh Liberation War. ** The Scottish Labour Party is formed as a breakaway from the UK-wide party. ** Super Bowl X in American football: The Pittsburgh Steelers defeat the Dallas Cowboys, 21–17, in Miami. * January 21 – First commercial Concorde flight, from London to Bahrain. * January 27 ** The United States vetoes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baita (architecture)
Baita (pl. ''baite'') is a term used mainly in Italy and France to refer to small dwellings of the central and western Alps. This word is found from the Lepontine to the Maritime alpine sections. Description ''Baite'' are huts usually constructed with dry-stone walls, although wood may also be used, and are typically roofed with substantial stone slabs known as ''piodi'' (''lose'' in Western Alps) which provide protection from heavy winter snowfalls. A wood and stone ''baita'' of the Val di Susa – for instance in the hamlet of Rhuilles – and Hautes-Alpes is usually called ''grange''. Sometimes the term improperly refers to modern and "rustic-chic" chalets. ''Baite'' are often clustered together in Alpine pastures where they are occupied seasonally by herders tending sheep, cattle or goats during the summer (transhumance). In recent years abandoned ''baite'', restored with varying degrees of respect, have also become popular as second homes and, to an extent, as holiday homes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Survey
A cave survey is a map of all or part of a cave system, which may be produced to meet differing standards of accuracy depending on the cave conditions and equipment available underground. Cave surveying and cartography, i.e. the creation of an accurate, detailed map, is one of the most common technical activities undertaken within a cave and is a fundamental part of speleology. Surveys can be used to compare caves to each other by length, depth and volume, may reveal clues on speleogenesis, provide a spatial reference for other areas of scientific study and assist visitors with route-finding. Traditionally, cave surveys are produced in two-dimensional form due to the confines of print, but given the three-dimensional environment inside a cave, modern techniques using computer aided design are increasingly used to allow a more realistic representation of a cave system. History The first known plan of a cave dates from 1546, and was of a man-made cavern in tufa called the Stufe di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst Plateau
The Karst Plateau or the Karst region ( sl, Kras, it, Carso), also locally called Karst, is a karst plateau region extending across the border of southwestern Slovenia and northeastern Italy. It lies between the Vipava Valley, the low hills surrounding the valley, the westernmost part of the Brkini Hills, northern Istria, and the Gulf of Trieste. The western edge of the plateau also marks the traditional ethnic border between Italians and Slovenes. The region gave its name to karst topography. For this reason, it is also referred to as the ''Classical Karst''. Geographical position The plateau rises quite steeply above the neighboring landscape, except for its northeastern side, where the steepness is less pronounced. The plateau gradually descends from the southeast to the southwest. On average it lies 334 m above sea level. Its western edge, known as the Karst Rim ( sl, Kraški rob), is a continuation of the Učka mountain range in eastern Istria, and rises to the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavers
Caving – also known as spelunking in the United States and Canada and potholing in the United Kingdom and Ireland – is the recreational pastime of exploring wild cave systems (as distinguished from show caves). In contrast, speleology is the scientific study of caves and the cave environment.Caving in New Zealand (from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, Accessed 2012-11.) The challenges involved in caving vary according to the cave being visited; in addition to the total absence of light beyond the entrance, negotiating pitches, squeezes, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Formation
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate ( gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.png)

