|
Gross Private Domestic Investment
Gross private domestic investment is the measure of physical investment used in computing GDP in the measurement of nations' economic activity. This is an important component of GDP because it provides an indicator of the future productive capacity of the economy. It includes replacement purchases plus net additions to capital assets plus investments in inventories. From 2002 to 2011 it amounted to 14.9% of GDP, and from 1945 to 2011 was 15.7% of GDP (BEA, USDC, 2013). Net investment is gross investment minus depreciation. Of the four categories of GDP (investment, consumption, net exports, and government spending Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual ... on goods and services) it is by far the least stable. Gross private domestic investment includes 4 types of invest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Activity
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on glossary of economics, these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productive Capacity
Productive capacity is the maximum possible output of an economy. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), no agreed-upon definition of maximum output exists. UNCTAD itself proposes: "the productive ''resources'', entrepreneurial ''capabilities'' and production ''linkages'' which together determine the capacity of a country to produce goods and services." The term may also be applied to individual resources or assets; for instance the productive capacity of an area of farmland Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bo .... Definition in more depth Productive capacity has a lot in common with a production possibility frontier (PPF) that is an answer to the question what the maximum production capacity of a certain economy is which means usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
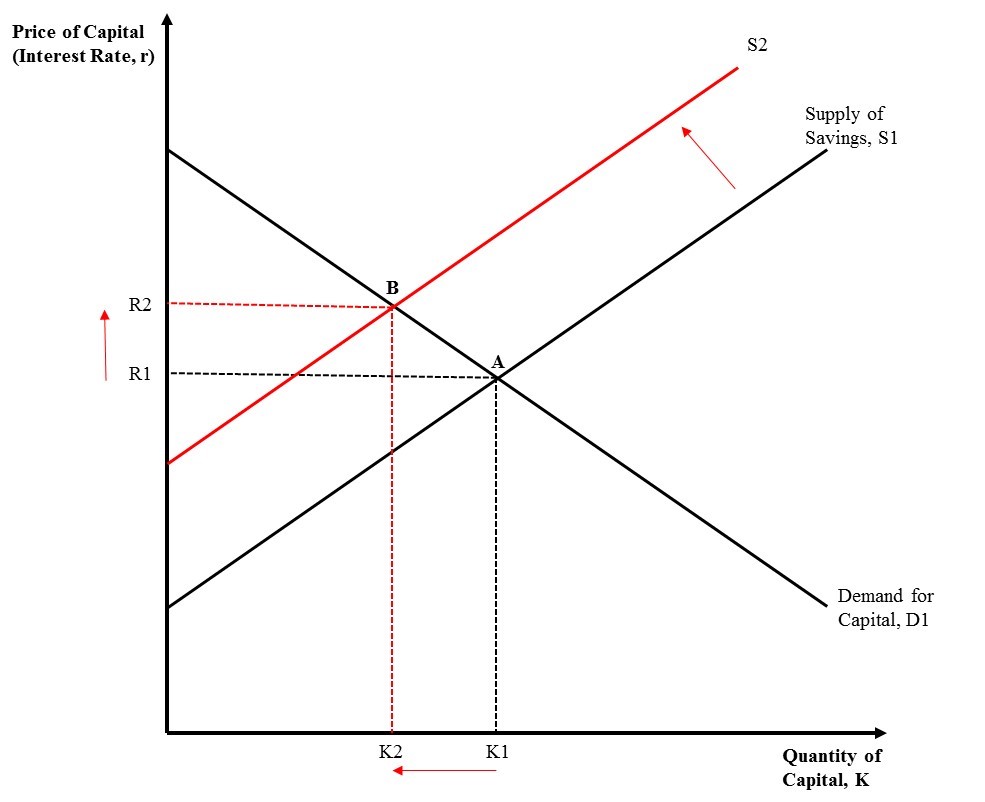
Capital (economics)
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. At the macroeconomic level, "the nation's capital stock includes buildings, equipment, software, and inventories during a given year." A typical example is the machinery used in factories. Capital can be increased by the use of the factors of production, which however excludes certain durable goods like homes and personal automobiles that are not used in the production of saleable goods and services. Adam Smith defined capital as "that part of man's stock which he expects to afford him revenue". In economic models, capital is an input in the production function. The total physical capital at any given moment in time is referred to as the capital stock (not to be confused with the capital stock of a business entity). Capital goods, real capital, or capital assets are already-produced, durable goods or any non-fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inventory Investment
Inventory investment is a component of gross domestic product (GDP). What is produced in a certain country is naturally also sold eventually, but some of the goods produced in a given year may be sold in a later year rather than in the year they were produced. Conversely, some of the goods sold in a given year might have been produced in an earlier year. The difference between goods produced (production) and goods sold (sales) in a given year is called inventory investment. The concept can be applied to the economy as a whole or to an individual firm, however this concept is generally applied in macroeconomics (economy as a whole). Unintended unsold stock of goods increases inventory investment. Definition of inventory investment *Inventory investment = production – sales Baumol, William J., and Alan Blinder Blinder, Alan S., ''Macroeconomics: Principles and Policy'', Southwestern College Publ., eleventh edition, 2008. Thus, if production per unit time exceeds sales per unit ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Investment
In economics, net investment is spending which increases the availability of fixed capital goods or means of production and goods inventories. It is the total spending on newly produced physical capital (fixed investment) and on inventories (inventory investment)—that is, gross investment—minus replacement investment, which simply replaces depreciated capital goods. It is productive capital formation plus net additions to the stock of housing and the stock of inventories Inventory (American English) or stock (British English) refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation. Inventory management is a discipline primarily about specifying the shap .... Investment {{Finance-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is the act of using resources to satisfy current needs and wants. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced goods and services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g. the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). Economists are particularly interested in the relationship betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Exports
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance of trade for goods versus one for services. The balance of trade measures a flow of exports and imports over a given period of time. The notion of the balance of trade does not mean that exports and imports are "in balance" with each other. If a country exports a greater value than it imports, it has a trade surplus or positive trade balance, and conversely, if a country imports a greater value than it exports, it has a trade deficit or negative trade balance. As of 2016, about 60 out of 200 countries have a trade surplus. The notion that bilateral trade deficits are bad in and of themselves is overwhelmingly rejected by trade experts and economists. Explanation The balance of trade forms part of the current account, which includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Spending
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual or collective needs of the community, is classed as government final consumption expenditure. Government acquisition of goods and services intended to create future benefits, such as infrastructure investment or research spending, is classed as government investment (government Gross fixed capital formation, gross capital formation). These two types of government spending, on final consumption and on gross capital formation, together constitute one of the major components of gross domestic product. Government spending can be financed by government borrowing, taxes, custom duties, the sale or lease of natural resources, and various fees like national park entry fees or licensing fees. When Governments choose to borrow money, they have to gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inventory
Inventory (American English) or stock (British English) refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production or utilisation. Inventory management is a discipline primarily about specifying the shape and placement of stocked goods. It is required at different locations within a facility or within many locations of a supply network to precede the regular and planned course of production and stock of materials. The concept of inventory, stock or work in process (or work in progress) has been extended from manufacturing systems to service businesses and projects, by generalizing the definition to be "all work within the process of production—all work that is or has occurred prior to the completion of production". In the context of a manufacturing production system, inventory refers to all work that has occurred—raw materials, partially finished products, finished products prior to sale and departure from the manufacturing system. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Accounts
National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting. By design, such accounting makes the totals on both sides of an account equal even though they each measure different characteristics, for example production and the income from it. As a method, the subject is termed national accounting or, more generally, social accounting.Nancy D. Ruggles, 1987. "social accounting," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 4, pp. 377–82. Stated otherwise, national accounts as ''systems'' may be distinguished from the economic data associated with those systems. While sharing many common principles with business accounting, national accounts are based on economic concepts. One conceptual construct for representing flows of all economic transactions that take place in an economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |