|
Grindometer
A grindometer is a device used to measure the particle size of suspension (chemistry), suspensions, typically inks such as those used in printing, or paints. It consists of a steel block with a channel of varying depth machined into it, starting at a convenient depth for the type of suspension to be measured, and becoming shallower until it ends flush with the block's surface. The depth of the groove is marked off on a graduation (instrument), graduated scale next to it. The suspension to be tested is poured into the deep end of the groove, and scraped towards the shallow end with a flat metal scraper. At the point where the depth of the groove equals the largest particles in the suspension, irregularities (for example pinholes in an ink sample) will become visible. The advantages of this method are that it uses a small sample and gives a very quick indication of the high end of the particle size distribution, allowing production processes to be followed in real time. The follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grindometer
A grindometer is a device used to measure the particle size of suspension (chemistry), suspensions, typically inks such as those used in printing, or paints. It consists of a steel block with a channel of varying depth machined into it, starting at a convenient depth for the type of suspension to be measured, and becoming shallower until it ends flush with the block's surface. The depth of the groove is marked off on a graduation (instrument), graduated scale next to it. The suspension to be tested is poured into the deep end of the groove, and scraped towards the shallow end with a flat metal scraper. At the point where the depth of the groove equals the largest particles in the suspension, irregularities (for example pinholes in an ink sample) will become visible. The advantages of this method are that it uses a small sample and gives a very quick indication of the high end of the particle size distribution, allowing production processes to be followed in real time. The follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension (chemistry)
In chemistry, a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture of a fluid that contains solid particles sufficiently large for sedimentation. The particles may be visible to the naked eye, usually must be larger than one micrometer, and will eventually settle, although the mixture is only classified as a suspension when and while the particles have not settled out. Properties A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve, but get suspended throughout the bulk of the solvent, left floating around freely in the medium. The internal phase (solid) is dispersed throughout the external phase (fluid) through mechanical agitation, with the use of certain excipients or suspending agents. An example of a suspension would be sand in water. The suspended particles are visible under a microscope and will settle over time if left undisturbed. This distinguishes a suspension from a colloid, in which the colloid particles are smaller and do not settle. Colloids a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
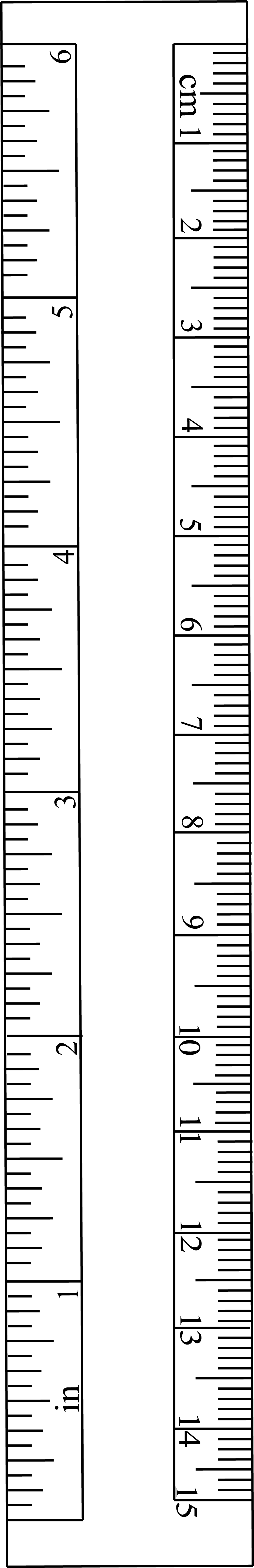
Graduation (instrument)
A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual scale, which can be present on a container, a measuring device, or the axes of a line plot, usually one of many along a line or curve, each in the form of short line segments perpendicular to the line or curve. Often, some of these line segments are longer and marked with a numeral, such as every fifth or tenth graduation. The scale itself can be linear (the graduations are spaced at a constant distance apart) or nonlinear. Linear graduation of a scale occurs mainly (but not exclusively) on straight measuring devices, such as a rule or measuring tape, using units such as inches or millimetres. Graduations can also be spaced at varying spatial intervals, such as when using a logarithmic, for instance on a measuring cup, can vary in scale due to the container's non- cylindrical shape. Graduations along a curve Circular graduations of a scale occur on a circular arc or limb of an instrument. In some cases, non-circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |