|
Grimaldi, Calabria
Grimaldi is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy. Grimaldi is referred to as ''Grimaldo'' in historic documents. In the local Calabrian dialect (a variation of Cosentino), the town is called ''Grimàudu'' or ''Grimàuru'', and the residents ''Grimaudisi'', although the Italian versions (Grimaldi and Grimaldesi) are today prevalent. Geography Grimaldi is located 29 km (18 mi) from Cosenza and rises to 650m above sea level. The territory of the municipality lies between 150 and 1,256 metres (492 and 4,120 ft.) above sea level. The comune extends from the Santa Lucerna mountains to the Savuto river valley to the south. History It is likely that Grimaldi owes its origins to the devastation experienced by the ancient territory of Pandosia, after the year 475 CE. The first settlement in the area may have been a small casale (hamlet) named Santa Caterina, around the year 872, when much of Calabria was experien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Peter
Saint Peter; he, שמעון בר יונה, Šimʿōn bar Yōnāh; ar, سِمعَان بُطرُس, translit=Simʿa̅n Buṭrus; grc-gre, Πέτρος, Petros; cop, Ⲡⲉⲧⲣⲟⲥ, Petros; lat, Petrus; ar, شمعون الصفـا, Sham'un al-Safa, Simon the Pure.; tr, Aziz Petrus (died between AD 64 and 68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Peter the Rock, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ, and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, early Christian Church. He is traditionally counted as the first bishop of Romeor List of popes, popeand also as the first bishop of Antioch. Based on contemporary historical data, his papacy is estimated to have spanned from AD 30 to his death, which would make him the longest-reigning pope, at anywhere from 34 to 38 years; however, the length of his reign has never been verified. According to Apostolic Age, Christian tradition, Peter was crucified in Rome und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancona
Ancona (, also , ) is a city and a seaport in the Marche region in central Italy, with a population of around 101,997 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona and of the region. The city is located northeast of Rome, on the Adriatic Sea, between the slopes of the two extremities of the promontory of Monte Conero, Monte Astagno and Monte Guasco. Ancona is one of the main ports on the Adriatic Sea, especially for passenger traffic, and is the main economic and demographic centre of the region. History Greek colony Ancona was populated as a region by Picentes since the 6th century BC who also developed a small town there. Ancona took a more urban shape by Greek settlers from Syracuse, Italy, Syracuse in about 387 BC, who gave it its name: ''Ancona'' stems from the Greek word (''Ankṓn''), meaning "elbow"; the harbour to the east of the town was originally protected only by the promontory on the north, shaped like an elbow. Greek merchants established a Tyrian pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Diaspora
, image = Map of the Italian Diaspora in the World.svg , image_caption = Map of the Italian diaspora in the world , population = worldwide , popplace = Brazil, Argentina, United States, France, Colombia, Canada, Peru, Uruguay, Australia, Venezuela, Germany, Switzerland, United Kingdom, Belgium, Chile and Paraguay , langs = Italian, other languages of Italy, English, French, Spanish, Portuguese and German , rels = Christianity (predominantly Catholicism) , related = Other Romance peoples The Italian diaspora is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy. There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Unification of Italy, and ended in the 1920s to the early 1940s with the rise of Fascist Italy.Pozzetta, George E., Bruno Ramirez, and Robert F. Harney. The Italian Diaspora: Migration across the Globe. Toronto: Multicultural History Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Italy
Southern Italy ( it, Sud Italia or ) also known as ''Meridione'' or ''Mezzogiorno'' (), is a macroregion of the Italian Republic consisting of its southern half. The term ''Mezzogiorno'' today refers to regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily (officially denominated as one entity ''Regnum Siciliae citra Pharum'' and ''ultra Pharum'', i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which had neither been part of said region nor of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alpine House of Savoy that would eventually annex the Bourbon-led and Southern Italian Kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ''Mezzogiorno'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
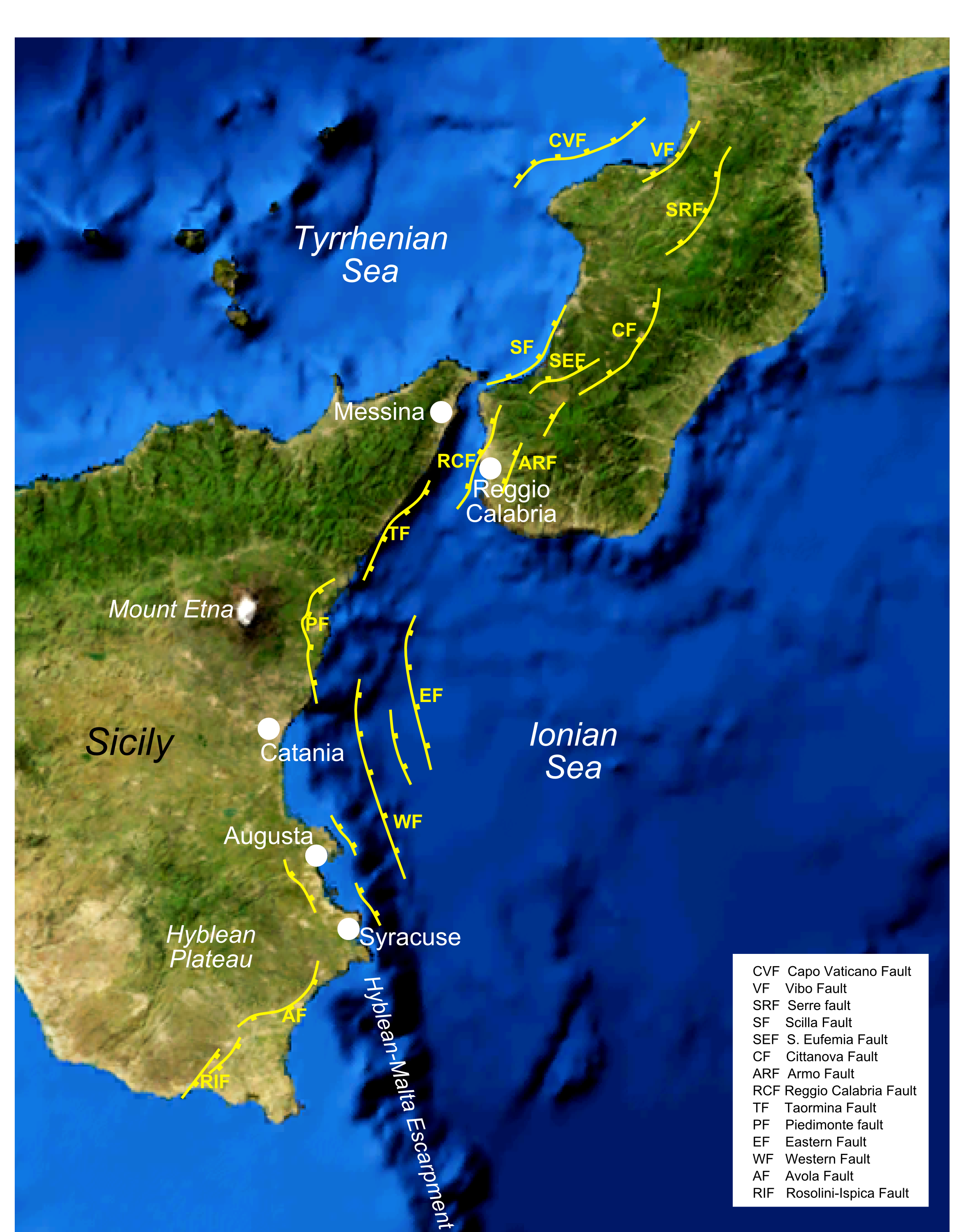
1638 Calabrian Earthquakes
A series of four mainshocks struck Calabria on March 27–28 and June 9, 1638. The first three earthquakes had moment magnitudes estimated to be 6.6–7.1 . On June 9, another mainshock estimated at 6.7 struck the same region, causing further damage and casualties. The four earthquakes resulted in as many as 30,000 fatalities. Tectonic setting The region of Calabria is located between the Tyrrhenian and Ionian Seas, where active extension is ongoing. Extension is accommodated by normal faults on the Tyrrhenian side in Calabria. The trend of normal faults extend southwards to the Strait of Messina, where they occur on the Ionian side in Sicily. Known as the Siculo–Calabrian rift, this active geological feature is characterized by its high seismicity of earthquakes up to 7.1. Geology The earthquake of March 27 occurred within the Crati Valley fault system, specifically on the Piano Lago and Savuto–Decollatura faults. The March 28 earthquakes ruptured the Mesima fault syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducat
The ducat () coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages from the 13th to 19th centuries. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide international acceptance over the centuries. Similarly named silver ducatons also existed. The gold ducat circulated along with the Florentine florin and preceded the modern British pound sterling and the United States dollar. Predecessors The word ''ducat'' is from Medieval Latin ''ducalis'' = "relating to a duke (or dukedom)", and initially meant "duke's coin" or a "duchy's coin". The first issue of scyphate billon coins modelled on Byzantine ''trachea'' was made by King Roger II of Sicily as part of the Assizes of Ariano (1140). It was to be a valid issue for the whole kingdom. The first issue bears the figure of Christ and the Latin inscription ''Sit tibi, Christe, datus, quem tu regis iste ducatus'' (meaning "O Christ, let thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan I Of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I ( it, Giovanna I; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1382; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381. Joanna was the eldest daughter of Charles, Duke of Calabria and Marie of Valois to survive infancy. Her father was the son of Robert the Wise, King of Naples, but he died before his father in 1328. Three years later, King Robert appointed Joanna as his heir and ordered his vassals to swear fealty to her. To strengthen Joanna's position, he concluded an agreement with his nephew, King Charles I of Hungary, about the marriage of Charles's younger son, Andrew, and Joanna. Charles I also wanted to secure his uncle's inheritance to Andrew, but King Robert named Joanna as his sole heir on his deathbed in 1343. He also appointed a regency council to govern his realms until Joanna's 21st birthday, but the regents could not actually take control of state administration afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiello Calabro
Aiello Calabro is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy. See also * Savuto river * 1905 Calabria earthquake Striking southern Italy on September 8, the 1905 Calabria earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The first major earthquake of the 20th century, it severely damaged parts of Lipari, Messin ... External links * Website Idem Cities and towns in Calabria {{Calabria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302), when the island of Sicily revolted and was conquered by the Crown of Aragon, becoming a separate kingdom also called the Kingdom of Sicily. In 1816, it reunified with the island of Sicily to form the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The territory of the Kingdom of Naples corresponded to the current Italian regions of Campania, Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Abruzzo, Molise and also included some areas of today's southern and eastern Lazio. Nomenclature The term "Kingdom of Naples" is in near-universal use among historians, but it was not used officially by the government. Since the Angevins remained in power on the Italian peninsula, they kept the original name of the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled between the 16th and 18th centuries (1516–1713) by kings from the Spanish branch of the House of Habsburg (also associated with its role in the history of Central and Eastern Europe). Habsburg Spain was a composite monarchy and a personal union. The Habsburg Hispanic Monarchs (chiefly Charles I and Philip II) reached the zenith of their influence and power ruling the Spanish Empire. They controlled territories over the five continents, including the Americas, the East Indies, the Low Countries, Belgium, Luxembourg, and territories now in Italy, France and Germany in Europe, the Portuguese Empire from 1580 to 1640, and various other territories such as small enclaves like Ceuta and Oran in North Africa. This period of Spanish history ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Spain, parts of what is now southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy (from 1442) and parts of Greece (until 1388). The component realms of the Crown were not united politically except at the level of the king, who ruled over each autonomous polity according to its own laws, raising funds under each tax structure, dealing separately with each ''Corts'' or ''Cortes'', particularly the Kingdom of Aragon, the Principality of Catalonia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |