|
Grey Turner's Sign
Grey Turner's sign refers to bruising of the flanks, the part of the body between the last rib and the top of the hip. The bruising appears as a blue discoloration, and is a sign of retroperitoneal hemorrhage, or bleeding behind the peritoneum, which is a lining of the abdominal cavity. Grey Turner's sign takes 24–48 hours to develop, and can predict a severe attack of acute pancreatitis. Grey Turner's sign may be accompanied by Cullen's sign. Both signs may be indicative of pancreatic necrosis with retroperitoneal or intra-abdominal bleeding. Grey Turner's sign is named after British surgeon George Grey Turner. Causes Causes include * Acute pancreatitis, whereby methemalbumin formed from digested blood tracks subcutaneously around the abdomen from the inflamed pancreas. * Pancreatic hemorrhage * Retroperitoneal hemorrhage * Blunt abdominal trauma * Ruptured / hemorrhagic ectopic pregnancy. * Spontaneous bleeding secondary to coagulopathy (congenital or acquired) * Aor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruise
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close enough to the epidermis such that the bleeding causes a visible discoloration. The bruise then remains visible until the blood is either absorbed by tissues or cleared by immune system action. Bruises which do not blanch under pressure can involve capillaries at the level of skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle, or bone. Bruises are not to be confused with other similar-looking lesions. (Such lesions include petechia (less than , resulting from numerous and diverse etiologies such as adverse reactions from medications such as warfarin, straining, asphyxiation, platelet disorders and diseases such as ''cytomegalovirus''), purpura (, classified as palpable purpura or non-palpable purpura and indicates various pathologic conditions such as thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flank
Flank may refer to: * Flank (anatomy), part of the abdomen ** Flank steak, a cut of beef ** Part of the external anatomy of a horse * Flank speed, a nautical term * Flank opening, a chess opening * A term in Australian rules football * The side of a military unit, as in a flanking maneuver * Flanking, a sound path in architectural acoustics Architectural acoustics (also known as building acoustics) is the science and engineering of achieving a good sound within a building and is a branch of acoustical engineering. The first application of modern scientific methods to architectura ... * Flanking region, a region of DNA in directionality * Rift flank (synonymous of rift shoulder), mountains belt on the sides of extensional rift basins See also * Flanker (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
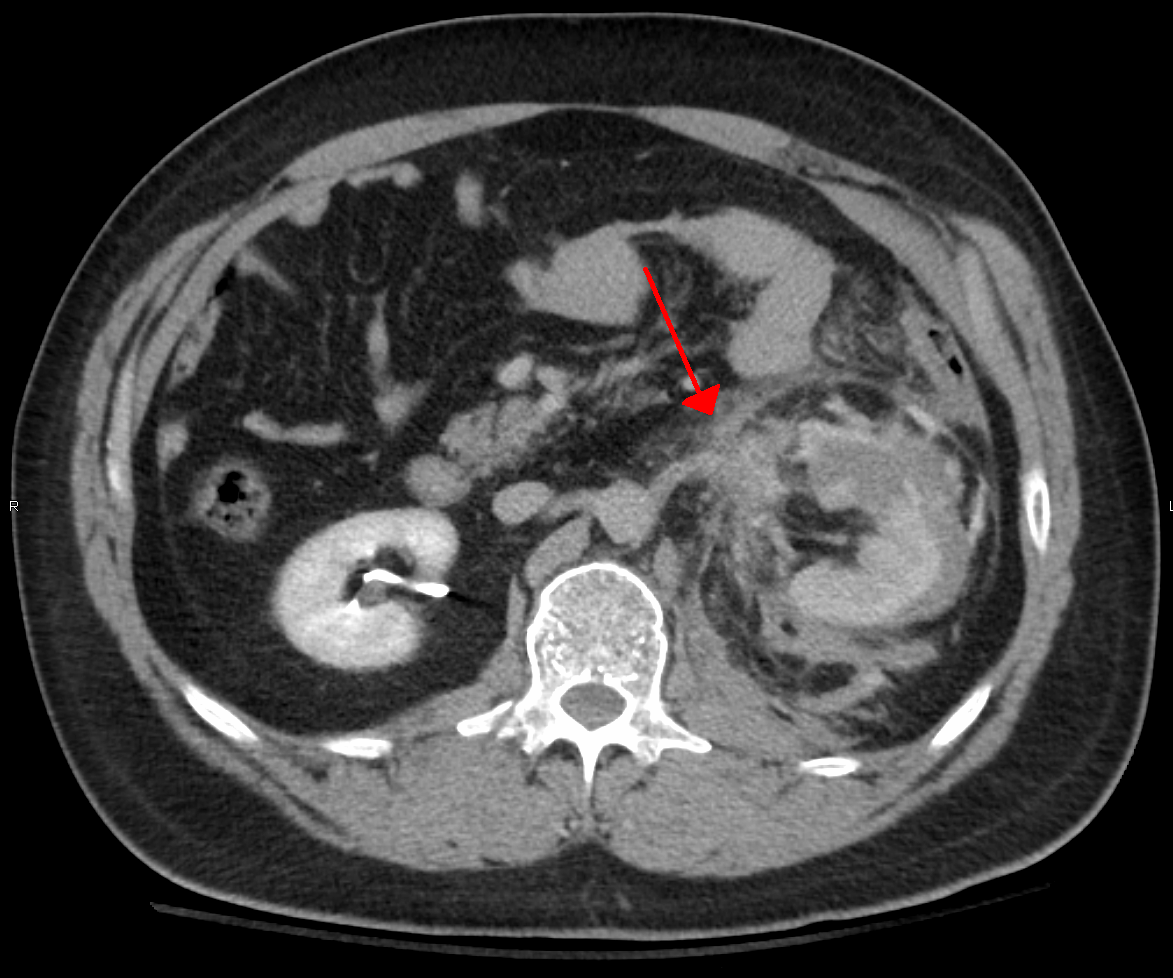
Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage
Retroperitoneal bleeding is an accumulation of blood in the retroperitoneal space. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal or upper leg pain, hematuria, and shock. It can be caused by major trauma or by non-traumatic mechanisms. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may include: * abdominal pain. * upper leg pain. * hematuria. * shock. Causes Retroperitoneal bleeds are most often caused by major trauma, such as from a traffic collisions or a fall. Less common non-traumatic causes including: * anticoagulation. * a ruptured aortic aneurysm. * a ruptured renal aneurysm. * acute pancreatitis. * malignancy. Retroperitoneal bleeds may also be iatrogenic, caused accidentally during medical procedures. Such procedures include cannulating the femoral artery for cardiac catheterization or for interventional radiology, and the administration of a psoas compartment nerve block. Diagnosis Neurology As well as initial symptoms, the accumulation of blood in the retroperitoneal space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. Signs and symptoms Common *severe epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases * nausea * vomiting *loss of appetite * fever *chills (shivering) *hemodynamic instability, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cullen's Sign
Cullen's sign is superficial edema and bruising in the subcutaneous fatty tissue around the umbilicus. It is named for gynecologist Thomas Stephen Cullen (1869–1953), who first described the sign in ruptured ectopic pregnancy in 1916.T.S. Cullen. Embryology, anatomy, and diseases of the umbilicus together with diseases of the urachus. Philadelphia, Saunders, and London, 1916. This sign takes 24–48 hours to appear and can predict acute pancreatitis, with mortality rising from 8–10% to 40%. It may be accompanied by Grey Turner's sign (bruising of the flank), which may then be indicative of pancreatic necrosis with retroperitoneal or intra-abdominal bleeding. Causes Causes include: * acute pancreatitis, where methemalbumin formed from digested blood tracks around the abdomen from the inflamed pancreas * bleeding from blunt abdominal trauma * bleeding from aortic rupture Aortic rupture is the rupture or breakage of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. Aortic rupture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as physicians before specializing in surgery. There are also surgeons in podiatry, dentistry, and veterinary medicine. It is estimated that surgeons perform over 300 million surgical procedures globally each year. History The first person to document a surgery was the 6th century BC Indian physician-surgeon, Sushruta. He specialized in cosmetic plastic surgery and even documented an open rhinoplasty procedure.Ira D. Papel, John Frodel, ''Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery'' His magnum opus ''Suśruta-saṃhitā'' is one of the most important surviving ancient treatises on medicine and is considered a foundational text of both Ayurveda and surgery. The treatise addresses all aspects of general medicine, but the translator G. D. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Grey Turner
George Grey Turner (8 September 1877 – 24 August 1951) was an English surgeon. He was born in North Shields and received his medical degree from Newcastle Medical School (then a part of the University of Durham). He received a Fellowship from the Royal College of Surgeons in 1903 and joined the staff of the Royal Infirmary. He served with the Royal Army Medical Corps in the First World War. As a young surgeon, he travelled around the world, being received by the Pope, Benito Mussolini, the King of Italy and King Alfonso of Spain. In 1927 he was made Professor of Surgery in the University of Durham. In 1934 he was elected President of the Medical Society of London and in 1935 delivered the Bradshaw Lecture at the Royal College of Surgeons. After the war, Grey Turner was briefly famous for performing one of the earliest operations to attempt the removal of a bullet from a soldier's heart. The bullet was never removed, but Grey Turner's surgery saved the patient's life. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. Signs and symptoms Common *severe epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases * nausea * vomiting *loss of appetite * fever *chills (shivering) *hemodynamic instability, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methemalbumin
Methemalbumin (MHA) is an albumin complex consisting of albumin and heme. This complex gives brown color to plasma and occurs in hemolytic and hemorrhagic disorders. Its presence in plasma is used to differentiate between hemorrhagic and edematous pancreatitis. The Schumm test is used to differentiate intravascular haemolysis from extravascular haemolysis, as in haemolytic anaemias Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly .... A positive result is indicative of intravascular haemolysis. References {{Albumins Proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue, and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of pinna, and scrotum * Blood vessels on rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blunt Force Trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound and bruise. Blunt trauma can result in contusions, abrasions, lacerations, internal hemorrhages, bone fractures, as well as death. Blunt trauma represents a significant cause of disability and death in people under the age of 35 years worldwide. Classification Blunt abdominal trauma Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT) represents 75% of all blunt trauma and is the most common example of this injury. 75% of BAT occurs in motor vehicle crashes, in which rapid deceleration may propel the driver into the steering wheel, dashboard, or seatbelt, causing contusions in less serious cases, or rupture of internal organs from briefly increased intraluminal pressure in the more serious, depending on the force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions the fetus is unable to survive. Overall, ectopic pregnancies are very rare, annually affecting less than 2% of pregnancies worldwide. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include pelvic inflammatory disease, often due to chlamydia infection; tobacco smoking; prior tubal surgery; a history of infertility; and the use of assisted reproductive technology. Those who have previously had an ectopic pregnancy are at much higher risk of having another one. Most ectopic pregnancies (90%) occur in the fallopian tube, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |