|
Gresford Disaster
The Gresford disaster occurred on 22 September 1934 at Gresford Colliery, near Wrexham, Denbighshire, when an explosion and underground fire killed 266 men. Gresford is one of Britain's worst coal mining disasters: a controversial inquiry into the disaster did not conclusively identify a cause, though evidence suggested that failures in safety procedures and poor mine management were contributory factors. Further public controversy was caused by the decision to seal the colliery's damaged sections permanently, meaning that only eleven of those who died were recovered. Background The Westminster and United Collieries Group began to sink the pit at Gresford in 1908. Two shafts were sunk apart: the Dennis and the Martin. They were named after Sir Theodore Martin, the company chairman, and Mabel Dennis, wife of the company managing director Henry Dyke Dennis, who had ceremonially cut the first sods for each of the respective shafts. Work was completed in 1911. The mine was one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandy, Gwersyllt
Pandy ( cy, Y Pandy; meaning the fulling mill) is a village near Gwersyllt and Rhosrobin, in Wrexham, Wrexham County Borough, Wales. The main entrance to Gresford Colliery stood in the village. Gresford Colliery Social Club is in the village and alongside it a memorial to the Gresford Disaster, which killed 266 men on September 22, 1934. Plas Acton Road originally linked the village to the main Chester Road, but was severed by the construction of the A483 by-pass. A footbridge crosses the new road maintaining the link for pedestrians. There are the remains of a mill on the River Alyn just below the village at the rear of the Pandy Business Park, in an area known as "The Wilderness". The Gresford Heath estate, built around the year 2000 on the site of the coalsheds for the former Colliery, doubled the population of the village. The naming reflects an attempt to raise house values in a former industrial village and to 'deWelshify' the village name. A new development of 9 luxury ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
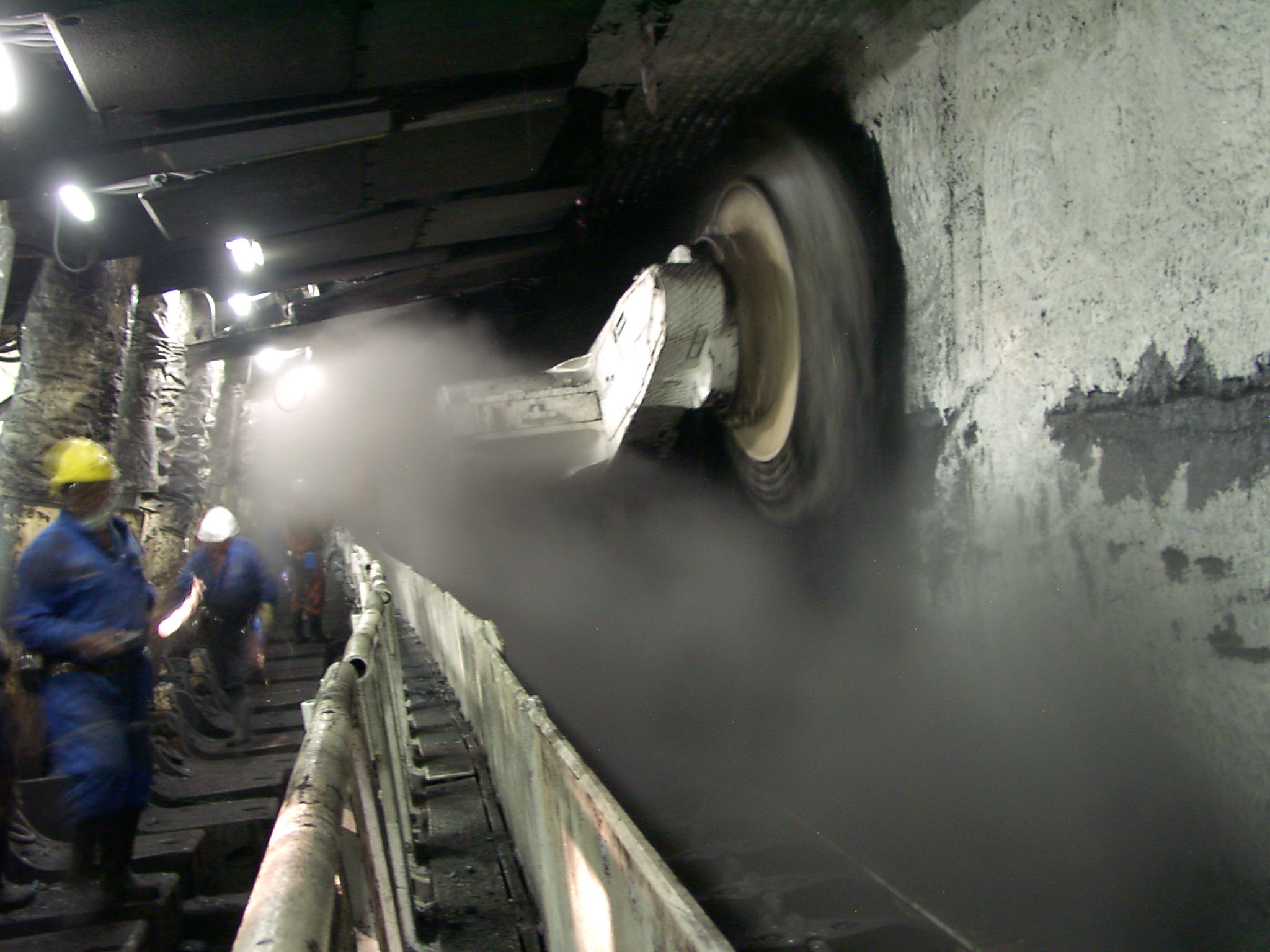
Longwall Mining
Longwall mining is a form of underground coal mining where a long wall of coal is mined in a single slice (typically thick). The longwall panel (the block of coal that is being mined) is typically long (but can be upto long) and wide. History The basic idea of longwall mining was developed in England in the late 17th century. Miners undercut the coal along the width of the coal face, removing coal as it fell, and used wooden props to control the fall of the roof behind the face. This was known as the Shropshire method of mining. While the technology has changed considerably, the basic idea remains the same, to remove essentially all of the coal from a broad coal face and allow the roof and overlying rock to collapse into the void behind, while maintaining a safe working space along the face for the miners. Starting around 1900, mechanization was applied to this method. By 1940, some referred to longwall mining as "the conveyor method" of mining, after the most prominent piec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for Work (human activity), work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * new technology, technologies and inventions * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * Policy, policies of the government * regulation and market (economics), market Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can influ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadside Ballad
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llay
Llay ( cy, Llai; meaning meadow; ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. It borders several other villages including Gwersyllt and Gresford. At the 2001 Census, the total population of the community of Llay, including Llay village, was 4,905, reducing to 4,814 at the 2011 Census. Prior to the 1960s, Llay was a coal mining village. Llay Main Colliery, at one time the largest colliery in Wales and after 1952 the deepest pit in the UK, was a major employer for the area before its coal reserves were exhausted in 1966.Llay Main Colliery BBC North East Wales History Llay first appears in mediaeval records as a - a small settlement wit ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Pony
A pit pony, otherwise known as a mining horse, was a horse, pony or mule commonly used underground in mines from the mid-18th until the mid-20th century. The term "pony" was sometimes broadly applied to any equine working underground.English Pit PoniesThe Colliery Engineer Vol. VIII, No. 1 (August 1887); pages 6-7. History The first known recorded use of ponies underground in Great Britain was in the Durham coalfield in 1750. Following the drowning deaths of 26 children when the Huskar Colliery in Silkstone flooded on 4 July 1838, "A report was published in ''The Times'', and the wider British public learned for the first time that women and children worked in the mines. There was a public outcry, led by politician and reformer Anthony Ashley Cooper, later Lord Shaftesbury," who then introduced the Mines and Collieries Act 1842 to Parliament which barred women, girls and boys under 10 (later amended to 13) from working underground, leading to the widespread use of horses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterdamp
Afterdamp is the toxic mixture of gases left in a mine following an explosion caused by methane-rich firedamp, which itself can initiate a much larger explosion of coal dust. The term is etymologically and practically related to other terms for underground mine gases—such as firedamp, white damp, and black damp, with afterdamp being composed, rather, primarily by carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and nitrogen, with highly toxic stinkdamp-constituent hydrogen sulfide possibly also present. However, the high content of carbon monoxide is the component that kills, preferentially combining with haemoglobin in the blood and thus depriving victims of oxygen. Globally, afterdamp has caused many of the casualties in disasters of pit coalfields, including British, such as the Senghenydd colliery disaster. Such disasters continue to afflict working mines, for instance in mainland China. Etymology The meaning of "damp" in this term, while most commonly understood to imply humidity, presents e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Mining
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the slope of a hill, driven horizontally into the ore seam. Random House dictionary says the origin of the term "drift mine" is an Americanism, circa 1885–1890. Drift is a more general mining term, meaning a near-horizontal passageway in a mine, following the bed (of coal, for instance) or vein of ore. A drift may or may not intersect the ground surface. A drift follows the vein, as distinguished from a crosscut that intersects it, or a level or gallery, which may do either. All horizontal or subhorizontal development openings made in a mine have the generic name of drift. These are simply tunnels made in the rock, with a size and shape depending on their use—for example, haulage, ventilation, or exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colliery Viewer
A colliery viewer or coal viewer was the manager of a coal mine or colliery. The term was mostly used in the late eighteenth to nineteenth centuries, in the UK. In modern use, the viewer would be the senior and responsible mining engineer at a site. Origins The role began as a person to represent the owner of the land, often an aristocrat, who had leased the rights to mine there to another who would 'work' the mine. One of the first formally recorded arrangements for such was at the Ironbridge Gorge in 1608, where Jesse Whittingham leased four adits from James Clifford, at a rent of £200 a year for five years. Clifford had acquired the lands of Wenlock Priory at Broseley in 1560, after the priory's dissolution in 1540. Several such monastic lands moved from traditional tenant farming to entrepreneurial mineral exploitation at this time, spurring the early industrial revolution, particularly around the Gorge. Land at this time was rarely sold, the aristocratic estates were in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |