|
Green Lane Hospital, Auckland
Green Lane Hospital in Auckland, New Zealand (now known as the Greenlane Clinical Centre) was a hospital with a national and international reputation for cardiology and cardiothoracic surgery, led by Douglas Robb (surgeon), Douglas Robb and Brian Barratt-Boyes. The original hospital, the Costley Home for the Aged Poor, opened in 1890. It was renamed the Auckland Infirmary in 1924 and then Green Lane Hospital in 1942 when it became a general hospital. The hospital's name was sometimes misspelt as Greenlane Hospital. In 2003 it became the Greenlane Clinical Centre when many of the services were moved to Auckland City Hospital. Costley Home for the Aged Poor The site for a future hospital was selected by Governor George Grey, Sir George Grey. In 1886 the land was handed by the Crown to the Auckland Hospital Board and further land was purchased using a bequest from the philanthropist Edward Costley. Costley's bequest also funded the first hospital building, the Costley Home for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACCESSIBILITY
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i.e. unassisted) and "indirect access" meaning compatibility with a person's assistive technology (for example, computer screen readers). Accessibility can be viewed as the "ability to access" and benefit from some system or entity. The concept focuses on enabling access for people with disabilities, or enabling access through the use of assistive technology; however, research and development in accessibility brings benefits to everyone. Accessibility is not to be confused with usability, which is the extent to which a product (such as a device, service, or environment) can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency, convenience, or satisfaction in a specified context of use. Accessibility is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCG Vaccine
Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as soon after birth as possible. In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated. Adults who do not have tuberculosis and have not been previously immunized, but are frequently exposed, may be immunized, as well. BCG also has some effectiveness against Buruli ulcer infection and other nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Additionally, it is sometimes used as part of the treatment of bladder cancer. Rates of protection against tuberculosis infection vary widely and protection lasts up to 20 years. Among children, it prevents about 20% from getting infected and among those who do get infected, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of 22 species of evergreen tree. The genus is part of the ancient conifer family Araucariaceae, a group once widespread during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, but now largely restricted to the Southern Hemisphere except for a number of extant Malesian ''Agathis''.de Laubenfels, David J. 1988. Coniferales. P. 337–453 in Flora Malesiana, Series I, Vol. 10. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. Description Mature kauri trees have characteristically large trunks, with little or no branching below the crown. In contrast, young trees are normally conical in shape, forming a more rounded or irregularly shaped crown as they achieve maturity.Whitmore, T.C. 1977. ''A first look at Agathis''. Tropical Forestry Papers No. 11. University of Oxford Commonwealth Forestry Institute. The bark is smooth and light grey to grey-brown, usually peeling into irregular flakes that become thicker on more mature trees. The branch struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
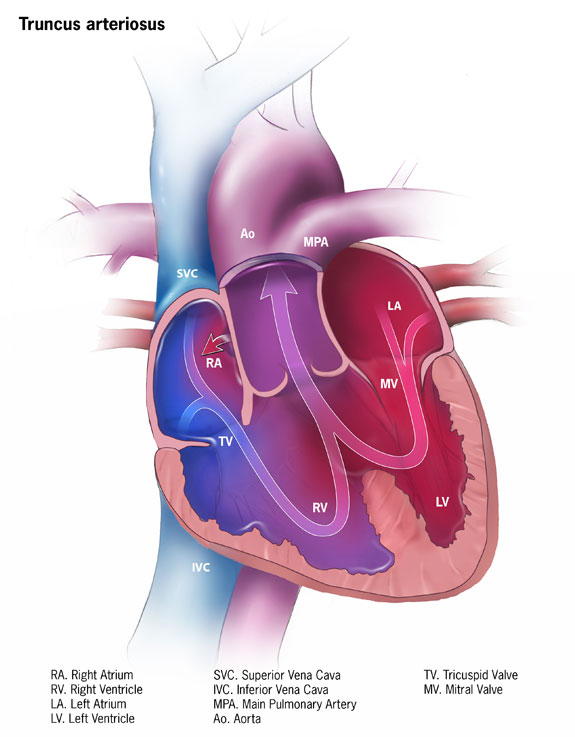
Ventricular Septal Defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes. The membranous portion, which is close to the atrioventricular node, is most commonly affected in adults and older children in the United States. It is also the type that will most commonly require surgical intervention, comprising over 80% of cases. Membranous ventricular septal defects are more common than muscular ventricular septal defects, and are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly. Signs and symptoms Ventricular septal defect is usually symptomless at birth. It usually manifests a few weeks after birth. VSD is an acyanotic congenital heart defect, aka a lef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memorial Plaque For First Heart-lung Bypass Operation, Greenlane Clinical Centre, Auckland, New Zealand
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of art such as sculptures, statues or fountains and parks. Larger memorials may be known as monuments. Types The most common type of memorial is the gravestone or the memorial plaque. Also common are war memorials commemorating those who have died in wars. Memorials in the form of a cross are called intending crosses. Online memorials are often created on websites and social media to allow digital access as an alternative to physical memorials which may not be feasible or easily accessible. When somebody has died, the family may request that a memorial gift (usually money) be given to a designated charity, or that a tree be planted in memory of the person. Those temporary or makeshift memorials are also called grassroots memoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery refers to a class of surgery involving rerouting a tubular body part. Types include: * Vascular bypass surgery such as coronary artery bypass surgery, a heart operation * Cardiopulmonary bypass, a technique used in coronary artery bypass surgery * Weight loss or Bariatric surgery: ** Vertical banded gastroplasty surgery or "stomach stapling", the upper part of the stomach is permanently stapled to create a smaller pouch ** Adjustable gastric band or "lap band", a band creates a pocket in the stomach that can be adjusted with a port placed just under the skin ** Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery, the small intestine is connected to the upper part of the stomach ** Partial ileal bypass surgery, shortening the final portion of the small intestine ** Popliteal bypass surgery, to treat diseased leg arteries above or below the knee ** Jejunojejunostomy, surgery that connects two portions of small intestine and is no longer used *** Ileojejunal bypass The ileojejunal bypas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralogy Of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are: *pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the right ventricle; * a ventricular septal defect, which is a hole allowing blood to flow between the two ventricles; * right ventricular hypertrophy, which is thickening of the right ventricular muscle; and * an overriding aorta, which is where the aorta expands to allow blood from both ventricles to enter. At birth, children may be asymptomatic or present with many severe symptoms. Later in infancy, there are typically episodes of bluish colour to the skin due to a lack of sufficient oxygenation, known as cyanosis. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement, they may undergo a "tet spell" where they turn cyanotic, have difficulty breathing, become limp, and occasionally lose consciousness. Other symptoms may include a heart murmur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Baby Syndrome
Blue baby syndrome can refer to conditions that cause cyanosis, or blueness of the skin, in babies as a result of low oxygen levels in the blood. This term has traditionally been applied to cyanosis as a result of: #Cyanotic heart disease, which is a category of congenital heart defect that results in low levels of oxygen in the blood. This can be caused by either reduced blood flow to the lungs or mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. # Methemoglobinemia, which is a disease defined by high levels of methemoglobin in the blood. Increased levels of methemoglobin prevent oxygen from being released into the tissues and result in hypoxemia. Although these are the most common causes of cyanosis, there are other potential factors that can cause a blue tint to a baby's skin or mucous membranes. These factors include hypoventilation, perfusion or ventilation differences in the lungs, and poor cardiac output of oxygenated blood, among others. The blue baby syndrome or cyanosis occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blalock–Thomas–Taussig Shunt
The Blalock–Thomas–Taussig shunt (BTT shunt), previously known as the Blalock–Taussig Shunt (BT shunt), is a surgical procedure used to increase blood flow to the lungs in some forms of congenital heart disease such as pulmonary atresia and tetralogy of Fallot, which are common causes of blue baby syndrome. The procedure involves connecting a branch of the subclavian artery or carotid artery to the pulmonary artery. In modern practice, this procedure is temporarily used to direct blood flow to the lungs and relieve cyanosis while the infant is waiting for corrective or definitive surgery when their heart is larger. The BTT shunt is used in the first step of the three-stage palliation (the Norwood procedure). __TOC__ Alternatives While the originally described Blalock–Thomas–Taussig shunt directly connected the subclavian and pulmonary arteries, in contemporary practice a modified version of the procedure, the mBTT shunt, is more commonly used. In the modified Bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Legends recount that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. The Wellington urban area, which only includes urbanised ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
''Patent ductus arteriosus'' (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ''ductus arteriosus'' fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has a higher pressure, to the pulmonary artery. Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure. The ''ductus arteriosus'' is a fetal blood vessel that normally closes soon after birth. In a PDA, the vessel does not close, but remains ''patent'' (open), resulting in an abnormal transmission of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. PDA is common in newborns with persistent respiratory problems such as hypoxia, and has a high occurrence in premature newborns. Premature newborns are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruakura
Ruakura is a semi-rural suburb of Hamilton City, in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The University of Waikato is nearby. The area lies to the east of urban Hamilton and to the west of State Highway 1B (a variant of State Highway 1 which avoids the urban area). Ruakura Agriculture Research Centre Waikato Agricultural College and Model Farm was set up in 1888, so that Ruakura is now synonymous with the Ruakura Agriculture Research Centre, the location of institutes such as AgResearch and Plant & Food Research. Areas of AgResearch's research at Ruakura include animal molecular biology (genomics and cloning), reproductive technologies, agricultural systems modelling, land management, dairy science, meat science, food processing technology and safety, and animal behaviour and welfare. Plant & Food Research's site in Hamilton is home to its blueberry nursery, its Bioengineering Group and its Food and Biological Chemistry laboratory. Work is also carried out on biological contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |