|
Green And Golden Bell Frog
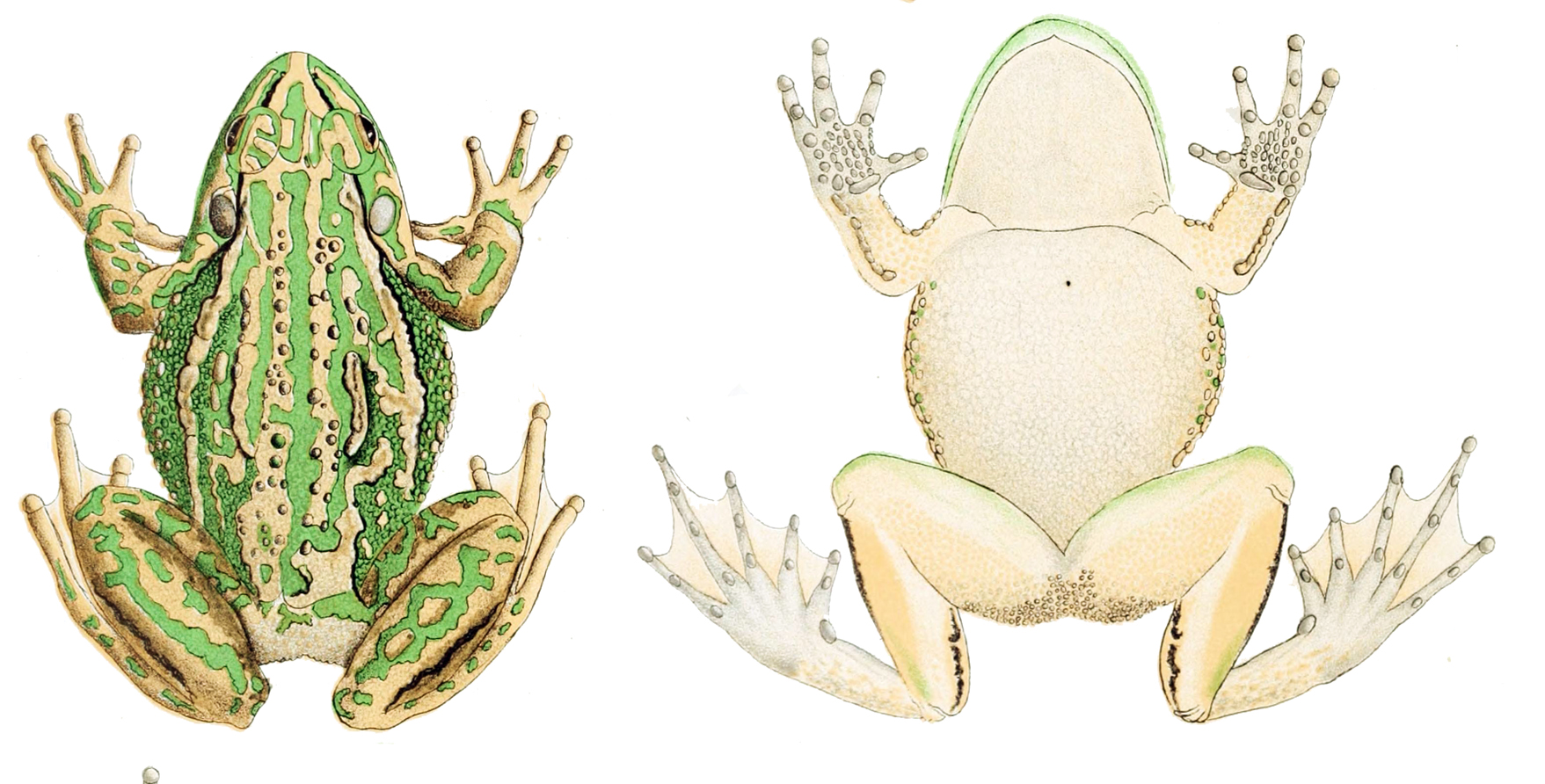
The green and golden bell frog (''Ranoidea aurea''), also named the green bell frog, green and golden swamp frog and green frog, is a species of ground-dwelling tree frog native to eastern Australia. Despite its classification and climbing abilities, it does not live in trees and spends almost all of its time close to ground level. It can reach up to in length, making it one of Australia's largest frogs. Coloured gold and green, the frogs are voracious eaters of insects, but will also eat larger prey, such as worms and mice. They are mainly diurnal, although this is mostly to warm in the sun. They tend to be less active in winter except in warmer or wetter periods, and breed in the warmer months. Males reach maturity after around 9 months, while for the larger females, this does not occur until they are two years old. The frogs can engage in cannibalism, and males frequently attack and injure one another if they infringe on one another's space. Many populations, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Lesson
René-Primevère Lesson (20 March 1794 – 28 April 1849) was a French surgeon, naturalist, ornithologist, and herpetologist. Biography Lesson was born at Rochefort, and entered the Naval Medical School in Rochefort at the age of sixteen. He served in the French Navy during the Napoleonic Wars; in 1811 he was third surgeon on the frigate ''Saale'', and in 1813 was second surgeon on the ''Regulus''.Persée Un pharmacien de la marine et voyageur naturaliste : R.-P Lesson In 1816 Lesson changed his classification to . He served on Duperrey's round-the-wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Gippsland
East Gippsland is the eastern region of Gippsland, Victoria, Australia covering 31,740 square kilometres (14%) of Victoria. It has a population of 80,114. Australian Bureau of Statistics2006 Census Community Profile Series: East Gippsland (Statistical Division). Released at 29/02/2008. LOCATION CODE: 250 STATE: VIC/ref> History The Shire of East Gippsland, also called Far East Gippsland, covers two-thirds (66%) of East Gippsland's area and holds half (50%) of its population. Australian Bureau of Statistics2006 Census. Community Profile Series: East Gippsland Shire (Statistical Subdivision). Released at 29/02/2008. LOCATION CODE: 25005 STATE: VIC/ref> The Shire of East Gippsland is confusingly also referred to simply as East Gippsland. It excludes the Shire of Wellington (Central Gippsland). This article (currently) refers mainly to "Far East Gippsland". East Gippsland's major towns include, from west to east, Bairnsdale (the largest town and administrative centre), Paynesville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet (Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Senat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunswick Heads
Brunswick Heads is a small town on the north coast of New South Wales, Australia in Byron Shire. At the , the town had a population of 1,737 people. History Originally inhabited by people of the Bundjalung people, Bundjalung nation, the Brunswick River was charted by Captain Rous in 1828. His visit was followed more than 20 years later by cedar cutters whose activities led to the first town in what is now Byron Shire. By the 1880s Brunswick Heads was a busy port with a small commercial centre. The township went into decline after the construction of the railway through Mullumbimby in 1894. From the 1920s, however, Brunswick's popularity for family seaside holidays returned. Holiday cottages from that period are still in evidence throughout the town. The early camping grounds along the foreshores later became caravan parks. Poet and painter Edwin Wilson (b. 1942) started school at Brunswick Heads, as recorded in "The Mullumbimby Kid". Geography Brunswick Heads is a small co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
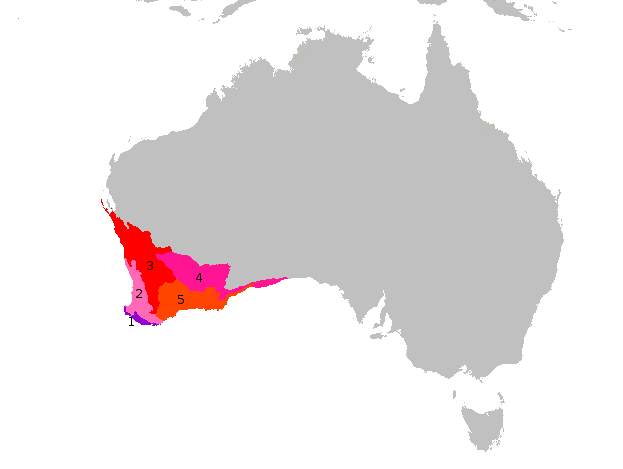
Litoria Aurea Range In Australia
''Litoria'' is a genus of hylid tree frogs, sometimes collectively referred to as Australasian treefrogs, that are native to Australia, the Bismarck Archipelago, the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, the Lesser Sunda Islands, and the Moluccan Islands. They are distinguishable from other tree frogs by the presence of horizontal irises, no pigmentation of the eyelids, and their distribution east and south from Wallacea. Over one hundred species are recognised and new species are still being added, such as the Pinocchio frog discovered in 2008 and described in 2019. The species within the genus ''Litoria'' are extremely variable in appearance, behaviour, and habitat. The smallest species is the javelin frog (''L. microbelos''), reaching a maximum snout–to–vent length of , while the largest, the giant tree frog (''L. infrafrenata''), reaches a size of . The appearance, behaviour, and habitat of each frog is usually linked. The small, darkly coloured frogs are generally terrestrial, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of , the second most populated state (after New South Wales) with a population of over 6.5 million, and the most densely populated state in Australia (28 per km2). Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south (with the exception of a small land border with Tasmania located along Boundary Islet), the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea (a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean) to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the northeast and the semi-arid north-west. The majority of the Victorian population is concentrated in the central-south area surrounding Port Phillip Bay, and in particular within the metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gippsland
Gippsland is a rural region that makes up the southeastern part of Victoria, Australia, mostly comprising the coastal plains to the rainward (southern) side of the Victorian Alps (the southernmost section of the Great Dividing Range). It covers an elongated area of located further east of the Shire of Cardinia (Melbourne's outermost southeastern suburbs) between Dandenong Ranges and Mornington Peninsula, and is bounded to the north by the mountain ranges and plateaus/highlands of the High Country (which separate it from Hume region in Victoria's northeast), to the southwest by the Western Port Bay, to the south and east by the Bass Strait and the Tasman Sea, and to the east and northeast by the Black-Allan Line (the easternmost section of the Victoria/New South Wales state border). The Gippsland region is generally divided by the Strzelecki Ranges and tributaries of the Gippsland Lakes into five statistical sub-regions — namely the West Gippsland, South Gippsland, Latro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Albumin
Serum albumin, often referred to simply as blood albumin, is an albumin (a type of globular protein) found in vertebrate blood. Human serum albumin is encoded by the ''ALB'' gene. Other mammalian forms, such as bovine serum albumin, are chemically similar. Serum albumin is produced by the liver, occurs dissolved in blood plasma and is the most abundant blood protein in mammals. Albumin is essential for maintaining the oncotic pressure needed for proper distribution of body fluids between blood vessels and body tissues; without albumin, the high pressure in the blood vessels would force more fluids out into the tissues. It also acts as a plasma carrier by non-specifically binding several hydrophobic steroid hormones and as a transport protein for hemin and fatty acids. Too much or too little circulating serum albumin may be harmful. Albumin in the urine usually denotes the presence of kidney disease. Occasionally albumin appears in the urine of normal persons following long period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulong, New South Wales
Ulong is a small village located on the Mid North Coast region, neighbouring the Northern Tablelands, of New South Wales, Australia. It has a community hall, public school, cafe-post office and an Ex-services Club. Facilities The village is serviced by the Ulong Ex-services Club, cafe with rural transaction centre, and the Eastern Dorrigo Community Hall. The hall has camping facilities available with kitchen, BBQ and shower facilities available Timms Park is situated on Ulong Creek with a picnic area including tables, bins and a toilet. The land surrounding the park was donated to the community by LEH Timms. Geography The village lies inland from Coffs Harbour by . Whilst a short distance, it takes 45 minutes to drive to, through the mountainous rainforest. Ulong is on the Eastern Dorrigo Plateau and sits some . Like the neighbouring village of Lowanna, the climate is markedly different from Coffs Harbour. Ulong is known as the "Village in the Valley". History Once larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranoidea Moorei
The motorbike frog (''Ranoidea moorei'') is a ground-dwelling tree frog of the subfamily Pelodryadinae found in Southwest Australia. Its common name is derived from the male frog's mating call, which sounds similar to a motorbike changing up through gears; it is also known as Moore's frog, the western bell frog, western green and golden bell frog, and western green tree frog. Taxonomy ''R. moorei'' is a member of the ''Ranoidea aurea'' complex (''Ranoidea aurea'', '' R. raniformis'' and '' "Litoria" castanea''). Description ''R. moorei'' is able to camouflage itself well, and ranges in colour from dark brown, through green, to gold. The underside is noticeably lighter, and usually ranges from very pale green to light brown. The light green of the groin and thigh distinguishes this species from its cogenor, '' Ranoidea cyclorhynchus'', which is darker and spotted with yellow there. Typical of tree frogs, its toe pads enable it to climb smooth vertical surfaces. Its hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranoidea Cyclorhyncha
The spotted-thighed tree frog (''Ranoidea cyclorhynchus'') is a species of tree frog in the subfamily Pelodryadinae, found in Western Australia. Description The frog is similar in appearance to its cogener, ''Ranoidea moorei'', bearing dark green or brownish patches with bronze or gold highlights on its back; this species can be differentiated by the numerous yellowish spots on the underside of the rear legs. Males may be up to 65 mm, females to 85 mm. The name Copland's rock frog is sometimes mistakenly applied to this species (it is actually '' Litoria coplandi''). The feet are unwebbed and have a prominent disc at the toes. Distribution and habitat It is endemic to Southwest Australia, as one of only four in that diverse genus to be found in the region. It occurs on the southern coastal areas, favouring permanent water and granite outcrops, but can be found at its northernmost extent in agricultural dams. Recorded sightings are also at Middle Island in the Archipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Litoria_everetti_Meleotegi_River%2C_Ermera_District%2C_Timor-Leste_(USNM_578928).jpg)


