|
Greater Sciatic Notch
The greater sciatic notch is a notch in the ilium, one of the bones that make up the human pelvis. It lies between the posterior inferior iliac spine (above), and the ischial spine (below). The sacrospinous ligament changes this notch into an opening, the greater sciatic foramen. The notch holds the piriformis, the superior gluteal vein and artery, and the superior gluteal nerve; the inferior gluteal vein and artery and the inferior gluteal nerve; the sciatic and posterior femoral cutaneous nerves; the internal pudendal artery and veins, and the nerves to the internal obturator and quadratus femoris muscles. Of these, the superior gluteal vessels and nerve pass out above the piriformis, and the other structures below it. The greater sciatic notch is wider in women (about 74.4 degrees on average) than in men (about 50.4 degrees). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilium (bone)
The ilium () (plural ilia) is the uppermost and largest part of the hip bone, and appears in most vertebrates including mammals and birds, but not bony fish. All reptiles have an ilium except snakes, although some snake species have a tiny bone which is considered to be an ilium. The ilium of the human is divisible into two parts, the body and the wing; the separation is indicated on the top surface by a curved line, the arcuate line, and on the external surface by the margin of the acetabulum. The name comes from the Latin (''ile'', ''ilis''), meaning "groin" or "flank". Structure The ilium consists of the body and wing. Together with the ischium and pubis, to which the ilium is connected, these form the pelvic bone, with only a faint line indicating the place of union. The body ( la, corpus) forms less than two-fifths of the acetabulum; and also forms part of the acetabular fossa. The internal surface of the body is part of the wall of the lesser pelvis and gives or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
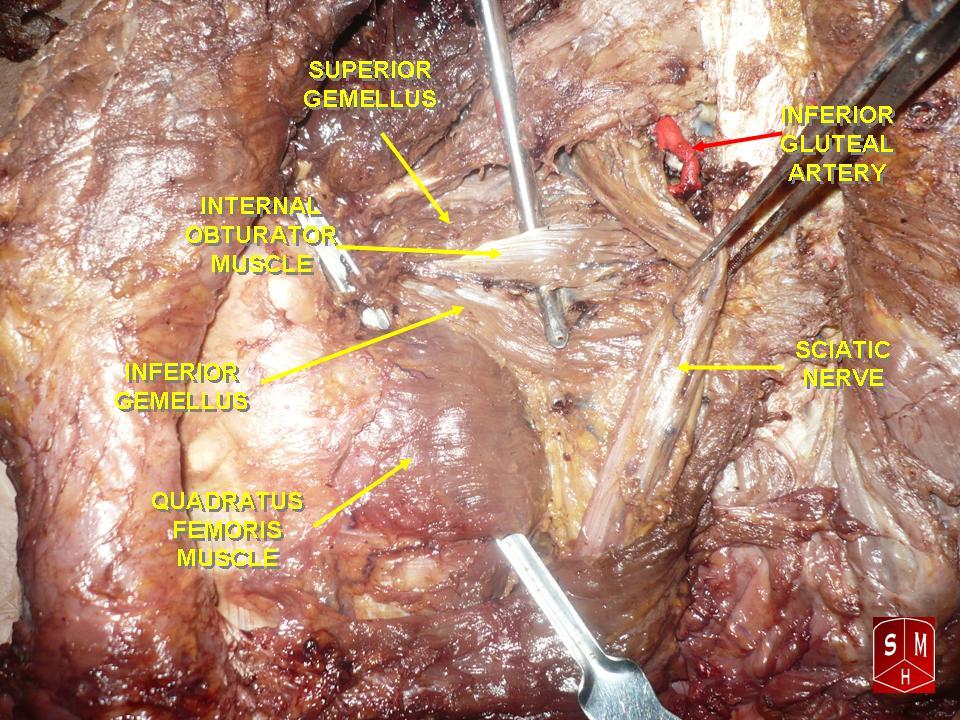
Inferior Gluteal Nerve
The inferior gluteal nerve is the main motor neuron that innervates the gluteus maximus muscle. It is responsible for the movement of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs. Injury to this nerve is rare but often occurs as a complication of posterior approach to the hip during hip replacement. When damaged, one would develop gluteus maximus lurch, which is a gait abnormality which causes the individual to 'lurch' backwards to compensate lack in hip extension. Anatomy The largest muscle of the posterior hip, gluteus maximus, is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve.Skalak, A. F., et al. "Relationship of Inferior Gluteal Nerves and Vessels: Target for Application of Stimulation Devices for the Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in Spinal Cord Injury." Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy 30.1 (2008): 41-45. Print. It branches out and then enters the deep surface of the gluteus maximus, the principal extensor of the thigh, and suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Sciatic Foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies most of its volume. The greater sciatic foramen is wider in women than in men. Structure It is bounded as follows: * anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the ilium. * posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament. * inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine. * superiorly by the anterior sacroiliac ligament. Function The piriformis, which exits the pelvis through the foramen, occupies most of its volume. The following structures also exit the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen: See also *Lesser sciatic foramen The lesser sciatic foramen is an opening (foramen) between the pelvis and the back of the thigh. The foramen is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Symbol
The degree symbol or degree sign, , is a typographical symbol that is used, among other things, to represent degrees of arc (e.g. in geographic coordinate systems), hours (in the medical field), degrees of temperature or alcohol proof. The symbol consists of a small superscript circle. History The word degree is equivalent to Latin gradus which, since the medieval period, could refer to any stage in a graded system of ranks or steps. The number of the rank in question was indicated by ordinal numbers, in abbreviation with the ordinal indicator (a superscript '' o''). Use of "degree" specifically for the degrees of arc, used in conjunction with Arabic numerals, became common in the 16th century, but this was without the use of an ordinal marker or degree symbol. Similarly, the introduction of the temperature scales with degrees in the 18th century was at first without such symbols, but with the word "gradus" spelled out. Use of the degree symbol was introduced for tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratus Femoris
The quadratus femoris is a flat, quadrilateral skeletal muscle. Located on the posterior side of the hip joint, it is a strong external rotator and adductor of the thigh, but also acts to stabilize the femoral head in the acetabulum. Quadratus femoris use in the Meyer's muscle pedicle grafting to prevent avascular necrosis of femur head. Course It originates on the lateral border of the ischial tuberosity of the ischium of the pelvis. From there, it passes laterally to its insertion on the posterior side of the head of the femur: the quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest and along the quadrate line, the vertical line which runs downward to bisect the lesser trochanter on the medial side of the femur. Along its course, quadratus is aligned edge to edge with the inferior gemellus above and the adductor magnus below, so that its upper and lower borders run horizontal and parallel. At its origin, the upper margin of the adductor magnus is separated from it by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
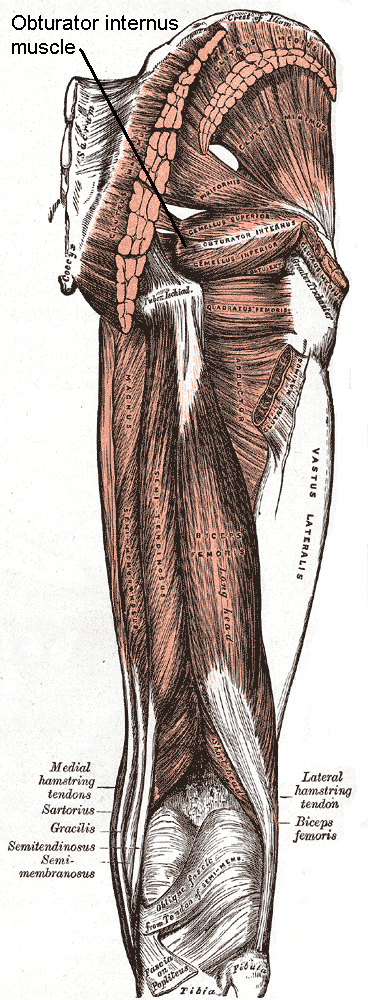
Internal Obturator
The internal obturator muscle or obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis. It exits the pelvic cavity through the lesser sciatic foramen. The internal obturator is situated partly within the lesser pelvis, and partly at the back of the hip-joint. It functions to help laterally rotate femur with hip extension and abduct femur with hip flexion, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum. Structure Origin The internal obturator muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis. It surrounds the obturator foramen. It is attached to the inferior pubic ramus and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim. It reaches from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front. It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Veins
The internal pudendal veins (internal pudic veins) are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudendal nerve. They begin in the deep veins of the vulva and of the penis, issuing from the bulb of the vestibule and the bulb of the penis, respectively. They accompany the internal pudendal artery, and unite to form a single vessel, which ends in the internal iliac vein. They receive the veins from the urethral bulb, the perineal and inferior hemorrhoidal veins. The deep dorsal vein of the penis Deep or The Deep may refer to: Places United States * Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia * Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah * Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania * Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary) ... communicates with the internal pudendal veins, but ends mainly in the pudendal plexus. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It is smaller in the female than in the male. Path It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. It runs on the lateral pelvic wall. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region. It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. It travels through the pudendal canal with the internal pudendal veins and the pudendal nerve. Branches The internal pudendal artery gives off the following branches: The deep artery of clitoris is a branch of the internal pudendal artery and supplies the clitoral crura. Another branch of the internal pudendal arter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) is a sensory nerve in the thigh. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum. Structure The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a nerve from the sacral plexus. It arises partly from the dorsal divisions of the S1 and S2, and from the ventral divisions of S2 and S3 sacral spinal nerves. It leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen below the piriformis muscle. It then descends beneath the gluteus maximus muscle with the inferior gluteal artery, and runs down the back of the thigh beneath the fascia lata. It runs over the long head of the biceps femoris to the back of the knee. It then pierces the deep fascia, and accompanies the small saphenous vein to about the middle of the back of the leg. Its terminal branches communicate with the sural nerve. Branches Its branches are all cutaneous, and are distributed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatic
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk from the L4 and L5 roots descends between the sacral promontory and ala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Gluteal Artery
The inferior gluteal artery (sciatic artery), the smaller of the two terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery, is distributed chiefly to the buttock and back of the thigh. It passes down on the sacral plexus of nerves and the piriformis muscle, behind the internal pudendal artery. It passes through the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen. It escapes from the pelvis between piriformis muscle and coccygeus muscle. It then descends in the interval between the greater trochanter of the femur and tuberosity of the ischium. It is accompanied by the sciatic nerve and the posterior femoral cutaneous nerves The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) is a sensory nerve in the thigh. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum. Structure ..., and covered by the gluteus maximus. It continues down the back of the thigh, supplying the sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |