|
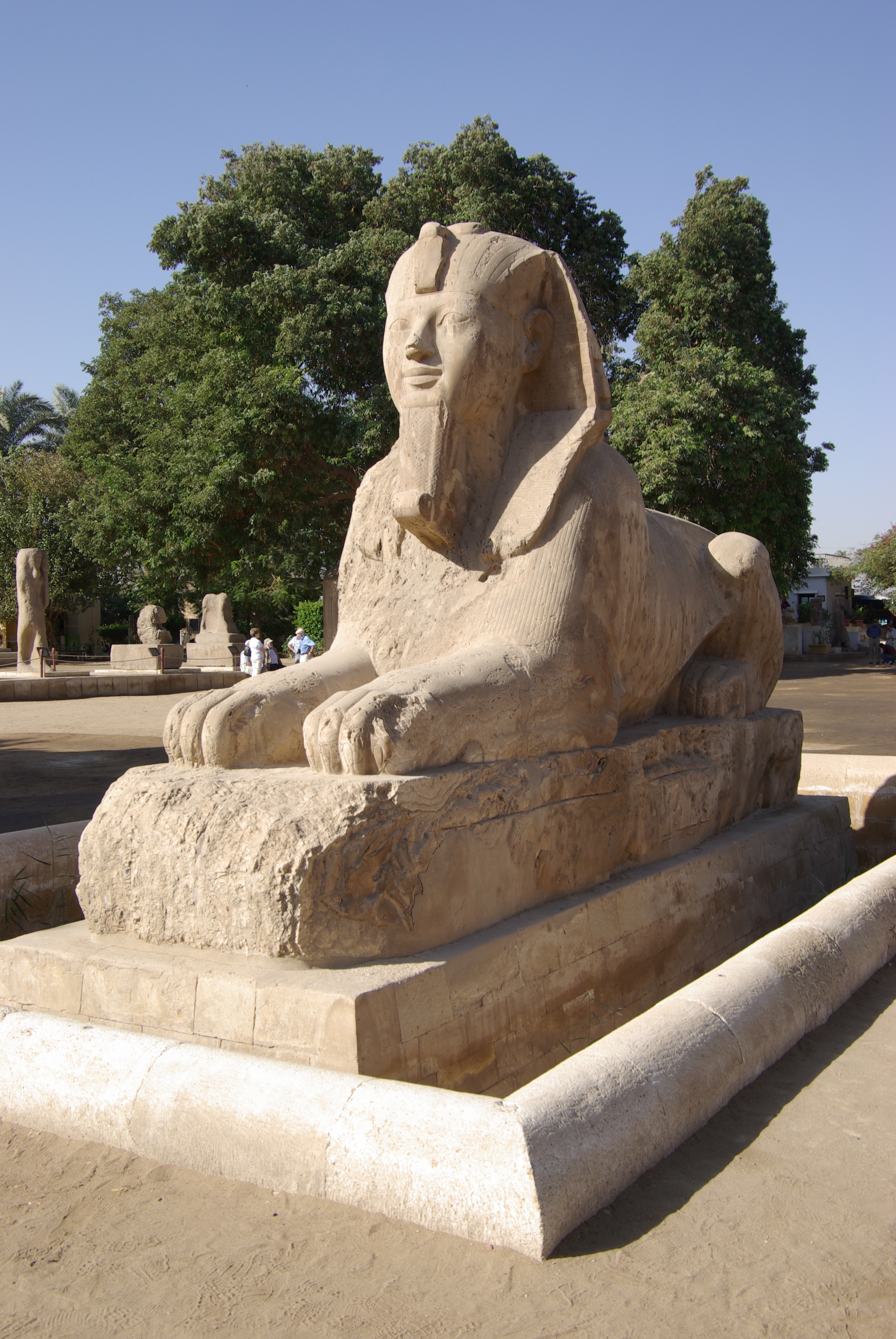
Great Sphinx Of Tanis
The Great Sphinx of Tanis is a granite sculpture of a sphinx, whose date may be as early as the 26th century BC. It was discovered in the ruins of the Temple of Amun-Ra in Tanis, Egypt's capital during the 21st Dynasty and the 23rd Dynasty. It was created much earlier, but when exactly remains debated with hypotheses of the 4th Dynasty or the 12th Dynasty. All that is left of its original inscription are the parts alluding to pharaohs Amenemhat II (12th Dynasty), Merneptah (19th Dynasty) and Shoshenq I (22nd Dynasty). The Louvre acquired it in 1826 as part of the second Egyptian collection of Henry Salt (Egyptologist), Henry Salt, whose purchase was led on behalf of the French state by Jean-François Champollion. Initially plans were made to place it outdoors, at the center of the Cour Carrée, but they were not implemented. Instead, the sphinx was exhibited in the museum's courtyard, since then known as the , from 1828 until 1848, when it was relocated to the , still now the mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sphinx Of Tanis
The Great Sphinx of Tanis is a granite sculpture of a sphinx, whose date may be as early as the 26th century BC. It was discovered in the ruins of the Temple of Amun-Ra in Tanis, Egypt's capital during the 21st Dynasty and the 23rd Dynasty. It was created much earlier, but when exactly remains debated with hypotheses of the 4th Dynasty or the 12th Dynasty. All that is left of its original inscription are the parts alluding to pharaohs Amenemhat II (12th Dynasty), Merneptah (19th Dynasty) and Shoshenq I (22nd Dynasty). The Louvre acquired it in 1826 as part of the second Egyptian collection of Henry Salt (Egyptologist), Henry Salt, whose purchase was led on behalf of the French state by Jean-François Champollion. Initially plans were made to place it outdoors, at the center of the Cour Carrée, but they were not implemented. Instead, the sphinx was exhibited in the museum's courtyard, since then known as the , from 1828 until 1848, when it was relocated to the , still now the mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central landmark of the city, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement (district or ward). At any given point in time, approximately 38,000 objects from prehistory to the 21st century are being exhibited over an area of 72,735 square meters (782,910 square feet). Attendance in 2021 was 2.8 million due to the COVID-19 pandemic, up five percent from 2020, but far below pre-COVID attendance. Nonetheless, the Louvre still topped the list of most-visited art museums in the world in 2021."The Art Newspaper", 30 March 2021. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
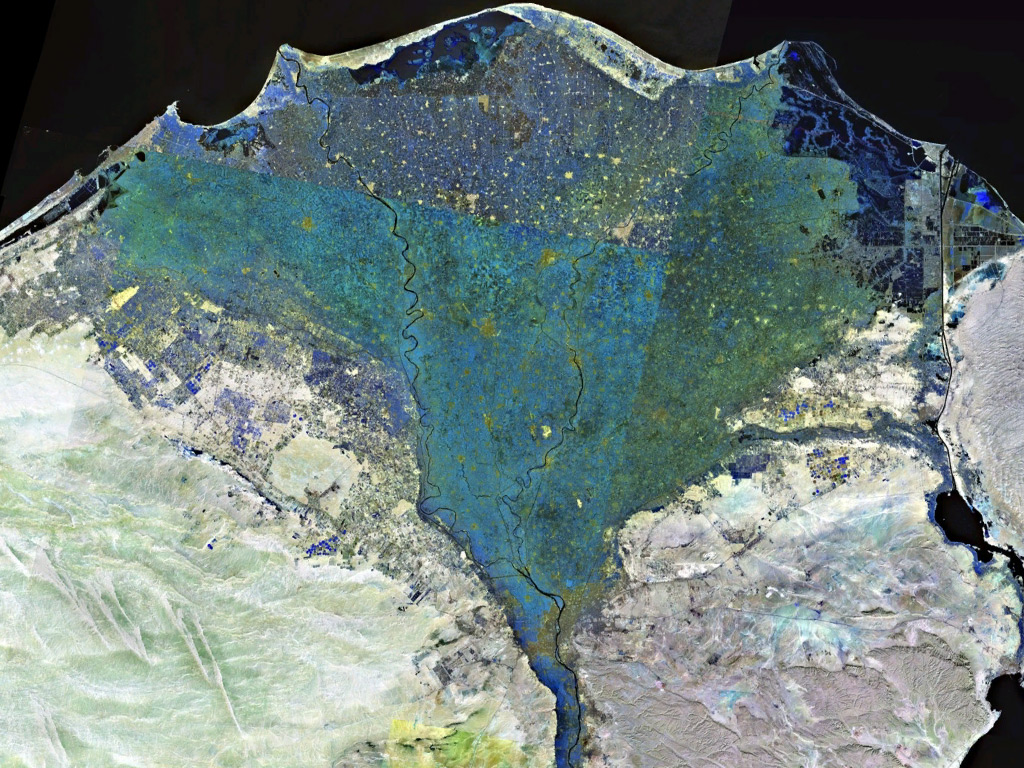
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters the coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sculptures Of Ancient Egypt
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sculptural processes originally used carving (the removal of material) and modelling (the addition of material, as clay), in stone, metal, ceramics, wood and other materials but, since Modernism, there has been an almost complete freedom of materials and process. A wide variety of materials may be worked by removal such as carving, assembled by welding or modelling, or moulded or cast. Sculpture in stone survives far better than works of art in perishable materials, and often represents the majority of the surviving works (other than pottery) from ancient cultures, though conversely traditions of sculpture in wood may have vanished almost entirely. However, most ancient sculpture was brightly painted, and this has been lost. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Antiquities Of The Louvre
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt. Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to: Nations and ethnic groups * Egyptians, a national group in North Africa ** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of recorded history ** Egyptian cuisine, the local culinary traditions of Egypt * Egypt, the modern country in northeastern Africa ** Egyptian Arabic, the language spoken in contemporary Egypt ** A citizen of Egypt; see Demographics of Egypt * Ancient Egypt, a civilization from c. 3200 BC to 343 BC ** Ancient Egyptians, ethnic people of ancient Egypt ** Ancient Egyptian architecture, the architectural structure style ** Ancient Egyptian cuisine, the cuisine of ancient Egypt ** Egyptian language, the oldest known language of Egypt and a branch of the Afroasiatic language family * Copts, the ethnic Egyptian Christian minority ** Coptic language or Coptic Egyptian, the latest stage of the Egyptian language, spoken in Egypt until the 17th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1826 Archaeological Discoveries
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album ''Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonly re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
26th-century BC Works
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphinx Of Memphis
The Sphinx of Memphis is a stone sphinx located near the remains of Memphis, Egypt. The carving was believed to take place between 1700 and 1400 BCE, which was during the 18th Dynasty. It is unknown which pharaoh is being honored and there are no inscriptions to supply information. The facial features imply that the Sphinx is honoring Hatshepsut, or Amenhotep II, or Amenhotep III. Discovery The Alabaster Sphinx was discovered in 1912, when an affiliate from the British School in America spotted a uniquely carved object jutting out of a sand hill. It was so far in the season that excavation was useless, but a year later in 1913 further digging displayed that the object was a Sphinx's tail. Composition The Sphinx of Memphis is also referred to as the Alabaster Sphinx of Memphis, or the Calcite Sphinx. It is the largest calcite statue ever discovered. The minerals alabaster or calcite in the sphinx's names refer to the yellowish white, soft stone it is carved from; arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Egyptian Antiquities Of The Louvre
The Department of Egyptian Antiquities of the Louvre (French: Département des Antiquités égyptiennes du Louvre) is a department of the Louvre that is responsible for artifacts from the Nile civilizations which date from 4,000 BC to the 4th century. The collection, comprising over 50,000 pieces, is among the world's largest, overviews Egyptian life spanning Ancient Egypt, the Middle Kingdom, the New Kingdom, Coptic art, and the Roman, Ptolemaic, and Byzantine periods.Nave, pp.42–43 History The department's origins lie in the royal collection, but it was augmented by Napoleon's 1798 expeditionary trip with Dominique Vivant, the future director of the Louvre.Mignot, pp 76, 77 After Jean-François Champollion translated the Rosetta Stone, Charles X decreed that an Egyptian Antiquities department be created. Champollion advised the purchase of three collections, formed by Edmé-Antoine Durand, Henry Salt and Bernardino Drovet; these additions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cour Carrée
The Cour Carrée (Square Court) is one of the main courtyards of the Louvre Palace in Paris. The wings surrounding it were built gradually, as the walls of the medieval Louvre were progressively demolished in favour of a Renaissance palace. Construction Between 1190 and 1215, Philip Augustus built the Wall of Philip II Augustus around Paris to protect the capital from the English. To reinforce this enclosure on the western side, he built the first incarnation of the Louvre, a large fortress with four high walls protected by a moat, towers, and a dungeon. Under King Charles V of France (1364-1380), with the population of Paris increasing, Paris spread well beyond the Philip Augustus wall. The king built a new enclosure encompassing the new quarters. As the Louvre Castle was now inside the new city walls, it lost much of its military value. The king renovated the castle to make it more comfortable, installing numerous windows, adding chimneys, statues, turrets and gardens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Champollion
Jean-François Champollion (), also known as Champollion ''le jeune'' ('the Younger'; 23 December 17904 March 1832), was a French philologist and orientalist, known primarily as the decipherer of Egyptian hieroglyphs and a founding figure in the field of Egyptology. Partially raised by his brother, the scholar Jacques Joseph Champollion-Figeac, Champollion was a child prodigy in philology, giving his first public paper on the decipherment of Demotic in his mid-teens. As a young man he was renowned in scientific circles, and spoke Coptic, Ancient Greek, Latin, Hebrew and Arabic. During the early 19th century, French culture experienced a period of 'Egyptomania', brought on by Napoleon's discoveries in Egypt during his campaign there (1798–1801) which also brought to light the trilingual Rosetta Stone. Scholars debated the age of Egyptian civilization and the function and nature of hieroglyphic script, which language if any it recorded, and the degree to which the signs were p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |