|
Graph Of Groups
In geometric group theory, a graph of groups is an object consisting of a collection of groups indexed by the vertices and edges of a graph, together with a family of monomorphisms of the edge groups into the vertex groups. There is a unique group, called the fundamental group, canonically associated to each finite connected graph of groups. It admits an orientation-preserving action on a tree: the original graph of groups can be recovered from the quotient graph and the stabilizer subgroups. This theory, commonly referred to as Bass–Serre theory, is due to the work of Hyman Bass and Jean-Pierre Serre. Definition A graph of groups over a graph is an assignment to each vertex of of a group and to each edge of of a group as well as monomorphisms and mapping into the groups assigned to the vertices at its ends. Fundamental group Let be a spanning tree for and define the fundamental group to be the group generated by the vertex groups and elements for each edge of with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such group (mathematics), groups and topology, topological and geometry, geometric properties of spaces on which these groups Group action (mathematics), act (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph (discrete mathematics), graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
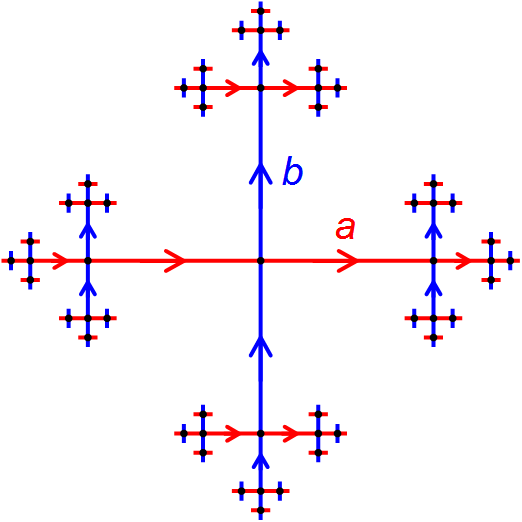
HNN Extension
In mathematics, the HNN extension is an important construction of combinatorial group theory. Introduced in a 1949 paper ''Embedding Theorems for Groups'' by Graham Higman, Bernhard Neumann, and Hanna Neumann, it embeds a given group ''G'' into another group ''G' '', in such a way that two given isomorphic subgroups of ''G'' are conjugate (through a given isomorphism) in ''G' ''. Construction Let ''G'' be a group with presentation G = \langle S \mid R\rangle , and let \alpha\colon H \to K be an isomorphism between two subgroups of ''G''. Let ''t'' be a new symbol not in ''S'', and define :G*_ = \left \langle S,t \mid R, tht^=\alpha(h), \forall h\in H \right \rangle. The group G*_ is called the ''HNN extension of'' ''G'' ''relative to'' α. The original group G is called the ''base group'' for the construction, while the subgroups ''H'' and ''K'' are the ''associated subgroups''. The new generator ''t'' is called the ''stable letter''. Key properties Since the presentation for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The London Mathematical Society
The London Mathematical Society (LMS) is one of the United Kingdom's learned societies for mathematics (the others being the Royal Statistical Society (RSS), the Institute of Mathematics and its Applications (IMA), the Edinburgh Mathematical Society and the Operational Research Society (ORS). History The Society was established on 16 January 1865, the first president being Augustus De Morgan. The earliest meetings were held in University College, but the Society soon moved into Burlington House, Piccadilly. The initial activities of the Society included talks and publication of a journal. The LMS was used as a model for the establishment of the American Mathematical Society in 1888. Mary Cartwright was the first woman to be President of the LMS (in 1961–62). The Society was granted a royal charter in 1965, a century after its foundation. In 1998 the Society moved from rooms in Burlington House into De Morgan House (named after the society's first president), at 57–5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-angled Artin Group
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex'' of the angle. Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles are also formed by the intersection of two planes. These are called dihedral angles. Two intersecting curves may also define an angle, which is the angle of the rays lying tangent to the respective curves at their point of intersection. ''Angle'' is also used to designate the measure of an angle or of a rotation. This measure is the ratio of the length of a circular arc to its radius. In the case of a geometric angle, the arc is centered at the vertex and delimited by the sides. In the case of a rotation, the arc is centered at the center of the rotation and delimited by any other point and its image by the rotation. History and etymology The word ''angle'' comes from the Latin word ''angulus'', meaning "corner"; cognate words are the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Gromov (mathematician)
Mikhael Leonidovich Gromov (also Mikhail Gromov, Michael Gromov or Misha Gromov; russian: link=no, Михаи́л Леони́дович Гро́мов; born 23 December 1943) is a Russian-French mathematician known for his work in geometry, analysis and group theory. He is a permanent member of IHÉS in France and a professor of mathematics at New York University. Gromov has won several prizes, including the Abel Prize in 2009 "for his revolutionary contributions to geometry". Biography Mikhail Gromov was born on 23 December 1943 in Boksitogorsk, Soviet Union. His Russian father Leonid Gromov and his Jewish mother Lea Rabinovitz were pathologists. His mother was the cousin of World Chess Champion Mikhail Botvinnik, as well as of the mathematician Isaak Moiseevich Rabinovich. Gromov was born during World War II, and his mother, who worked as a medical doctor in the Soviet Army, had to leave the front line in order to give birth to him. When Gromov was nine years old, his mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruhat–Tits Building
In mathematics, a building (also Tits building, named after Jacques Tits) is a combinatorial and geometric structure which simultaneously generalizes certain aspects of flag manifolds, finite projective planes, and Riemannian symmetric spaces. Buildings were initially introduced by Jacques Tits as a means to understand the structure of exceptional groups of Lie type. The more specialized theory of Bruhat–Tits buildings (named also after François Bruhat) plays a role in the study of -adic Lie groups analogous to that of the theory of symmetric spaces in the theory of Lie groups. Overview The notion of a building was invented by Jacques Tits as a means of describing simple algebraic groups over an arbitrary field. Tits demonstrated how to every such group one can associate a simplicial complex with an action of , called the spherical building of . The group imposes very strong combinatorial regularity conditions on the complexes that can arise in this fashion. By tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link (geometry)
The link in a simplicial complex is a generalization of the neighborhood of a vertex in a graph. The link of a vertex encodes information about the local structure of the complex at the vertex. Link of a vertex Given an abstract simplicial complex and v a vertex in V(X), its link \operatorname(v,X) is a set containing every face \tau \in X such that v\not\in \tau and \tau\cup \ is a face of . * In the special case in which is a 1-dimensional complex (that is: a graph), \operatorname(v,X) contains all vertices u\neq v such that \ is an edge in the graph; that is, \operatorname(v, X)=\mathcal(v)=the neighborhood of v in the graph. Given a geometric simplicial complex and v\in V(X), its link \operatorname(v,X) is a set containing every face \tau \in X such that v\not\in \tau and there is a simplex in X that has v as a vertex and \tau as a face. Equivalently, the join v \star \tau is a face in X. * As an example, suppose v is the top vertex of the tetrahedron at the left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Graph Theory
This is a glossary of graph theory. Graph theory is the study of graphs, systems of nodes or vertices connected in pairs by lines or edges. Symbols A B C D E F G H I K L M N O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAT(k) Space
In mathematics, a \mathbf(k) space, where k is a real number, is a specific type of metric space. Intuitively, triangles in a \operatorname(k) space are "slimmer" than corresponding "model triangles" in a standard space of constant curvature k. In a \operatorname(k) space, the curvature is bounded from above by k. A notable special case is k=0; complete \operatorname(0) spaces are known as "Hadamard spaces" after the French mathematician Jacques Hadamard. Originally, Aleksandrov called these spaces “\mathfrak_k domain”. The terminology \operatorname(k) was coined by Mikhail Gromov in 1987 and is an acronym for Élie Cartan, Aleksandr Danilovich Aleksandrov and Victor Andreevich Toponogov (although Toponogov never explored curvature bounded above in publications). Definitions For a real number k, let M_k denote the unique complete simply connected surface (real 2-dimensional Riemannian manifold) with constant curvature k. Denote by D_k the diameter of M_k, which is \in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simplicial Complex
In mathematics, a simplicial complex is a set composed of points, line segments, triangles, and their ''n''-dimensional counterparts (see illustration). Simplicial complexes should not be confused with the more abstract notion of a simplicial set appearing in modern simplicial homotopy theory. The purely combinatorial counterpart to a simplicial complex is an abstract simplicial complex. To distinguish a simplicial from an abstract simplicial complex, the former is often called a geometric simplicial complex.'', Section 4.3'' Definitions A simplicial complex \mathcal is a set of simplices that satisfies the following conditions: :1. Every face of a simplex from \mathcal is also in \mathcal. :2. The non-empty intersection of any two simplices \sigma_1, \sigma_2 \in \mathcal is a face of both \sigma_1 and \sigma_2. See also the definition of an abstract simplicial complex, which loosely speaking is a simplicial complex without an associated geometry. A simplicial ''k''-complex \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properly Discontinuous
In mathematics, a group action on a space (mathematics), space is a group homomorphism of a given group (mathematics), group into the group of transformation (geometry), transformations of the space. Similarly, a group action on a mathematical structure is a group homomorphism of a group into the automorphism group of the structure. It is said that the group ''acts'' on the space or structure. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that structure. For example, the group of Euclidean isometry, Euclidean isometries acts on Euclidean space and also on the figures drawn in it. For example, it acts on the set of all triangles. Similarly, the group of symmetries of a polyhedron acts on the vertex (geometry), vertices, the edge (geometry), edges, and the face (geometry), faces of the polyhedron. A group action on a vector space is called a Group representation, representation of the group. In the case of a finite-dimensional vector space, it allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter–Dynkin Diagram
In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram (or Coxeter diagram, Coxeter graph) is a graph with numerically labeled edges (called branches) representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors (or reflecting hyperplanes). It describes a kaleidoscopic construction: each graph "node" represents a mirror (domain facet) and the label attached to a branch encodes the dihedral angle order between two mirrors (on a domain ridge), that is, the amount by which the angle between the reflective planes can be multiplied to get 180 degrees. An unlabeled branch implicitly represents order-3 (60 degrees), and each pair of nodes that is not connected by a branch at all (such as non-adjacent nodes) represents a pair of mirrors at order-2 (90 degrees). Each diagram represents a Coxeter group, and Coxeter groups are classified by their associated diagrams. Dynkin diagrams are closely related objects, which differ from Coxeter diagrams in two respects: firstly, branches labeled "4" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |