|
Gralise
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. It is a first-line medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given gabapentin for diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia have a meaningful benefit. Sleepiness and dizziness are the most common side effects. Serious side effects include an increased risk of suicide, respiratory depression, and allergic reactions. Lower doses are recommended in those with kidney disease. Gabapentin acts by decreasing activity of a subset of calcium channels. Gabapentin was first approved for use in 1993. It has been available as a generic medication in the United States since 2004. In 2020, it was the tenth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 49million prescriptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabapentinoid
Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which block α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs). This site has been referred to as the ''gabapentin receptor'' ( α2δ subunit), as it is the target of the drugs gabapentin and pregabalin. Clinically used gabapentinoids include gabapentin, pregabalin, and mirogabalin, as well as a gabapentin prodrug, gabapentin enacarbil. Additionally, phenibut has been found to act as a gabapentinoid in addition to its action of functioning as a GABAB receptor agonist. Further analogues like imagabalin are in clinical trials but have not yet been approved. Other gabapentinoids which are used in scientific research but have not been approved for medical use include atagabalin, 4-methylpregabalin and PD-217,014. Medical uses Gabapentinoids are approved for the treatment of epilepsy, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs may block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to the voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GAT-1 GABA transporter, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gated calcium channels, SV2A, and α2δ. By blocking sodium or ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nortriptyline
Nortriptyline, sold under the brand name Pamelor, among others, is a medication used to treat depression. This medicine is used for: neuropathic pain, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), smoking cessation and anxiety. As with many antidepressants, its use for young people with depression and other psychiatric disorders may be limited due to increased suicidality in the 18-24 population initiating treatment. Nortriptyline is a less preferred treatment for ADHD and stopping smoking. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurry vision, sleepiness, low blood pressure with standing, and weakness. Serious side effects may include seizures, an increased risk of suicide in those less than 25 years of age, urinary retention, glaucoma, mania, and a number of heart issues. Nortriptyline may cause problems if taken during pregnancy. Use during breastfeeding appears to be relatively safe. It is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) and is believed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pain
Central pain syndrome is a neurological condition consisting of constant, moderate to severe pain due to damage to the central nervous system (CNS) which causes a sensitization of the pain system. The extent of pain and the areas affected are related to the cause of the injury. Signs and symptoms Pain can either be relegated to a specific part of the body or spread to the entire body. It is typically constant, and may be moderate to severe in intensity. Those who are afflicted describe it as being stuck in a loop of pain. It is often made worse by touch, movement, emotions, barometric pressure and temperature changes, usually cold temperatures along with many other similar 'triggers'. Cold temperatures regularly make the burning pain worse in certain body parts. Burning pain is the most common sensation, but patients also report pins and needles, pressing, lacerating, aching, and extreme bursts or constant sharp or unremitting excruciating pain. Individuals may have reduced sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, or trifacial neuralgia is a long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is a form of neuropathic pain. There are two main types: typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The typical form results in episodes of severe, sudden, shock-like pain in one side of the face that lasts for seconds to a few minutes. Groups of these episodes can occur over a few hours. The atypical form results in a constant burning pain that is less severe. Episodes may be triggered by any touch to the face. Both forms may occur in the same person. It is regarded as one of the most painful disorders known to medicine, and often results in depression. The exact cause is unknown, but believed to involve loss of the myelin of the trigeminal nerve. This might occur due to compression from a blood vessel as the nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Epilepsy
Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain (which can be seen, for example, on electroencephalography, EEG). Generalized seizure occurs due to abnormalities in both hemispheres. Generalized epilepsy is ''primary'' because the epilepsy is the originally diagnosed condition itself, as opposed to ''secondary'' epilepsy, which occurs as a symptom of a diagnosed condition. Generalized seizures happened when there were abnormal activities in both hemispheres at the same time. Almost all areas of the brain are affected by electrical impulses. Manifestation Generalized seizures can be either absence seizures, myoclonic seizures, clonic seizures, tonic-clonic seizures or atonic seizures. Generalized seizures occur in various seizure syndromes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Seizures
Focal seizures (also called partial seizures and localized seizures) are seizures which affect initially only one hemisphere of the brain. The brain is divided into two hemispheres, each consisting of four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. A focal seizure is generated in and affects just one part of the brain – a whole hemisphere or part of a lobe. Symptoms will vary according to where the seizure occurs. When seizures occur in the frontal lobe the patient may experience a wave-like sensation in the head. When seizures occur in the temporal lobe, a feeling of déjà vu may be experienced. When seizures are localized to the parietal lobe, a numbness or tingling may occur. With seizures occurring in the occipital lobe, visual disturbances or hallucinations have been reported. , Epilepsy S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
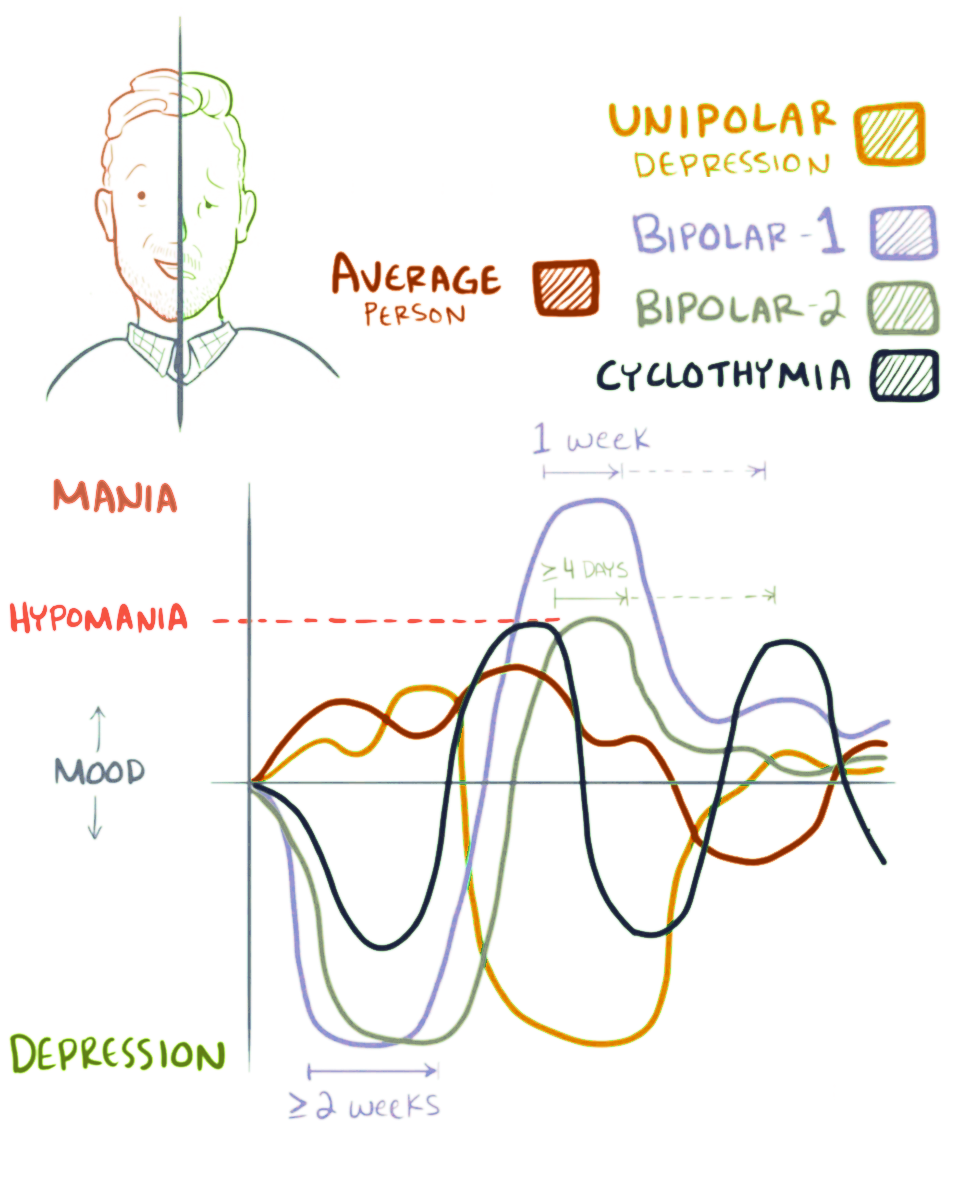
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physical and cognitive symptoms, such as restlessness, irritability, easy fatiguability, difficulty concentrating, increased heart rate, chest pain, abdominal pain, and a variety of other symptoms that may vary based on the individual. In casual discourse, the words ''anxiety'' and ''fear'' are often used interchangeably. In clinical usage, they have distinct meanings: anxiety is defined as an unpleasant emotional state for which the cause is either not readily identified or perceived to be uncontrollable or unavoidable, whereas fear is an emotional and physiological response to a recognized external threat. The umbrella term ''anxiety disorder'' refers to a number of specific disorders that include fears (phobias) or anxiety symptoms. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Seizure
Focal seizures (also called partial seizures and localized seizures) are seizures which affect initially only one hemisphere of the brain. The brain is divided into two hemispheres, each consisting of four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. A focal seizure is generated in and affects just one part of the brain – a whole hemisphere or part of a lobe. Symptoms will vary according to where the seizure occurs. When seizures occur in the frontal lobe the patient may experience a wave-like sensation in the head. When seizures occur in the temporal lobe, a feeling of déjà vu may be experienced. When seizures are localized to the parietal lobe, a numbness or tingling may occur. With seizures occurring in the occipital lobe, visual disturbances or hallucinations have been reported. , Epilepsy S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)