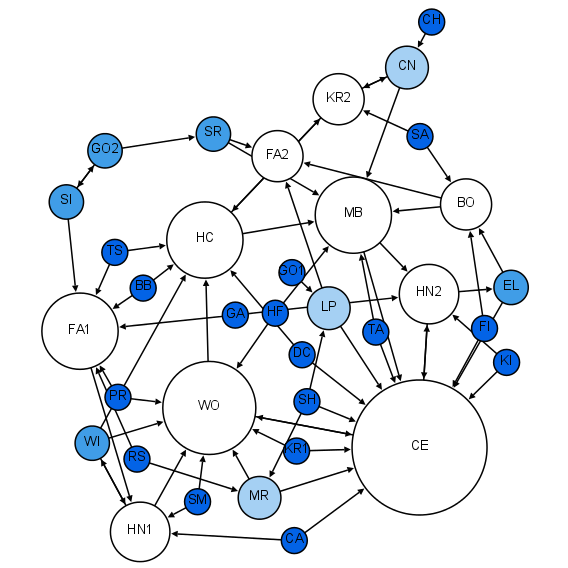
|
Gradient Network
In network science, a gradient network is a directed subnetwork of an undirected "substrate" computer network, network where each node (networking), node has an associated scalar potential and one out-link that points to the node with the smallest (or largest) potential in its neighborhood, defined as the union of itself and its Neighbourhood (graph theory), neighbors on the substrate network. Definition Transport takes place on a fixed network G = G(V,E) called the substrate graph. It has ''N'' nodes, V = \ and the set of edges E = \ . Given a node ''i'', we can define its set of neighbors in G by Si(1) = . Let us also consider a scalar field, ''h'' = defined on the set of nodes V, so that every node i has a scalar value ''h''''i'' associated to it. Gradient ∇''h''''i'' on a network: ∇h''i= (i, μ(i))'' i.e. the directed edge from ''i'' to ''μ(i)'', where ''μ''(''i'') ∈ Si(1) ∪ , and hμ has the maximum value in . ''Gradient network'' : ''∇G = ∇G (V, F) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, Cognitive network, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential statistics, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Degree Distributions Of Gradient Network And Substrate (BA Model)
Degree may refer to: As a unit of measurement * Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement ** Degree of geographical latitude ** Degree of geographical longitude * Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics * Degree (temperature), any of various units of temperature measurement * Degree API, a measure of density in the petroleum industry * Degree Baumé, a pair of density scales * Degree Brix, a measure of sugar concentration * Degree Gay-Lussac, a measure of the alcohol content of a liquid by volume, ranging from 0° to 100° * Degree proof, or simply proof, the alcohol content of a liquid, ranging from 0° to 175° in the UK, and from 0° to 200° in the U.S. * Degree of curvature, a unit of curvature measurement, used in civil engineering * Degrees of freedom (mechanics), the number of displacements or rotations needed to define the position and orientation of a body * Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry), a concept describing depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements (Data link, links, Node (networking), nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial Fieldbus, fieldbusses and computer networks. Network topology is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. It is an application of graph theory wherein communicating devices are modeled as nodes and the connections between the devices are modeled as links or lines between the nodes. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network (e.g., device location and cable installation), while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two different networks, yet their logical topologies may be identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Dynamics
Network dynamics is a research field for the study of networks whose status changes in time. The dynamics may refer to the structure of connections of the units of a network, to the collective internal state of the network, or both. The networked systems could be from the fields of biology, chemistry, physics, sociology, economics, computer science, etc. Networked systems are typically characterized as complex systems consisting of many units coupled by specific, potentially changing, interaction topologies. For a dynamical systems In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a Function (mathematics), function describes the time dependence of a Point (geometry), point in an ambient space, such as in a parametric curve. Examples include the mathematical models ...' approach to discrete network dynamics, see sequential dynamical system. See also References Networks {{combin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comparison Between Enhanced And Normal Approaches (packet-processing Capability)
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when decidin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Average Packet Number As A Function Of Degree (congestion Graph)
In ordinary language, an average is a single number or value that best represents a set of data. The type of average taken as most typically representative of a list of numbers is the arithmetic mean the sum of the numbers divided by how many numbers are in the list. For example, the mean or average of the numbers 2, 3, 4, 7, and 9 (summing to 25) is 5. Depending on the context, the most representative statistic to be taken as the average might be another measure of central tendency, such as the mid-range, median, mode or geometric mean. For example, the average personal income is often given as the median the number below which are 50% of personal incomes and above which are 50% of personal incomes because the mean would be higher by including personal incomes from a few billionaires. General properties If all numbers in a list are the same number, then their average is also equal to this number. This property is shared by each of the many types of average. Another universal pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Congestion Coefficient For Random Graphs And Scale-free Networks
Congestion may refer to: Medicine *Excessive fluid in tissues, vessels, or both, including: ** Edema, abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitium, manifesting as swelling *** Peripheral edema, edema in peripheral body parts such as limbs and feet *** Pulmonary edema, edema in the lungs that impairs breathing ** Congestive heart failure, heart failure resulting in congestion in one or more organs ** Nasal congestion, the blockage of nasal passages due to swollen membranes ** Prostatic congestion, a medical condition that happens when the prostate becomes swollen by excess fluid Other uses * Network congestion, reduced quality of service when a network is carrying more data than it can handle * Traffic congestion, vehicles clogging streets and highways * Congestion pricing Congestion pricing or congestion charges is a system of surcharging users of public goods that are subject to congestion through excess demand, such as through higher peak charges for use of bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scale-free Network
A scale-free network is a network whose degree distribution follows a power law, at least asymptotically. That is, the fraction ''P''(''k'') of nodes in the network having ''k'' connections to other nodes goes for large values of ''k'' as : P(k) \ \sim \ k^\boldsymbol where \gamma is a parameter whose value is typically in the range 2<\gamma<3 (wherein the second moment ( scale parameter) of is infinite but the first moment is finite), although occasionally it may lie outside these bounds. The name "scale-free" could be explained by the fact that some moments of the degree distribution are not defined, so that the network does not have a characteristic scale or "size". and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Star Network Vs Ring Network
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its total mass mainly determines its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Congestion
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of congestion is that an incremental increase in offered load leads either only to a small increase or even a decrease in network throughput. Network protocols that use aggressive retransmissions to compensate for packet loss due to congestion can increase congestion, even after the initial load has been reduced to a level that would not normally have induced network congestion. Such networks exhibit two stable states under the same level of load. The stable state with low throughput is known as congestive collapse. Networks use congestion control and congestion avoidance techniques to try to avoid collapse. These include: exponential backoff in protocols such as CSMA/CA in 802.11 and the similar CSMA/C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Barabási–Albert Model
The Barabási–Albert (BA) model is an algorithm for generating random scale-free network, scale-free complex network, networks using a preferential attachment mechanism. Several natural and human-made systems, including the Internet, the World Wide Web, citation analysis, citation networks, and some social networks are thought to be approximately scale-free and certainly contain few nodes (called hubs) with unusually high degree as compared to the other nodes of the network. The BA model tries to explain the existence of such nodes in real networks. The algorithm is named for its inventors Albert-László Barabási and Réka Albert. Concepts Many observed networks (at least approximately) fall into the class of scale-free networks, meaning that they have power law, power-law (or scale-free) degree distributions, while random graph models such as the Erdős–Rényi model, Erdős–Rényi (ER) model and the Watts and Strogatz model, Watts–Strogatz (WS) model do not exhibit po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Erdős–Rényi Model
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Erdős–Rényi model refers to one of two closely related models for generating random graphs or the evolution of a random network. These models are named after Hungarians, Hungarian mathematicians Paul Erdős and Alfréd Rényi, who introduced one of the models in 1959. Edgar Gilbert introduced the other model contemporaneously with and independently of Erdős and Rényi. In the model of Erdős and Rényi, all graphs on a fixed vertex set with a fixed number of edges are equally likely. In the model introduced by Gilbert, also called the Erdős–Rényi–Gilbert model, each edge has a fixed probability of being present or absent, statistical independence, independently of the other edges. These models can be used in the probabilistic method to prove the existence of graphs satisfying various properties, or to provide a rigorous definition of what it means for a property to hold for almost all graphs. Definition There are two clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |