|
Graded Potential
Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary in size, as opposed to being all-or-none. They include diverse potentials such as receptor potentials, electrotonic potentials, subthreshold membrane potential oscillations, slow-wave potential, pacemaker potentials, and synaptic potentials, which scale with the magnitude of the stimulus. They arise from the summation of the individual actions of ligand-gated ion channel proteins, and decrease over time and space. They do not typically involve voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels.. "Chapter 6. Ligand-gated channels of fast chemical synapses." These impulses are incremental and may be excitatory or inhibitory. They occur at the postsynaptic dendrite in response to presynaptic neuron firing and release of neurotransmitter, or may occur in skeletal, smooth, or cardiac muscle in response to nerve input. The magnitude of a graded potential is determined by the strength of the stimulus. EPSPs Graded potentials that mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1223 Graded Potentials-02
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential.Purves et al. Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Incorporated; 2008. IPSP were first investigated in motorneurons by David P. C. Lloyd, John Eccles and Rodolfo Llinás in the 1950s and 1960s. The opposite of an inhibitory postsynaptic potential is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), which is a synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron ''more'' likely to generate an action potential. IPSPs can take place at all chemical synapses, which use the secretion of neurotransmitters to create cell to cell signalling. Inhibitory presynaptic neurons release neurotransmitters that then bind to the postsynaptic receptors; this induces a change in the permeability of the postsynaptic neuronal membrane to particular ions. An electric current that changes the postsynaptic membrane potential to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
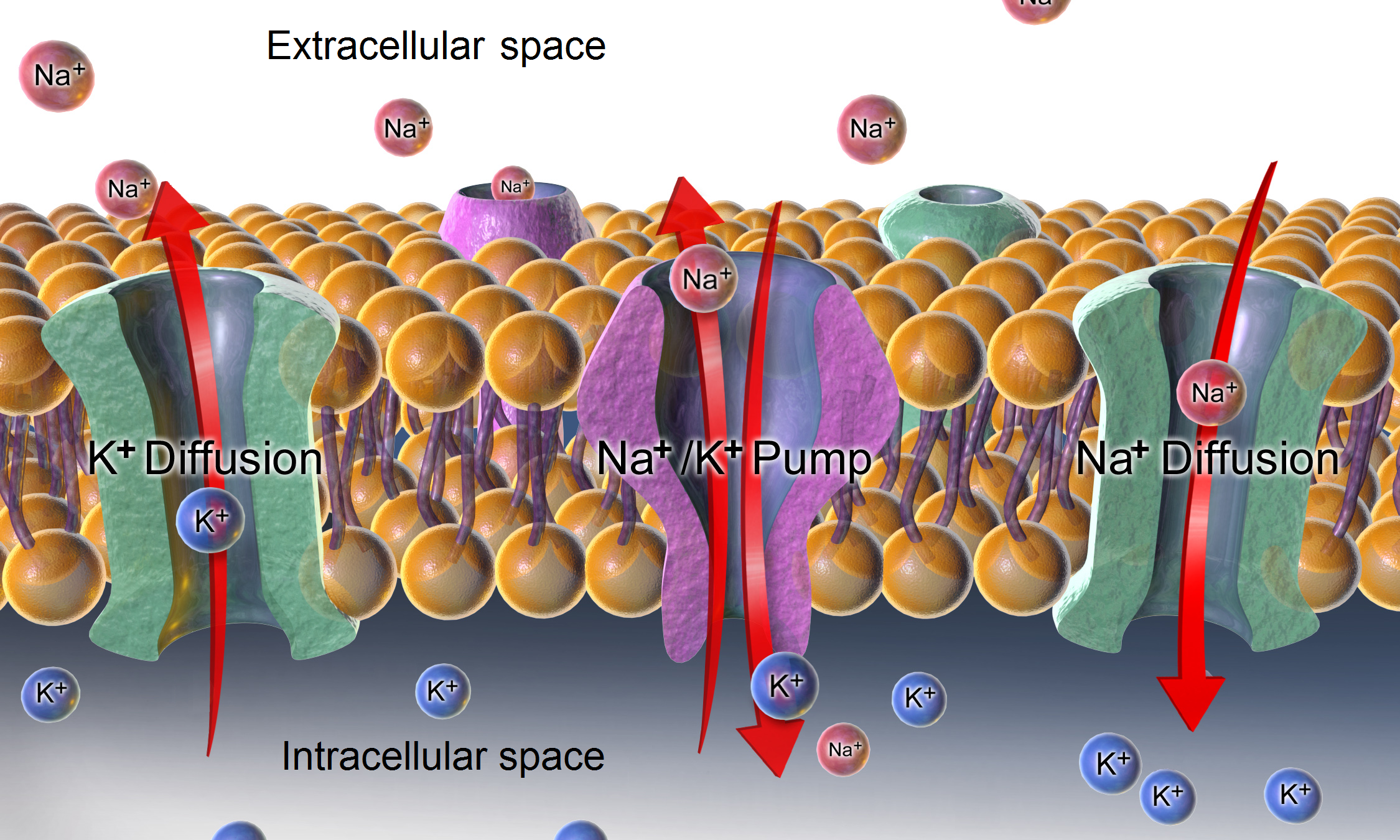
Resting Membrane Potential
A relatively static membrane potential which is usually referred to as the ground value for trans-membrane voltage. The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Vesicle
In a neuron, synaptic vesicles (or neurotransmitter vesicles) store various neurotransmitters that are released at the synapse. The release is regulated by a voltage-dependent calcium channel. Vesicles are essential for propagating nerve impulses between neurons and are constantly recreated by the cell. The area in the axon that holds groups of vesicles is an axon terminal or "terminal bouton". Up to 130 vesicles can be released per bouton over a ten-minute period of stimulation at 0.2 Hz. In the visual cortex of the human brain, synaptic vesicles have an average diameter of 39.5 nanometers (nm) with a standard deviation of 5.1 nm. Structure Synaptic vesicles are relatively simple because only a limited number of proteins fit into a sphere of 40 nm diameter. Purified vesicles have a protein:phospholipid ratio of 1:3 with a lipid composition of 40% phosphatidylcholine, 32% phosphatidylethanolamine, 12% phosphatidylserine, 5% phosphatidylinositol, and 10% chole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocytosis
Exocytosis () is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (e.g., neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell ('' exo-'' + ''cytosis''). As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. In exocytosis, membrane-bound secretory vesicles are carried to the cell membrane, where they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Calcium Channel
Voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), also known as voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs), are a group of voltage-gated ion channels found in the membrane of excitable cells (''e.g.'', muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the calcium ion Ca2+. These channels are slightly permeable to sodium ions, so they are also called Ca2+-Na+ channels, but their permeability to calcium is about 1000-fold greater than to sodium under normal physiological conditions. At physiologic or resting membrane potential, VGCCs are normally closed. They are activated (''i.e.'': opened) at depolarized membrane potentials and this is the source of the "voltage-gated" epithet. The concentration of calcium (Ca2+ ions) is normally several thousand times higher outside the cell than inside. Activation of particular VGCCs allows a Ca2+ influx into the cell, which, depending on the cell type, results in activation of calcium-sensitive potassium channels, muscular contraction, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon Terminal
Axon terminals (also called synaptic boutons, terminal boutons, or end-feet) are distal terminations of the telodendria (branches) of an axon. An axon, also called a nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses called action potentials away from the neuron's cell body, or soma, in order to transmit those impulses to other neurons, muscle cells or glands. Neurons are interconnected in complex arrangements, and use electrochemical signals and neurotransmitter chemicals to transmit impulses from one neuron to the next; axon terminals are separated from neighboring neurons by a small gap called a synapse, across which impulses are sent. The axon terminal, and the neuron from which it comes, is sometimes referred to as the "presynaptic" neuron. Nerve impulse release Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles that cluster beneath the axon terminal membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse. The axonal terminals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Potential
In electrophysiology, the threshold potential is the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential. In neuroscience, threshold potentials are necessary to regulate and propagate signaling in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Most often, the threshold potential is a membrane potential value between –50 and –55 mV, but can vary based upon several factors. A neuron's resting membrane potential (–70 mV) can be altered to either increase or decrease likelihood of reaching threshold via sodium and potassium ions. An influx of sodium into the cell through open, voltage-gated sodium channels can depolarize the membrane past threshold and thus excite it while an efflux of potassium or influx of chloride can hyperpolarize the cell and thus inhibit threshold from being reached. Discovery Initial experiments revolved around the concept that any electrical change that is brought about in neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming positively char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of ''negative'' ions into the cell or positive ions ''out'' of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC). EPSPs, like IPSPs, are graded (i.e. they have an additive effect). When multiple EPSPs occur on a single patch of postsynaptic membrane, their combined effect is the sum of the individual EPSPs. Larger EPSPs result in greater membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exception of the optic nerve (cranial nerve II), along with the retina. The second cranial nerve is not a true peripheral nerve but a tract of the diencephalon. Cranial nerve ganglia, as with all ganglia, are part of the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |