|
Gotha Go 244
The Gotha Go 244 was a transport aircraft used by the ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II. Development The Go 244 was the powered version of the Gotha Go 242 military glider transport. Studies for powered versions of the Go 242 began early in the design of the glider, with one early proposal being for modification to allow a single Argus As 10C engine to be temporarily attached to the nose of the glider to allow recovery back to base after use. This idea was rejected, but the alternative of a permanently powered twin-engined version was taken forward.''Air International'' December 1989, p. 291. Three Go 242s were modified as prototypes of the powered Go 244, fitted with varying surplus radial engines. The first prototype, the Go 244 V1 was powered by two 660 hp (492 kW) BMW 132, while the second prototype had 700 hp (522 kW) Gnome-Rhône 14Ms — and the third 750 hp (560 kW) Shvetsov M-25 A engines, with this model of Aviadvigatel, Shvetsov OKB engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothaer Waggonfabrik
''Gothaer Waggonfabrik'' (''Gotha'', GWF) was a German manufacturer of rolling stock established in the late nineteenth century at Gotha. During the two world wars, the company expanded into aircraft building. World War I In World War I, Gotha was the manufacturer of a highly successful series of bombers based on a 1914 design by Oskar Ursinus, but heavily reimagined by Hans Burkhard. From 1917, the Burkhard-designed twin pusher biplane bomber aircraft were capable of carrying out strategic bombing missions over England, the first heavier-than-air aircraft used in this role. Several dozen of these bombers were built in a number of subtypes - the Ursinus-based Gotha G.I, and the succeeding Burkhard-designed G.II, G.III, G.IV, and G.V. This last variant was the most prolific, with thirty-six in squadron service at one point. Inter war years Whilst Germany was prohibited from military aircraft manufacture by the Treaty of Versailles, Gotha returned to its railway endeavou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha Aircraft
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the end of monarchy in Germany in 1918. The House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha originating here spawned many European rulers, including the royal houses of the United Kingdom, Belgium, Portugal (until 1910) and Bulgaria (until 1946). In the Middle Ages, Gotha was a rich trading town on the trade route ''Via Regia'' and between 1650 and 1850, Gotha saw a cultural heyday as a centre of sciences and arts, fostered by the dukes of Saxe-Gotha. The first duke, Ernest the Pious, was famous for his wise rule. In the 18th century, the ''Almanach de Gotha'' was first published in the city. The publisher Justus Perthes and the encyclopedist Joseph Meyer made Gotha a leading centre of German publishing around 1800. In the early 19th century, Gotha was a bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940s German Military Transport Aircraft
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus and Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar become Roman Consuls. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 100 days ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air International
''AIR International'' is a British aviation magazine covering current defence aerospace and civil aviation topics. It has been in publication since 1971 and is currently published by Key Publishing Ltd. History and profile The magazine was first published in June 1971 with the name ''Air Enthusiast''. In January 1974 its title was changed to ''Air Enthusiast International'' and finally to ''Air International'' in July 1974. ''Air International'' is published by Key Publishing Limited. The magazine has its headquarters in Stamford, Lincolnshire. Sister publications include ''Air Forces Monthly'', '' Airliner World'', ''Airports International'' and ''FlyPast A flypast is a ceremonial or honorific flight by an aircraft or group of aircraft. The term flypast is used in the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth. In the United States, the terms flyover and flyby are used. Flypasts are often tied in w ...''. References External links List of Air International issues with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Military Aircraft Of Germany
This list of military aircraft of Germany includes prototype, pre-production, and operational types. No distinction is drawn here between different services until 1991. In 1990, the various air arms of the former German Democratic Republic were absorbed by their counterparts in the Federal Republic of Germany. Some types that had been operated by the GDR were no longer in service by then, and these are so noted. Before 1919 * Albatros D.II * Albatros D.III * Albatros D.V * Albatros D.Va * Daimler L.6 * Fokker D.I * Fokker D.II * Fokker D.III * Fokker D.IV * Fokker D.V * Fokker D.VI * Fokker D.VII * Fokker D.VIIF * Fokker D.VIII * Fokker Dr.I * Fokker E.I * Fokker E.III * Fokker E.IV * Fokker E.V * Halberstadt D.I * Halberstadt D.II * Halberstadt D.III * Halberstadt D.V * Junkers D.I * Kondor D.VI * Kondor E.III * Naglo D.II * Pfalz D.III * Pfalz D.IIIa * Pfalz D.VIII * Pfalz D.XII * Pfalz D.XV * Pfalz Dr.I * Pfalz E.I * Pfalz E.II * Roland D.I * Roland D. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World War II Military Aircraft Of Germany
This list covers aircraft of the German Luftwaffe during the Second World War from 1939 to 1945. Numerical designations are largely within the RLM designation system. The Luftwaffe officially existed from 1933–1945 but training had started in the 1920s, before the Nazi seizure of power, and many aircraft made in the inter-war years were used during World War II. The main list highlights the most significant aircraft that participated and includes minor types. Pre-war aircraft not used after 1938 are excluded, as are projects and aircraft that did not fly. Listed roles are those for which the aircraft were being used during the war – many obsolete pre-war combat aircraft remained in use as trainers rather than in their original more familiar roles. Captured or acquired aircraft are listed separately as many were used only for evaluation while those available in large enough numbers were commonly used as trainers, while a small number were usen the Reich Aviation Ministry's list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild C-82 Packet
The C-82 Packet is a twin-engine, twin-boom cargo aircraft designed and built by Fairchild Aircraft. It was used briefly by the United States Army Air Forces and the successor United States Air Force following World War II. Design and development Developed by Fairchild, the C-82 was intended as a heavy-lift cargo aircraft to succeed prewar civilian designs like the Curtiss C-46 Commando and Douglas C-47 Dakota using non-critical materials in its construction, primarily plywood and steel, so as not to compete with the production of combat aircraft. However, by early 1943 changes in specifications resulted in plans for an all-metal aircraft. The aircraft was designed for a number of roles, including cargo carrier, troop transport, parachute drop, medical evacuation, and glider towing. It featured a rear-loading ramp with wide doors and an empennage set 14 feet (4.3 m) off the ground that permitted trucks and trailers to back up to the doors without obstruction. The single p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
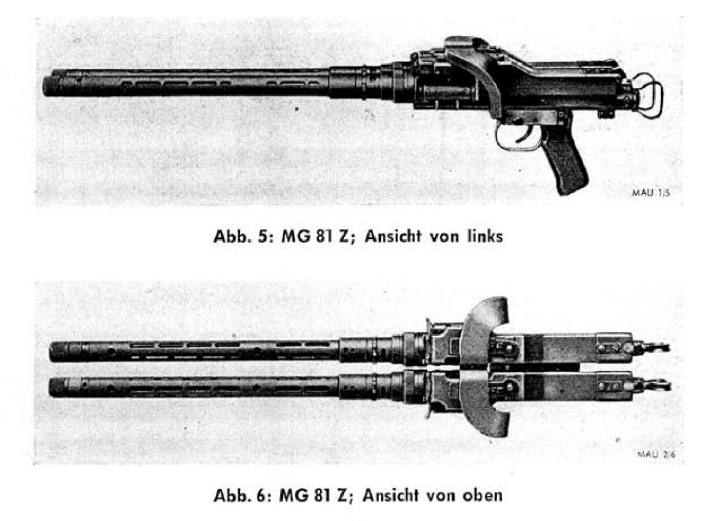
MG 81 Machine Gun
The MG 81 was a German belt fed 7.92×57mm Mauser machine gun which was used in flexible installations in World War II Luftwaffe aircraft, in which capacity it replaced the older drum magazine-fed MG 15. The MG 81 was developed by Mauser as a derivative of their successful MG 34 general-purpose machine gun. Development focus was to reduce production cost and time and to optimize the machine gun for use in aircraft. Developed in 1938/1939, it was in production from 1940 to 1945. A special twin-mount MG 81Z (the Z suffix stands for ''Zwilling'', meaning "twin") was introduced in 1942. It paired up two of the weapons on one mount to provide even more firepower with a maximum cyclic rate of fire of 3,200 rounds per minute without requiring much more space than a standard machine gun. Towards the end of the war many specimens were delivered to the army and equipped for use in ground battles with shoulder rest and bipod. Applications The MG 81Z was found in many unique installations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MG 15 Machine Gun
The MG 15 was a German 7.92 mm machine gun designed specifically as a hand-manipulated defensive gun for combat aircraft during the early 1930s. By 1941 it was replaced by other types and found new uses with ground troops. History The MG 15 was developed from the MG 30, which was designed by Rheinmetall using the locking system invented by Louis Stange in the mid to late 1920s. Though it shares the MG 15 designation with the earlier gun built by Bergmann, the MG 15nA (for ''neuer Art'', meaning new model having been modified from an earlier design) has nothing in common with the World War II gun except the model number. The World War I gun used a tipping lock system while the WWII aircraft gun uses a rotating bolt/lockring. The World War II MG 15 was used in nearly all Luftwaffe aircraft with a flexible-mount defensive position. It was a modular design with various attachments that could be quickly attached or removed. The bolt mechanism acted as a traditional open-bolt ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |