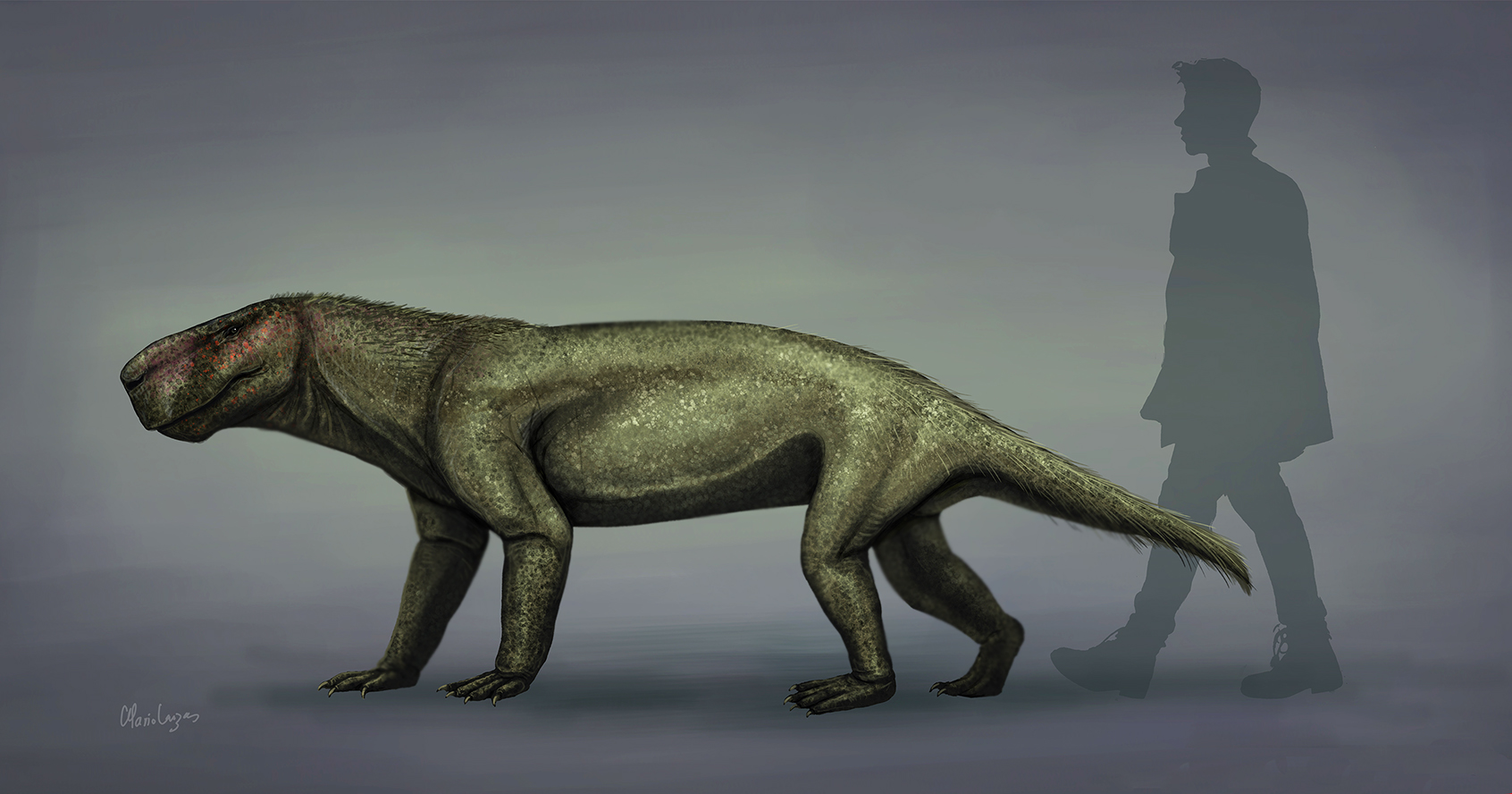|
Gorgonops
''Gorgonops'' (from el, Γοργών 'Gorgon' and 'eye, face', literally 'Gorgon eye' or 'Gorgon face') is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids, of which it is the type genus, having lived during the Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), about 260–254 million years ago in what is now South Africa. Despite its popularity, ''Gorgonops'' is a medium-sized gorgonopsian (about long maximum), regularly confused by the general public with the more massive '' Inostrancevia'', known from Russia, due to their similar appearance and the various media that tend to refer them by the name of the group they belong rather than by their genus names, which does not help in differentiation. History of discovery The holotype of the type species, ''Gorgonops torvus'', was in 1876 one of the first therapsids described, by Richard Owen, who also coined the name "Dinosauria" on the basis of the first known dinosaur fossils. It was also used as the type for which Richard Lydekker described the famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonops Torvus1DB
''Gorgonops'' (from el, Γοργών 'Gorgon' and 'eye, face', literally 'Gorgon eye' or 'Gorgon face') is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids, of which it is the type genus, having lived during the Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), about 260–254 million years ago in what is now South Africa. Despite its popularity, ''Gorgonops'' is a medium-sized gorgonopsian (about long maximum), regularly confused by the general public with the more massive ''Inostrancevia'', known from Russia, due to their similar appearance and the various media that tend to refer them by the name of the group they belong rather than by their genus names, which does not help in differentiation. History of discovery The holotype of the type species, ''Gorgonops torvus'', was in 1876 one of the first therapsids described, by Richard Owen, who also coined the name "Dinosauria" on the basis of the first known dinosaur fossils. It was also used as the type for which Richard Lydekker described the fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
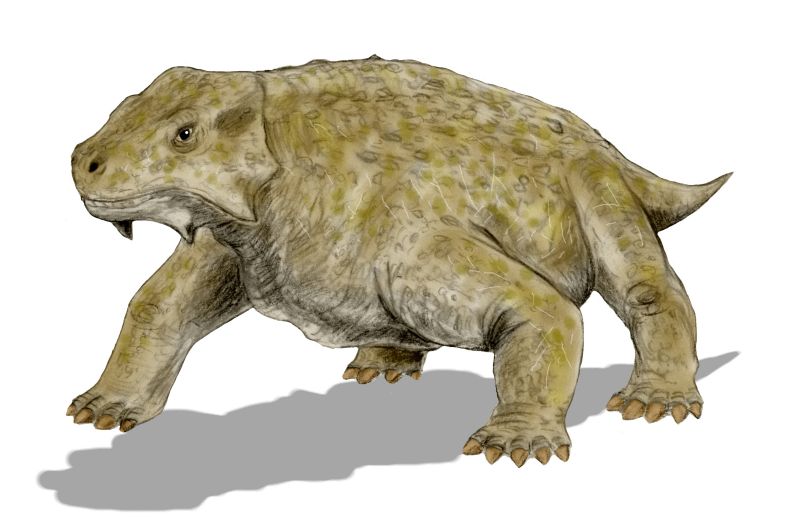
Gorgonops BW
''Gorgonops'' (from el, Γοργών 'Gorgon' and 'eye, face', literally 'Gorgon eye' or 'Gorgon face') is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids, of which it is the type genus, having lived during the Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), about 260–254 million years ago in what is now South Africa. Despite its popularity, ''Gorgonops'' is a medium-sized gorgonopsian (about long maximum), regularly confused by the general public with the more massive ''Inostrancevia'', known from Russia, due to their similar appearance and the various media that tend to refer them by the name of the group they belong rather than by their genus names, which does not help in differentiation. History of discovery The holotype of the type species, ''Gorgonops torvus'', was in 1876 one of the first therapsids described, by Richard Owen, who also coined the name "Dinosauria" on the basis of the first known dinosaur fossils. It was also used as the type for which Richard Lydekker described the fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inostrancevia
''Inostrancevia'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous therapsids, containing the largest members of gorgonopsians, predators characterized by long, saber-tooth-like canines. The various species inhabited European Russia during the Upper Tatarian (Vyatskian), a Russian regional stage equivalent to the Wuchiapingian and Changhsingian stage of the Late Permian period, dating from approximately 259 to 252.3 million years ago. The genus name was described posthumously, after the Bolshevik Revolution, by the Russian paleontologist Vladimir P. Amalitsky in 1922, in honor of geologist Aleksandr Inostrantsev. The first fossils attributed to ''I. alexandri'' are found in Arkhangelsk Oblast, near the Northern Dvina at the end of the 19th century, making it the first gorgonopsian known from Russia, the only place outside Africa where they are officially recognized. Some fossils of the species in question are among the most complete remains of gorgonopsians ever identified to date, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuchiapingian
In the geologic timescale, the Wuchiapingian or Wujiapingian (from in the Liangshan area of Hanzhong, Shaanxi Province) is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the lower or earlier of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Wuchiapingian spans the time between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Capitanian and followed by the Changhsingian. Regional stages with which the Wuchiapingian is coeval or overlaps include the Djulfian or Dzhulfian, Longtanian, Rustlerian, Saladoan, and Castilian. Stratigraphic definitions The Wuchiapingian was first used in 1962, when the Lopingian Series of southwestern China was divided in the Changhsingian and Wuchiapingian Formations. In 1973 the Wuchiapingian was first used as a chronostratigraphic unit (i.e. a stage, as opposed to a formation, which is a lithostratigraphic unit). The base of the Wuchiapingian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record where the conodont species ''Clarkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. Therapsids evolved from " pelycosaurs", specifically within the Sphenacodontia, more than 279.5 million years ago. They replaced the "pelycosaurs" as the dominant large land animals in the Middle Permian through to the Early Triassic. In the aftermath of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, therapsids declined in relative importance to the rapidly diversifying reptiles during the Middle Triassic. The therapsids include the cynodonts, the group that gave rise to mammals (Mammaliaformes) in the Late Triassic, around 225 million years ago. Of the non-mammalian therapsids, only cynodonts survived beyond the end of the Triassic, with the only oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone
The ''Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the lower Teekloof Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching approximately , occur from east of Sutherland through to Beaufort West and Victoria West, to areas south of Graaff-Reinet. Its northernmost exposures occur west/north-west of Colesberg. The '' Tropidostoma'' Assemblage Zone is the fourth biozone of the Beaufort Group. The name of the biozone refers to '' Tropidostoma microtrema'', a herbivorous dicynodont therapsid. This biozone is characterized by the presence of this species in association with another dicynodont species, '' Endothiodon uniseries''. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the current eight biozones were discovered by Andrew Geddes Bain in 1856. However, it was not until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone found in the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a majorly fossiliferous and geologically important geological group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops located in the Teekloof Formation north-west of Beaufort West in the Western Cape, in the upper Middleton and lower Balfour Formations respectively from Colesberg of the Northern Cape to east of Graaff-Reinet in the Eastern Cape. The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Late Permian in age. The name of the biozone refers to ''Cistecephalus'', a small, burrowing dicynodont therapsid. It is characterized by the presence of this species, known especially from the upper sections of this biozone, and the first appearance of the dicynodont ''Aulacephalodon''. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaur
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species '' Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurus
''Pareiasaurus'' is an extinct genus of pareiasauromorph reptile from the Permian period. It was a typical member of its family, the pareiasaurids, which take their name from this genus. Fossils have been found in the Beaufort Group. Description ''Pareiasaurus'' is a large quadruped, about long, with elephantine legs, walking in a typically reptilian posture. The skull is broad and the snout short. Its skull had several spine- and wart-like protrusions. ''Pareiasauruss leaf-shaped teeth, ideal for biting through tough plant fibers, indicate it was a herbivore. Even the palate The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separ ... had teeth. Species ''P. nasicornis'' (Haughton and Boonstra, 1929) is from the ''Tropidostoma'' Zone, Karoo basin, South Africa. This early form is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Classification
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. Among other things, a taxonomy can be used to organize and index knowledge (stored as documents, articles, videos, etc.), such as in the form of a library classification system, or a search engine taxonomy, so that users can more easily find the information they are searching for. Many taxonomies are hierarchies (and thus, have an intrinsic tree structure), but not all are. Originally, taxonomy referred only to the categorisation of organisms or a particular categorisation of organisms. In a wider, more general sense, it may refer to a categorisation of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such a categorisation. Taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon")." Taxonomy is different from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimravidae
Nimravidae is an extinct family of carnivorans, sometimes known as false saber-toothed cats, whose fossils are found in North America and Eurasia. Not considered to belong to the true cats (family Felidae), the nimravids are generally considered closely related and classified as a distinct family in the suborder Feliformia. Fossils have been dated from the Middle Eocene through the Late Miocene epochs (Bartonian through Tortonian stages, 40.4–7.2 million years ago), spanning about . The barbourofelids, which were formerly classified as a subfamily of the Nimravidae, were reassigned to their own distinct family Barbourofelidae in 2004. However, some recent studies suggest the barbourofelids are a branch of the nimravids, suggesting that this debate might not be settled yet. Morphology and evolution Most nimravids had muscular, low-slung, cat-like bodies, with shorter legs and tails than are typical of cats. Unlike extant Feliformia, the nimravids had a different bone structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |