|
Gordon Battelle
Gordon Battelle (10 August 1883 – 21 September 1923) was the founder of Battelle Memorial Institute, a non-profit independent research and development organization. Birth, death and family Gordon Battelle was born in Covington, Kentucky, to Ohio industrialist Colonel John Gordon Battelle (1845-1918) and his wife Annie Maude Battelle née Norton (1865-1925). He was named for his grandfather, prominent Methodist minister Gordon Battelle, who had helped found the state of West Virginia before dying of disease as a chaplain in the American Civil War. John Gordon Battelle had become a pioneer in the steel industry as owner of Columbus Iron & Steel Company. His wife, Annie Maude Norton Battelle, was a suffragette. They married in Memphis, Tennessee in 1881, where John Gordon Battelle had moved from Wheeling, West Virginia to establish an iron manufacturing company. The family moved to the Cincinnati, Ohio metropolitan area (which includes Covington) as John Gordon Battelle establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battelle Memorial Institute
Battelle Memorial Institute (more widely known as simply Battelle) is a private nonprofit applied science and technology development company headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Battelle is a charitable trust organized as a nonprofit corporation under the laws of the State of Ohio and is exempt from taxation under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code because it is organized for charitable, scientific and education purposes. The institute opened in 1929 but traces its origins to the 1923 will of Ohio industrialist Gordon Battelle which provided for its creation and his mother Annie Maude Norton Battelle who left the bulk of the family fortune to the institute after her death in 1925. Originally focusing on contract research and development work in the areas of metals and material science, Battelle is now an international science and technology enterprise that explores emerging areas of science, develops and commercializes technology, and manages laboratories for custome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals; that is, the way in which science is applied to the production of metals, and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commoner
A commoner, also known as the ''common man'', ''commoners'', the ''common people'' or the ''masses'', was in earlier use an ordinary person in a community or nation who did not have any significant social status, especially a member of neither royalty, nobility, nor any part of the aristocracy. Depending on culture and period, other elevated persons (such members of clergy) may have had higher social status in their own right, or were regarded as commoners if lacking an aristocratic background. This class overlaps with the legal class of people who have a property interest in common land, a longstanding feature of land law in England and Wales. Commoners who have rights for a particular common are typically neighbors, not the public in general. History Various states throughout history have governed, or claimed to govern, in the name of ''the common people''. In Europe, a distinct concept analogous to ''common people'' arose in the Classical civilization of ancient Rome aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific method for additional detail.) It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, given that cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the observation. It involves formulating hypotheses, via induction, based on such observations; the testability of hypotheses, experimental and the measurement-based statistical testing of deductions drawn from the hypotheses; and refinement (or elimination) of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings. These are ''principles'' of the scientific method, as distinguished from a definitive series of steps applicable to all scientific enterprises. Although procedures vary from one field of inquiry to another, the underlying process is frequently the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Lawn Cemetery (Columbus, Ohio)
Green Lawn Cemetery is a historic private rural cemetery located in Columbus, Ohio in the United States. Organized in 1848 and opened in 1849, the cemetery was the city's premier burying ground in the 1800s and beyond. An American Civil War memorial was erected there in 1891, and chapel constructed in 1902. With , it is Ohio's second-largest cemetery. History Franklinton Cemetery was the first cemetery established in what later became Columbus. It was built on land donated by Lucas Sullivant on River Street near Souder Avenue in 1799. Many of the early settlers of Franklinton and Columbus were buried there. The North Graveyard followed in 1812, and the East Graveyard in 1841. A Roman Catholic cemetery opened in 1848 (although it had been in use as early as 1846). Establishment of Green Lawn By the mid-1840s, growing settlement in the area left the Franklinton, North, and East cemeteries too small to accommodate more burials. On February 24, 1848, the Ohio General Assembly enact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
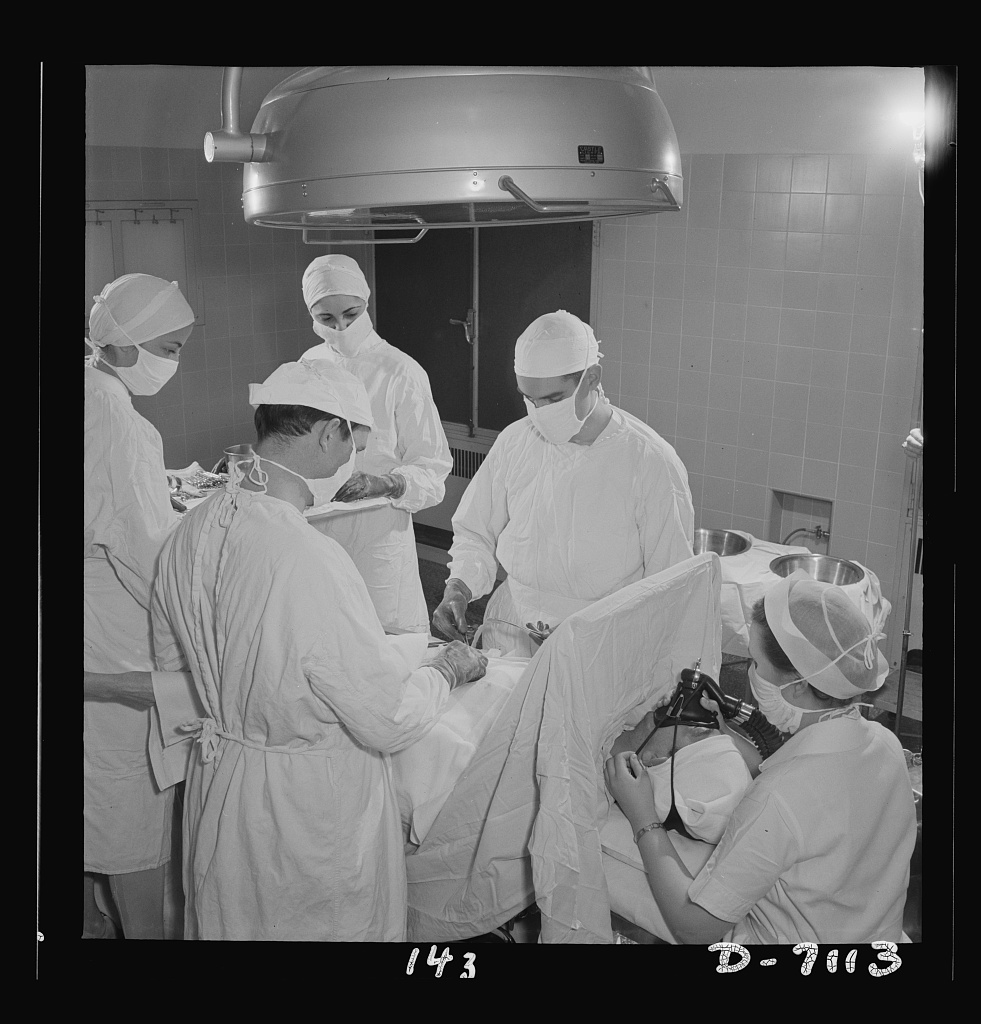
Appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acute appendicitis. Appendectomy may be performed Laparoscopic surgery, laparoscopically (as minimally invasive surgery) or as an open operation. Over the 2010s, surgical practice has increasingly moved towards routinely offering laparoscopic appendicectomy; for example in the United Kingdom over 95% of adult appendicectomies are planned as laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy is often used if the diagnosis is in doubt, or in order to leave a less visible surgical scar. Recovery may be slightly faster after laparoscopic surgery, although the laparoscopic procedure itself is more expensive and resource-intensive than open surgery and generally takes longer. Advanced pelvic sepsis occasionally requires a lower midline laparotomy. Complicated ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mine Water
Pit water, mine water or mining water is water that collects in a mine and which has to be brought to the surface by water management methods in order to enable the mine to continue working. Origin Although all water that enters pit workings originates from atmospheric precipitation, the miner distinguishes between surface water and groundwater. Surface water enters the pit through openings in the mine at the surface of the ground, such as tunnel portals or shaft entrances. During heavy rain, water seeps into the earth and forms ground water when it meets layers of impervious rock. Pit water is mainly interstitial water and groundwater that seeps into the mine workings.Carl Hartmann: Handwörterbuch der Berg-, Hütten- u. Salzwerkskunde der Mineralogie und Geognosie. Third volume, 2nd edition, Buchhandlung Bernhard Friedrich Voigt, Weimar, 1860 See also * Acid mine drainage Acid mine drainage, acid and metalliferous drainage (AMD), or acid rock drainage (ARD) is the outflow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlies an ore or mineral body and is displaced during mining without being processed. The extraction of minerals from ore can be done two ways: placer mining, which uses water and gravity to concentrate the valuable minerals, or hard rock mining, which pulverizes the rock containing the ore and then relies on chemical reactions to concentrate the sought-after material. In the latter, the extraction of minerals from ore requires comminution, i.e., grinding the ore into fine particles to facilitate extraction of the target element(s). Because of this comminution, tailings consist of a slurry of fine particles, ranging from the size of a grain of sand to a few micrometres. Mine tailings are usually produced from the mill in slurry form, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joplin, Missouri
Joplin is a city in Jasper County, Missouri, Jasper and Newton County, Missouri, Newton counties in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of Missouri. The bulk of the city is in Jasper County, while the southern portion is in Newton County. Joplin is the largest city located within both Jasper and Newton Counties - even though it is not the county seat of either county (Carthage, Missouri, Carthage is the seat of Jasper County while Neosho, Missouri, Neosho is the seat of Newton County). With a population of 51,762 as of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, Joplin is the List of cities in Missouri, 13th most-populous city in the state. The city covers an area of 35.69 square miles (92.41 km2) on the outer edge of the Ozarks, Ozark Mountains. Joplin is the main hub of the three-county Joplin-Miami, MO-OK MSA, Joplin-Miami, Missouri-Oklahoma Metro area, which is home to 210,077 people making it the 5th largest metropolitan area in Missouri. In May 2011, the city was 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
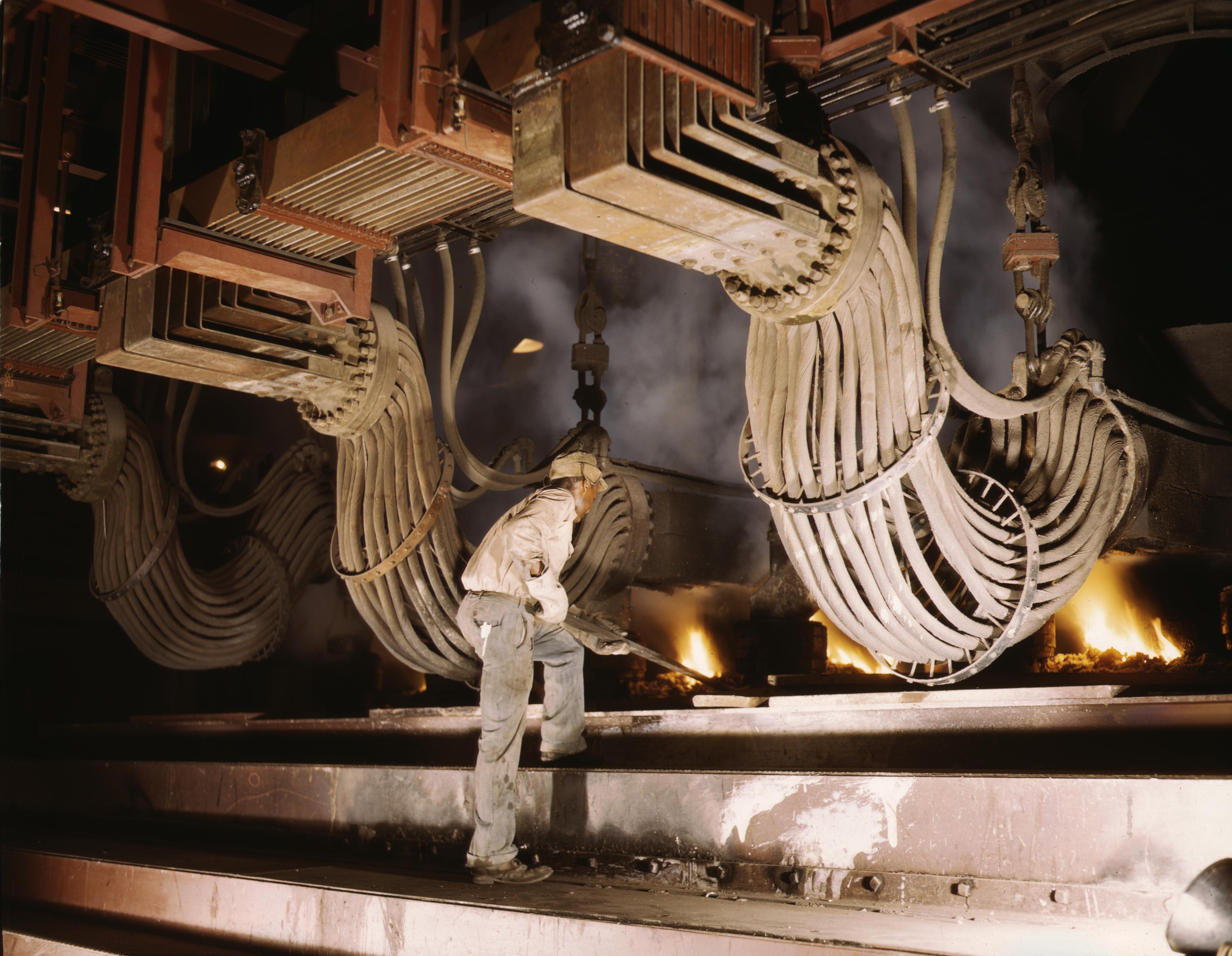
Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures due to the lower potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide (). Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is converted into steel. The carbon source acts as a chemical reactant to remove oxygen from the ore, yielding the purified metal element as a product. The carbon source is oxidized in two stages. First, the carbon (C) combusts with oxygen (O2) in the air to produce carbon monoxide (CO). Second, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |