|
Goongarrie National Park
Goongarrie National Park is a national park in Western Australia, east of Perth and about north of Kalgoorlie, Western Australia, Kalgoorlie. The park was part of Goongarrie Station (Australian agriculture), Station that was purchased by the Government of Western Australia, state government in 1995. The area also includes the abandoned townsite of Goongarrie, Western Australia, Goongarrie. The name comes from nearby Lake Gongarrie which is Indigenous Australian in origin and of unknown meaning. Infrastructure in the park was upgraded in 2007 after it received $70,000 in funding from the government. The park is dominated by arid zone woodlands and is situated along the mulga-eucalypt line. Species of acacia and eucalypt make up the bulk of the vegetation. The southern end of Lake Marmion can be found at the northern end of the park along with many smaller salt lakes and Dry lake, clay pans. Goongarrie is the transition area between the Coolgardie bioregion, Coolgardie and Murc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalgoorlie, Western Australia
Kalgoorlie is a city in the Goldfields–Esperance region of Western Australia, located east-northeast of Perth at the end of the Great Eastern Highway. It is sometimes referred to as Kalgoorlie–Boulder, as the surrounding urban area includes the historic townsite of Boulder and the local government area is the City of Kalgoorlie–Boulder. Kalgoorlie-Boulder lies on the traditional lands of the Wangkatja group of peoples.The name "Kalgoorlie" is derived from the Wangai word ''Karlkurla'' or ''Kulgooluh'', meaning "place of the silky pears". The city was established in 1893 during the Western Australian gold rushes. It soon replaced Coolgardie as the largest settlement on the Eastern Goldfields. Kalgoorlie is the ultimate destination of the Goldfields Water Supply Scheme and the Golden Pipeline Heritage Trail. The nearby Super Pit gold mine was Australia's largest open-cut gold mine for many years. At August 2021, Kalgoorlie–Boulder had an estimated urban population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Marmion
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Established In 1978
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Parks Of Western Australia
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world. It contains no fewer than separate Protected Areas with a total area of (land area: – 6.30% of the state’s area). Ninety-eight of these are National Parks, totalling (2.14% of the state’s area). Protected areas of Western Australia Conservation Parks As of 2014, the following 58 conservation parks are listed as part of the National Reserve System with a total area of . *Blackbutt * Boyagarring * Brooking Gorge *Burra *Camp Creek *Cane River * Coalseam *Dardanup *Devonian Reef *Geikie Gorge *Goldfields Woodlands * Gooralong *Hester *Kerr *Korijekup * Lane Poole *Laterite *Len Howard *Leschenault Peninsula * Leschenaultia * Lupton *Monte Bello Islands *Mount Manning - Helena And Aurora Ranges *Muja * Penguin Island *Rapids * Rowles Lagoon * Shell Beach *Totadgin *Unnamed WA01333 *Unnamed WA17804 *Unnamed WA23088 *Unnamed WA23920 *Unnamed WA24657 *Unnamed WA28740 *Unnamed WA29901 *U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of Western Australia
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world. It contains no fewer than separate Protected Areas with a total area of (land area: – 6.30% of the state’s area). Ninety-eight of these are National Parks, totalling (2.14% of the state’s area). Protected areas of Western Australia Conservation Parks As of 2014, the following 58 conservation parks are listed as part of the National Reserve System with a total area of . *Blackbutt * Boyagarring * Brooking Gorge *Burra *Camp Creek *Cane River * Coalseam *Dardanup *Devonian Reef *Geikie Gorge *Goldfields Woodlands * Gooralong *Hester *Kerr *Korijekup * Lane Poole *Laterite *Len Howard *Leschenault Peninsula * Leschenaultia * Lupton *Monte Bello Islands *Mount Manning - Helena And Aurora Ranges *Muja * Penguin Island *Rapids * Rowles Lagoon * Shell Beach *Totadgin *Unnamed WA01333 *Unnamed WA17804 *Unnamed WA23088 *Unnamed WA23920 *Unnamed WA24657 *Unnamed WA28740 *Unnamed WA29901 *U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation For Australia
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison Bioregion
The Murchison is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West region of Western Australia, Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River, Western Australia, Murchison River and has an area of . Traditionally the region is known as ''The Murchison''. Geography The landscape is characterised by low hills and mesas, separated by colluvium flats and alluvial plains. The western portion of the bioregion is drained by the upper Murchison River (Western Australia), Murchison and Wooramel River, Wooramel rivers, which drain westwards towards the coast.Anthony Desmond, Mark Cowan and Alanna Chant (2001). "Murchison 2 (MUR2 – Western Murchison subregion)", in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. The Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001/ref> Toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
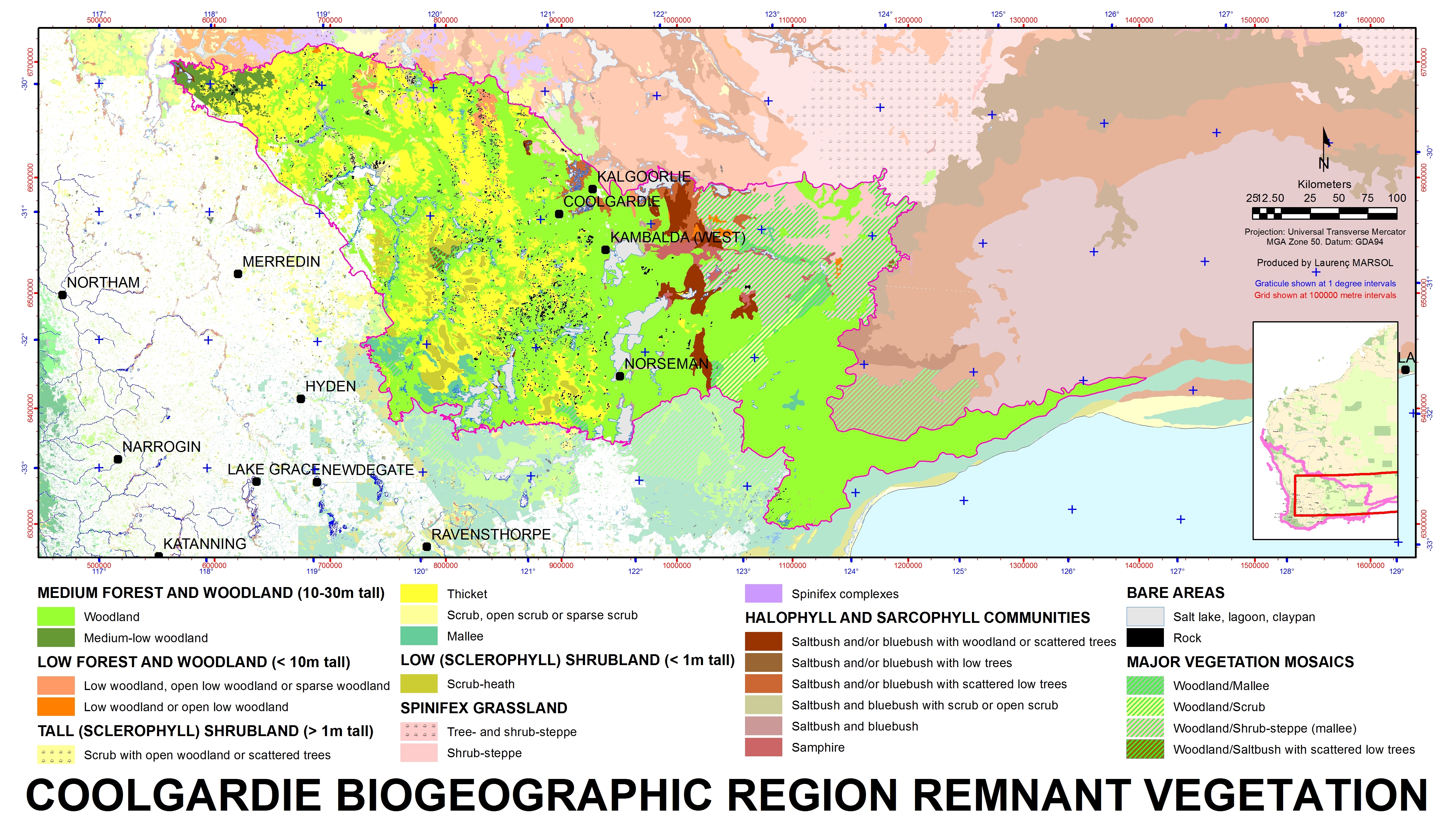
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Lake
A dry lake bed, also known as a playa, is a basin or depression that formerly contained a standing surface water body, which disappears when evaporation processes exceeds recharge. If the floor of a dry lake is covered by deposits of alkaline compounds, it is known as an alkali flat. If covered with salt, it is known as a '' salt flat.'' Terminology If its basin is primarily salt, then a dry lake bed is called a '' salt pan'', ''pan'', or ''salt flat'' (the latter being a remnant of a salt lake). ''Hardpan'' is the dry terminus of an internally drained basin in a dry climate, a designation typically used in the Great Basin of the western United States. Another term for dry lake bed is ''playa''. The Spanish word ''playa'' () literally means "beach". Dry lakes are known by this name in some parts of Mexico and the western United States. This term is used e.g. on the Llano Estacado and other parts of the Southern High Plains and is commonly used to address paleolake sediments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lakes, and may also be pink lakes on account of their colour. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. One saline lake classification differentiates between: *subsaline: 0.5–3‰ (0.05-0.3%) *hyposaline: 3–20‰ (0.3-2%) *mesosaline: 20–50‰ (2-5%) *hypersaline: greater than 50‰ (5%) Properties Salt lakes form when the water flowing into the lake, containing salt or minerals, cannot leave because the lake is endorheic (terminal). The water then evaporates, leaving behind any dissolved salts and thus increasing its salinity, making a salt lake an excellent place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalypt
Eucalypt is a descriptive name for woody plants with capsule fruiting bodies belonging to seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australasia: ''Eucalyptus'', '' Corymbia'', '' Angophora'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum''. Taxonomy For an example of changing historical perspectives, in 1991, largely genetic evidence indicated that some prominent ''Eucalyptus'' species were actually more closely related to ''Angophora'' than to other eucalypts; they were accordingly split off into the new genus ''Corymbia''. Although separate, all of these genera and their species are allied and it remains the standard to refer to the members of all seven genera ''Angophora'', ''Corymbia'', ''Eucalyptus'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' as "eucalypts" or as the eucalypt group. The extant genera ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' comprise six k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |