|
Golomb Ruler
In mathematics, a Golomb ruler is a set of marks at integer positions along a ruler such that no two pairs of marks are the same distance apart. The number of marks on the ruler is its ''order'', and the largest distance between two of its marks is its ''length''. Translation and reflection of a Golomb ruler are considered trivial, so the smallest mark is customarily put at 0 and the next mark at the smaller of its two possible values. Golomb rulers can be viewed as a one-dimensional special case of Costas arrays. The Golomb ruler was named for Solomon W. Golomb and discovered independently by and . Sophie Piccard also published early research on these sets, in 1939, stating as a theorem the claim that two Golomb rulers with the same distance set must be congruent. This turned out to be false for six-point rulers, but true otherwise. There is no requirement that a Golomb ruler be able to measure ''all'' distances up to its length, but if it does, it is called a ''perfec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golomb Ruler-4
Golomb or Gollomb is a surname derived from a phonetical approximation of the Polish word " gołąb" (meaning "dove"). It may refer to: * Abraham Golomb (1888–1982) Yiddish-language teacher and writer *Eliyahu Golomb (1893–1945), leader of the Jewish defense effort in Mandate Palestine * Michael Golomb (1909–2008), American mathematician and educator * Rudy Gollomb (1911–1991), American football player * Solomon W. Golomb (1932–2016), American mathematician and engineer ** Golomb ruler ** Golomb coding Golomb coding is a lossless data compression method using a family of data compression codes invented by Solomon W. Golomb in the 1960s. Alphabets following a geometric distribution will have a Golomb code as an optimal prefix code, making Golomb ... See also * * Gołąb (surname) Jewish surnames Polish-language surnames {{Dove-surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injective Function
In mathematics, an injective function (also known as injection, or one-to-one function) is a function that maps distinct elements of its domain to distinct elements; that is, implies . (Equivalently, implies in the equivalent contrapositive statement.) In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of one element of its domain. The term must not be confused with that refers to bijective functions, which are functions such that each element in the codomain is an image of exactly one element in the domain. A homomorphism between algebraic structures is a function that is compatible with the operations of the structures. For all common algebraic structures, and, in particular for vector spaces, an is also called a . However, in the more general context of category theory, the definition of a monomorphism differs from that of an injective homomorphism. This is thus a theorem that they are equivalent for algebraic structures; see for more d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Ev ..., in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Ruler
A perfect ruler of length \ell is a ruler with integer markings a_1=0 < a_2 < \dots < a_n=\ell, for which there exists an integer such that any is uniquely expressed as the difference for some . This is referred to as an -perfect ruler. An optimal perfect ruler is one of the smallest length for fixed values of and . Example A 4-perfect ruler of length is given by . To verify this, we need to show that every pos ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pál Turán
Pál Turán (; 18 August 1910 – 26 September 1976) also known as Paul Turán, was a Hungarian mathematician who worked primarily in extremal combinatorics. He had a long collaboration with fellow Hungarian mathematician Paul Erdős, lasting 46 years and resulting in 28 joint papers. Life and education Turán was born into a Jewish family in Budapest on 18 August 1910.At the same period of time, Turán and Erdős were famous answerers in the journal '' KöMaL''. He received a teaching degree at the University of Budapest in 1933 and the PhD degree under Lipót Fejér in 1935 at Eötvös Loránd University. As a Jew, he fell victim to numerus clausus, and could not get a university job for several years. He was sent to labour service at various times from 1940-44. He is said to have been recognized and perhaps protected by a fascist guard, who, as a mathematics student, had admired Turán's work. Turán became associate professor at the University of Budapest in 1945 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Erdős
Paul Erdős ( hu, Erdős Pál ; 26 March 1913 – 20 September 1996) was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered around discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics. Erdős published around 1,500 mathematical papers during his lifetime, a figure that remains unsurpassed. He firmly believed mathematics to be a social activity, living an itinerant lifestyle with the sole purpose of writing mathematical papers with other mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptotically Optimal
In computer science, an algorithm is said to be asymptotically optimal if, roughly speaking, for large inputs it performs at worst a constant factor (independent of the input size) worse than the best possible algorithm. It is a term commonly encountered in computer science research as a result of widespread use of big-O notation. More formally, an algorithm is asymptotically optimal with respect to a particular resource if the problem has been proven to require of that resource, and the algorithm has been proven to use only These proofs require an assumption of a particular model of computation, i.e., certain restrictions on operations allowable with the input data. As a simple example, it's known that all comparison sorts require at least comparisons in the average and worst cases. Mergesort and heapsort are comparison sorts which perform comparisons, so they are asymptotically optimal in this sense. If the input data have some ''a priori'' properties which can be explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Transformer
A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary. Current transformers, along with voltage or potential transformers, are instrument transformers. Instrument transformers scale the large values of voltage or current to small, standardized values that are easy to handle for measuring instruments and protective relays. The instrument transformers isolate measurement or protection circuits from the high voltage of the primary system. A current transformer provides a secondary current that is accurately proportional to the current flowing in its primary. The current transformer presents a negligible load to the primary circuit.Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty (ed), ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers, Eleventh Edition'', Mc-Graw Hill,1978, 0-07-020974-X, pp. 10-51 - 10-57 Current transformers are the current-sensing uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust, and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is . The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Studies indicate that 90% of the mass in most galaxies is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermodulation Interference
Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by nonlinearities or time variance in a system. The intermodulation between frequency components will form additional components at frequencies that are not just at harmonic frequencies (integer multiples) of either, like harmonic distortion, but also at the sum and difference frequencies of the original frequencies and at sums and differences of multiples of those frequencies. Intermodulation is caused by non-linear behaviour of the signal processing (physical equipment or even algorithms) being used. The theoretical outcome of these non-linearities can be calculated by generating a Volterra series of the characteristic, or more approximately by a Taylor series. Practically all audio equipment has some non-linearity, so it will exhibit some amount of IMD, which however may be low enough to be imperceptible by humans. Due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
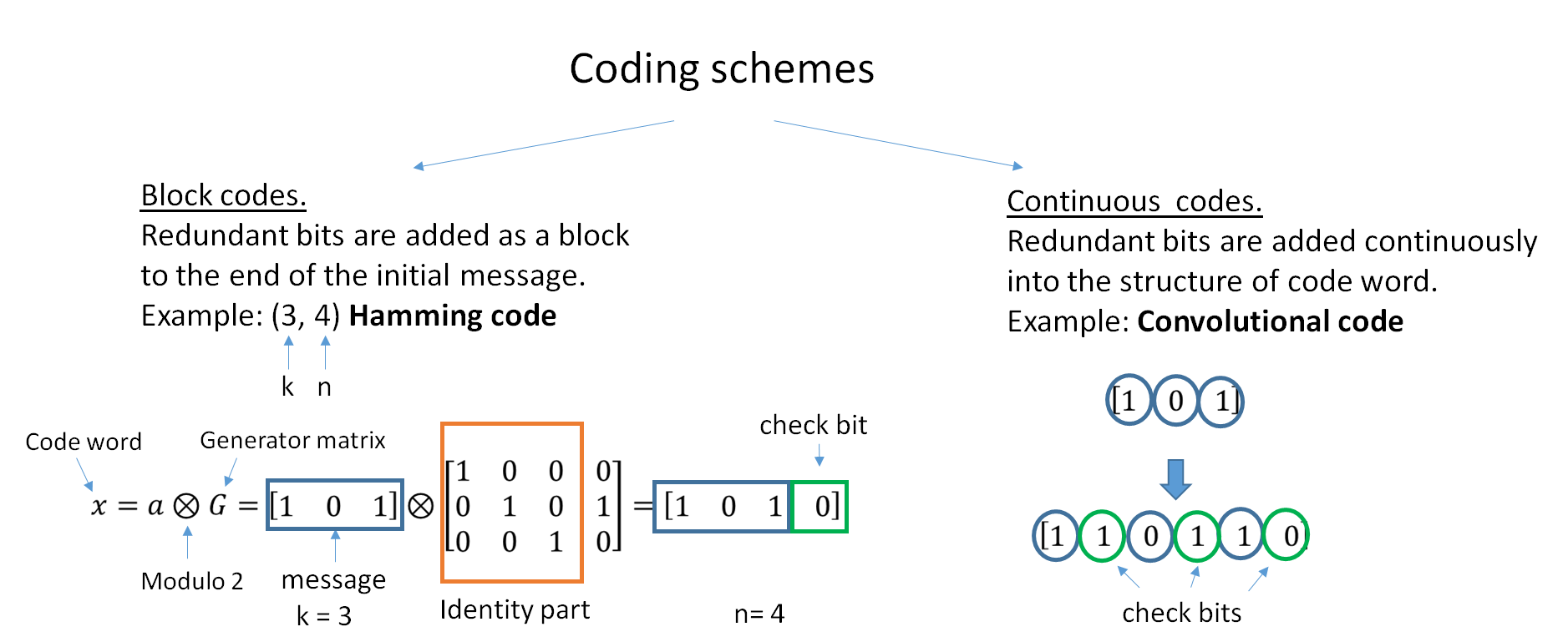
Error Correcting Code
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |