|
Golant
Golant ( kw, Golnans) is a village in south Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is on the west bank of the River Fowey and in the civil parish of St Sampson. Golant is about two miles (3 km) north of Fowey and seven miles (11 km) east of St Austell. Golant church is dedicated to St Sampson of Dol. The poet John Betjeman remarked that its pews were "extremely uncomfortable, recall the fidgets of Gus and Flora in '' Ravenshoe''". The church was mentioned in the book ''England’s Thousand Best Churches'' by Simon Jenkins. The village is on the Saints' Way long-distance footpath. History A once well-used ford crossed the river near Golant. During the English Civil War in 1644 a 10,000-strong parliamentary army fought Royalist forces in area. King Charles was in the area during the campaign. The Earl of Essex and other prominent parliamentarians escaped by boat to Plymouth. many 17th century cannonballs and musket balls have been found in the area. Golant Halt was a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Sampson's Church, Golant
St Sampson's Church is the Church of England parish church of the village of Golant, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom; it is dedicated to St Sampson of Dol. St Sampson's features in Simon Jenkins's book ''England's Thousand Best Churches'', in which it is described as "warm and welcoming". The poet John Betjeman remarked that its pews were "extremely uncomfortable, recall the fidgets of Gus and Flora in '' Ravenshoe''". It is open every day of the year, holds services every Sunday and evening prayer every Thursday evening at 6 o’clock. Its choir sings every 2nd and 4th Sunday of the month. History Saint Samson of Dol Although Cornwall has more saints than any other county in the UK, Saint Sampson is one of the better known ones. He sometimes stayed in Golant while travelling to Brittany and became the archbishop of Dol. Many Cornish saints travelling from Ireland to France ''via'' the south Cornish coast stopped on the way (sometimes in or near the village). There is now a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golant Railway Station
Golant railway station was opened on 1 July 1896 by the Great Western Railway. It was a simple platform on the waterside at the south end of Golant village, next to a level crossing that gave access to a slipway. It was the only intermediate station between Lostwithiel and Fowey. The line had been built by the Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway but had fallen into disuse until reopened by the Cornwall Minerals Railway which was amalgamated into the Great Western Railway on the same day that Golant was opened. The station was unstaffed. The instructions to staff stated that "no luggage is to be labelled to Golant. Passengers who may be travelling from Golant to stations on the main line beyond Lostwithiel must re-book at that station, and have their luggage labelled to their destination at Lostwithiel." The railway including Golant was closed to passengers through part of the Second World War as Fowey was the main port for loading ammunition for the US 29th Division that landed on O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Sampson, Cornwall
St Sampson is a civil parish in mid-Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The population at the 2011 census was 260. Formally known as the parish of Golant (Golant is a small village on the west bank of the Fowey river) the parish is bounded on the north by Lanlivery, on the east by the river Fowey which separates it from St Winnow, St Veep and Lanteglos-by-Fowey, on the south by Fowey, and on the west by Tywardreath. The small church has a holy well by the south porch and is dedicated to St Sampson, by whose name the parish is usually known. The church was probably all built at the same time and was dedicated in 1509. There is a low western tower. Features of interest include bench ends made into a pulpit and a sculpture of the head of Christ (perhaps Italian). Penquite House near Golant was designed by George Wightwick George Wightwick (26 August 1802 – 9 July 1872) was a British architect based in Plymouth, and possibly the first architectural journalist. In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
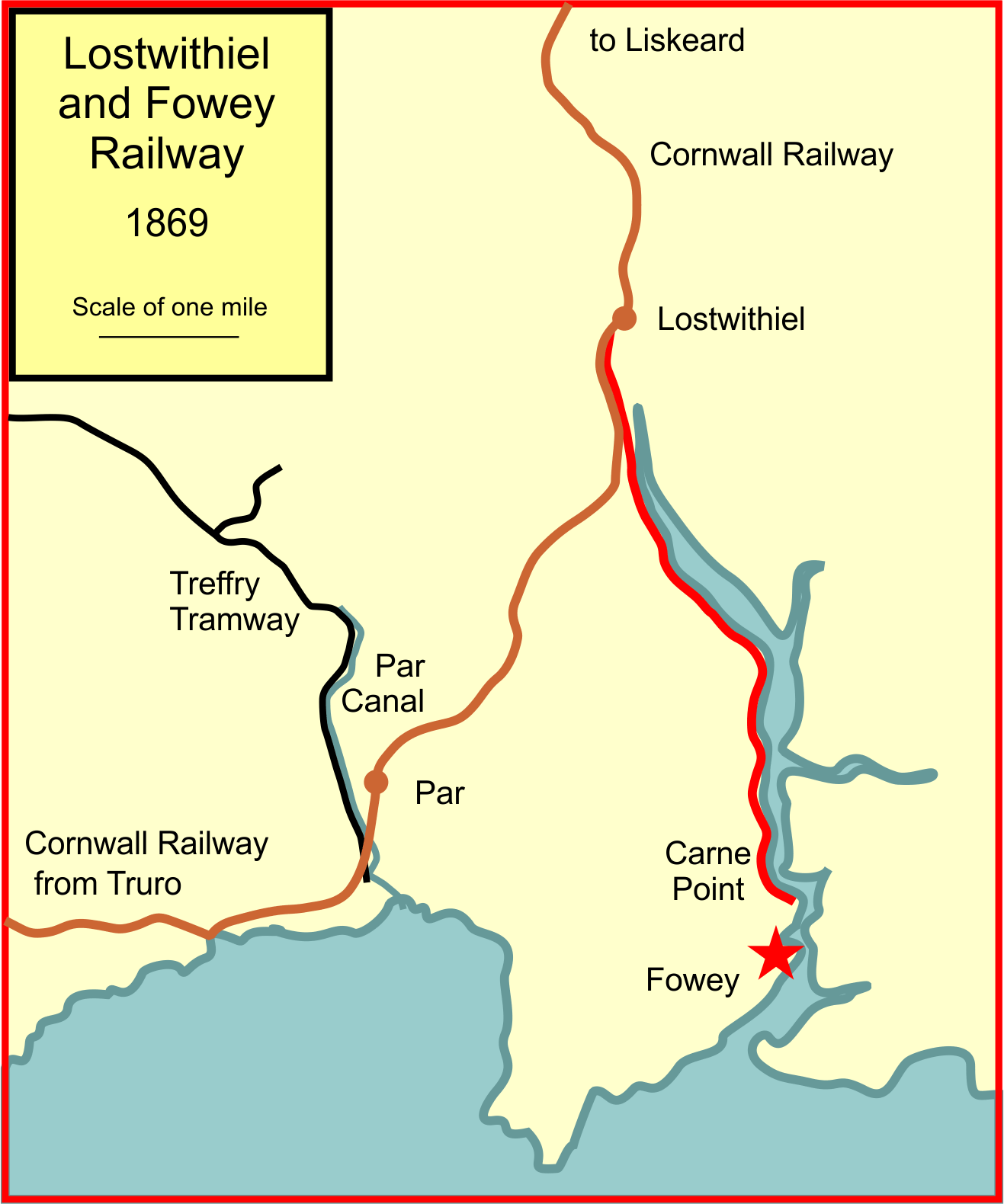
Lostwithiel And Fowey Railway
The Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway opened in 1869 as a broad gauge railway linking the port of Fowey in Cornwall with the Cornish Main Line at Lostwithiel. Its main traffic was china clay. The company ran into financial difficulties and closed in 1880, but the line was purchased by the Cornwall Minerals Railway and reopened in 1895. A passenger service operated, but it was withdrawn in 1965, and the line reverted to the conveyance of china clay; it remains open for that traffic at the present day. Chronology * 1862 Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway Act * 1869 Line opened * 1874 Cornwall Minerals Railway opens from Par to Fowey * 1880 Service suspended * 1892 Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway Company dissolved * 1895 Reopened by Cornwall Minerals Railway * 1968 Par to Fowey line closed History Promoters of an independent company conducted negotiations with the Cornwall Railway in 1861, regarding the construction of a branch line from that railway at Lostwithiel to a location at Caffa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fowey Estuary
The River Fowey ( ; kw, Fowi) is a river in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It rises at Fowey Well (originally kw, Fenten Fowi, meaning ''spring of the river Fowey'') about north-west of Brown Willy on Bodmin Moor, not far from one of its tributaries rising at Dozmary Pool and Colliford Lake, passes Lanhydrock House, Restormel Castle and Lostwithiel, then broadens below Milltown before joining the English Channel at Fowey. The estuary is called Uzell ( kw, Usel, meaning ''howling place''). It is only navigable by larger craft for the last . There is a ferry between Fowey and Bodinnick. The first road crossing going upstream is in Lostwithiel. The river has seven tributaries, the largest being the River Lerryn. The section of the Fowey Valley between Doublebois and Bodmin Parkway railway station is known as the Glynn Valley ( kw, Glyn, meaning ''deep wooded valley''). The valley is the route of both the A38 trunk road and the railway line (built by the Cornwall Railway i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Fowey
The River Fowey ( ; kw, Fowi) is a river in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It rises at Fowey Well (originally kw, Fenten Fowi, meaning ''spring of the river Fowey'') about north-west of Brown Willy on Bodmin Moor, not far from one of its tributaries rising at Dozmary Pool and Colliford Lake, passes Lanhydrock House, Restormel Castle and Lostwithiel, then broadens below Milltown before joining the English Channel at Fowey. The estuary is called Uzell ( kw, Usel, meaning ''howling place''). It is only navigable by larger craft for the last . There is a ferry between Fowey and Bodinnick. The first road crossing going upstream is in Lostwithiel. The river has seven tributaries, the largest being the River Lerryn. The section of the Fowey Valley between Doublebois and Bodmin Parkway railway station is known as the Glynn Valley ( kw, Glyn, meaning ''deep wooded valley''). The valley is the route of both the A38 trunk road and the railway line (built by the Cornwall Railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Sampson Of Dol
Samson of Dol (also Samsun; born late 5th century) was a Cornish saint, who is also counted among the seven founder saints of Brittany with Pol Aurelian, Tugdual or Tudwal, Brieuc, Malo, Patern (Paternus) and Corentin. Born in southern Wales, he died in Dol-de-Bretagne, a small town in north Brittany. Life The primary source for his biography is the ''Vita Sancti Samsonis'', written sometime between 610 and 820 and clearly based on earlier materials. It gives useful details of contacts between churchmen in Britain, Ireland and Brittany. Samson was the son of Amon of Demetia and Anna of Gwent. His father's brother married his mother's sister so that their son Maglor was Samson's cousin twice over. Due to a prophecy concerning his birth his parents placed him under the care of Illtud, Abbot of Llantwit Fawr, where he was raised and educated. Samson later sought a greater austerity than his school provided, and so moved to Llantwit's daughter house, the island monastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saints' Way
The Saints' Way ( kw, Forth an Syns) is a long-distance footpath in mid Cornwall, England, UK. History and description The footpath runs from Padstow parish church in the north via Luxulyan to Fowey parish church in the south, a distance of 28.5 miles (45.6 km); if the route via Lanlivery is followed the distance is 29 miles (46.6 km). The path is well marked and guide books are available. There are two main branches in the way. One starts at Fowey, runs west to Tywardreath, then north through St Blazey, and Luxulyan. The other runs north from Fowey to Golant and Lanlivery. The branches meet close to Helman Tor. Part of the route is a bridleway so can be used by horse-riders. The Saints' Way follows a possible route of early Christian travellers making their way from Ireland to the Continent. Rather than risk the difficult passage around Land's End they could disembark from ships on the North Cornish coast and progress to ports such as Fowey on foot. Between 55 - 50AD a R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
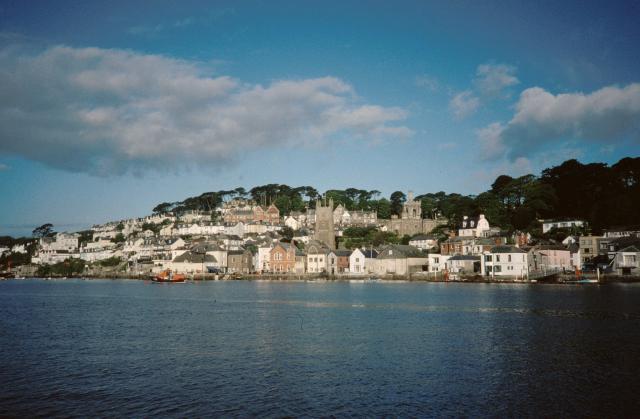
Fowey
Fowey ( ; kw, Fowydh, meaning 'Beech Trees') is a port town and civil parish at the mouth of the River Fowey in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town has been in existence since well before the Norman invasion, with the local church first established some time in the 7th century; the estuary of the River Fowey forms a natural harbour which enabled the town to become an important trading centre. Privateers also made use of the sheltered harbourage. The Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway brought China clay here for export. History Early history The Domesday Book survey at the end of the 11th century records manors at Penventinue and Trenant, and a priory was soon established nearby at Tywardreath. the prior granted a charter to people living in Fowey itself. This medieval town ran from a north gate near Boddinick Passage to a south gate at what is now Lostwithiel Street; the town extended a little way up the hillside and was bounded on the other side by the river where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which amalgamated it with the remaining independent railways within its territory, and it was finally merged at the end of 1947 when it was nationalised and became the Western Region of British Railways. The GWR was called by some "God's Wonderful Railway" and by others the "Great Way Round" but it was famed as the "Holiday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Stone Roses
The Stone Roses were an English Rock music, rock band formed in Manchester in 1983. One of the pioneering groups of the Madchester movement in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the band's classic and most prominent lineup consisted of vocalist Ian Brown, guitarist John Squire, bassist Mani (musician), Mani and drummer Reni (musician), Reni. The band released their debut album, ''The Stone Roses (album), The Stone Roses'', in 1989. The album was a breakthrough success for the band and received critical acclaim, many regarding it as one of the greatest British albums ever recorded. At this time the group decided to capitalise on their success by signing to a major label. Their record label at the time, Silvertone Records (1980), Silvertone, would not let them out of their contract, which led to a long legal battle that culminated with the band signing with Geffen Records in 1991. The Stone Roses released their second album, ''Second Coming (The Stone Roses album), Second Coming'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive administration of the country/kingdom. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |