|
Godbout, Quebec
Godbout is a village municipality in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It is located at the mouth of the Godbout River on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River. Godbout is accessible via Quebec Route 138 and by ferry from Matane. Environment A map of the Ecological regions of Quebec places the Gobout area in ecological region 5g Hautes collines de Baie-Comeau — Sept-Îles in the eastern fir/white birch domain of the boreal zone. The Godbout River is known as one of the best of Quebec's salmon rivers and also holds speckled trout. About of the river is managed by a zone d'exploitation contrôlée (managed use zone), the Zec des Rivières-Godbout-et-Mistassini. The downstream Cap-Nord section is owned by a private club, but the right to fish it may be obtained through an agreement with the ZEC. The Petite-Rivière-Godbout Old Forest is about northwest of the village of Godbou. History The native Innu hunted and fished near the mouth of the river that they ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Municipalities In Quebec
The following is a list of the types of local and supralocal territorial units in Quebec, including those used solely for statistical purposes, as defined by the Ministry of Municipal Affairs, Regions and Land Occupancy and compiled by the Institut de la statistique du Québec. Not included are the urban agglomerations in Quebec, which, although they group together multiple municipalities, exercise only what are ordinarily local municipal powers. A list of local municipal units in Quebec by regional county municipality can be found at List of municipalities in Quebec. Local municipalities All municipalities (except cities), whether township, village, parish, or unspecified ones, are functionally and legally identical. The only difference is that the designation might serve to disambiguate between otherwise identically named municipalities, often neighbouring ones. Many such cases have had their names changed, or merged with the identically named nearby municipality since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission De Toponymie Du Québec
The Commission de toponymie du Québec (English: ''Toponymy Commission of Québec'') is the Government of Québec's public body responsible for cataloging, preserving, making official and publicize Québec's place names and their origins according to the province's toponymy rules. It also provides recommendations to the government with regard to toponymic changes. Its mandate covers the namings of: * natural geographical features (lakes, rivers, mountains, etc.) * constructed features (dams, embankments, bridges, etc.) * administrative units (wildlife sanctuaries, administrative regions, parks, etc.) * inhabited areas (villages, towns, Indian reserves, etc.) * roadways (streets, roads, boulevards, etc.) A child agency of the Office québécois de la langue française, it was created in 1977 through jurisdiction defined in the Charter of the French Language to replace the Commission of Geography, created in 1912. See also * Toponymy * Toponym'elles * Office québécois de la lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Albanel
Charles Albanel (1616 – 11 January 1696), born in Ardes or Auvergne, was a French missionary explorer in Canada, and a Jesuit priest. Life Charles Albanel entered the Society of Jesus in 1633 at Toulouse. In 1635 he began teaching at various Jesuit colleges, studied philosophy at Billom and theology at Tournon. He sailed for Canada in 1649 and arrived at Quebec in late August. A month later he was sent to Fort Ville-Marie, Ville-Marie. He wintered among the Innu people, Montagnais, and in the spring traveled to Tadoussac to tend those suffering from fever. In July 1660, on a return from Trois-Rivières with Pierre de Voyer d'Argenson, Vicomte de Mouzay, Governor Voyer d'Argenson, their boat was attached by Iroquois. In August, René Ménard was sent west from Montreal with a trading party of Ottawa and the fur traders Radisson and Groseilliers, heading for what is now northern Wisconsin, aiming to establish a mission among the Ottawa. Albanel met Ménard at Montreal and was to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Île D'Orléans
Île d'Orléans (; en, Island of Orleans) is an island located in the Saint Lawrence River about east of downtown Quebec City, Quebec, Canada. It was one of the first parts of the province to be colonized by the French, and a large percentage of French Canadians can trace ancestry to early residents of the island. The island has been described as the "microcosm of traditional Quebec and as the birthplace of francophones in North America." It has about 7,000 inhabitants, spread over 6 villages. The island is accessible from the mainland via the Île d'Orléans Bridge from Beauport. Route 368 is the sole provincial route on the island, which crosses the bridge and circles the perimeter of the island. At the village of Sainte-Pétronille toward the western end of the island, a viewpoint overlooks the impressive ''Chute Montmorency'' (Montmorency Falls), as well as a panorama of the St. Lawrence River and Quebec City. Île d'Orléans is twinned with ''Île de Ré'' in Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
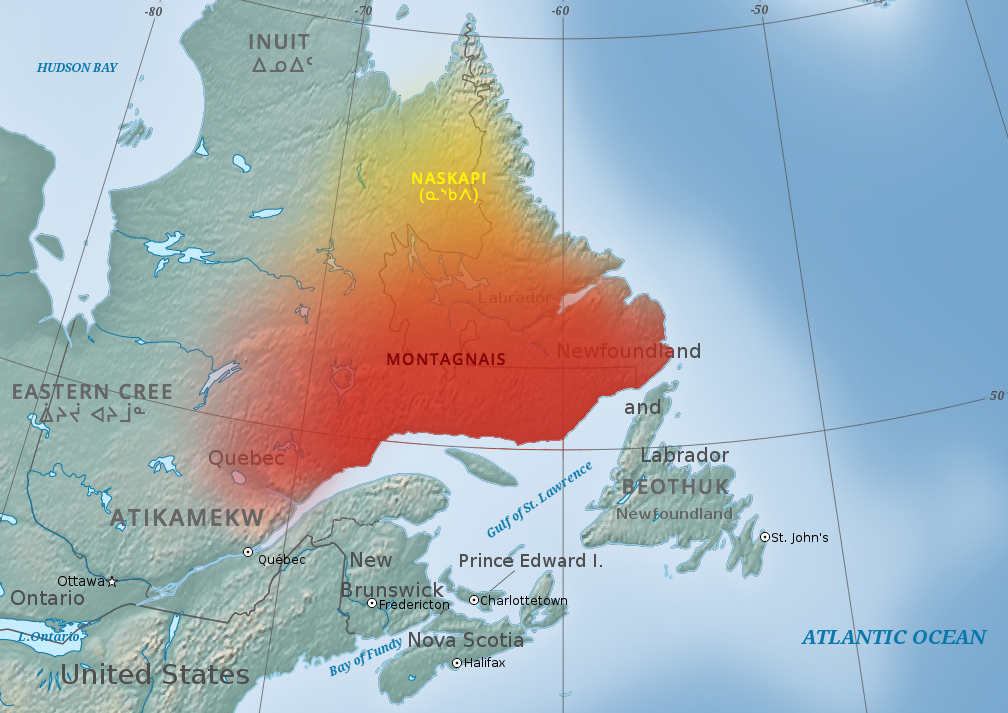
Innu
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petite-Rivière-Godbout Old Forest
The Petite-Rivière-Godbout Old Forest (french: Forêt ancienne de la Petite-Rivière-Godbout) is a protected area of old-growth forest in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, classified as an exceptional forest ecosystem. Location The Petite-Rivière-Godbout Old Forest is in the municipality of Gobdbout in the Manicouagan Regional County Municipality. It is about northwest of the village of Godbout on the north shore of the Estuary of Saint Lawrence. The forest is administered by Quebecʻs Ministry of Natural Resources, Wildlife and Parks, Forest Environment Directorate. It was designated old-growth forest in 2003, and has IUCN management category III. The forest has an area of . The terrain is moderately rugged, with tall hills covered by thin glacial till and many rocky escarpments. The forest is on the southern slope of a steep hill looking over the Rat Musqué Lake and the Little Godbout River (Petite rivière Godbout). A map of the Ecological regions of Quebec places the Gobo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zec Des Rivières-Godbout-et-Mistassini
The Zec des Rivières-Godbout-et-Mistassini (known until 1996 "Zec de la rivière-Godbout") is a "zone d'exploitation contrôlée" (controlled harvesting zone (ZEC)) in the municipalities of Franquelin and Godbout, in Manicouagan Regional County Municipality (RCM), in the administrative region of Côte-Nord, in Quebec, in Canada. Zec administers the lower segments of the Godbout River and Mistassini River (Franquelin) which are used for recreative salmon fishing. Geography ''Godbout River'' The Godbout River flows from north to south, in the municipality of Franquelin, then Godbout. It flows into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, west of the town of Godbout and the Bay of Godbout. After crossing the route138, the river still flows 3.2 km to the southeast to its mouth along a sandbar separating the Bay of Molson, located on the west side. Downstream of the route138, there are four small islands on the river, of which Gilmour Island and Laws Island. Godbout River has 29 sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone D'exploitation Contrôlée
A ''zone d'exploitation contrôlée'' (in French; acronym ZEC) is a "Controlled harvesting zone" located in public lands areas of Quebec, in Canada. ZECs are a system of territorial infrastructures set up in 1978 by the Government of Quebec to take over from private hunting, fishing and trapping clubs (as a result of "Operation wildlife management") to provide timely access to recreational activities to the general public like hunting and fishing. Administration They are non profit organisations managed by honorary administrators whose primary responsibility is to manage fishing and hunting activities and see to wildlife conservation on their respective territories. ZEC objectives: # Wildlife conservation (hunters and anglers must report their catch) # Access to wildlife resources # User participation # Operations must be financially self-sufficient ZECs fill a much larger economic place than fishing and hunting clubs did as they also promote all types of recreational and tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Regions Of Quebec
The Ecological regions of Quebec are regions with specific types of vegetation and climates as defined by the Quebec Ministry of Forests, Wildlife and Parks. Given the size of this huge province, there is wide variation from the temperate deciduous forests of the southwest to the arctic tundra of the extreme north. Vegetation zones Quebec covers more than of land between 45° and 62° north, with vegetation that varies greatly from south to north. Most of the natural vegetation is forest, with various species of trees and other plants, and these forests are the habitat for diverse fauna. Energy, precipitation and soil are all important factors in determining what can grow. The climate influences the natural disturbances that affect forests: western Quebec has a drier climate than the east, and experiences more fires. For most species these disturbances are not disasters, and some need them to regenerate. The climate in Quebec supports rich deciduous forest in the southern region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matane
Matane is a town on the Gaspé Peninsula in Quebec, Canada, on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River at the mouth of the Matane River. The town is the seat for the La Matanie Regional County Municipality. In addition to Matane itself, the town's territory also includes the communities of Petit-Matane and Saint-Luc-de-Matane. There is a ferry service which crosses the river to Baie-Comeau and Godbout on the north shore as well as a rail ferry service to Baie-Comeau and Sept-Îles. Etymology The name Matane was first assigned to the river by Samuel de Champlain as "''Mantanne''" in 1603. Its meaning is open to different interpretations, with the most common one being that it comes from the Mi'kmaq word ''mtctan'' meaning "beaver pond", since the region had an abundant beaver population. It could also be a Maliseet word for "spinal cord", referring to the course of the Matane River; or from the word ''Mattawa''/''Matawin'', meaning "meeting of the waters". Finally, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec Route 138
Route 138 is a major highway in the Canadian province of Quebec, following the entire north shore of the Saint Lawrence River past Montreal to the temporary eastern terminus in Kegashka on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. The western terminus is in Elgin, at the border with New York State south-west of Montreal (connecting with New York State Route 30 at the Trout River Border Crossing). Part of this highway is known as the '' Chemin du Roy'', or King's Highway, which is one of the oldest highways in Canada. It passes through the Montérégie, Lanaudière, Mauricie, Capitale-Nationale and Côte-Nord regions of Quebec. In Montreal, Highway 138 runs via Sherbrooke Street, crosses the Pierre Le Gardeur Bridge to Charlemagne and remains a four-lane road until exiting Repentigny. This highway takes a more scenic route than the more direct Autoroute 40 between Montreal and Quebec City. It crosses the Saguenay River via a ferry which travels between Baie-Sainte-Catherine and Tadouss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting the American Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean, and forming the primary drainage outflow of the Great Lakes Basin. The river traverses the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, as well as the U.S. state of New York, and demarcates part of the international boundary between Canada and the United States. It also provides the foundation for the commercial St. Lawrence Seaway. Names Originally known by a variety of names by local First Nations, the St. Lawrence became known in French as ''le fleuve Saint-Laurent'' (also spelled ''St-Laurent'') in 1604 by Samuel de Champlain. Opting for the ''grande riviere de sainct Laurens'' and ''fleuve sainct Laurens'' in his writings and on his maps, de Champlain supplanted previous Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |