|
Gobhi Paratha
Gobi paratha ( hi, गोभी पराठा; "cauliflower paratha") is a type of paratha or (flatbread), originating from the Indian subcontinent The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ..., that is stuffed with flavored cauliflower and vegetables. It can be consumed as breakfast or an appetizer. Preparation The dough is made from flour. The stuffing is made from cauliflower and a mix of spices such as cumin, ginger, and turmeric powder. The filling is placed in the rolled dough, folded into a ball, and rolled out again. The paratha is cooked on the stovetop. Gobi paratha are often eaten with raita. See also * List of bread dishes References External links Gobhi Paratha recipeभारतीय परांठा लिस्ट Indian cuisine Indian breads [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka."Indian subcontinent". ''Oxford Dictionary of English, New Oxford Dictionary of English'' () New York: Oxford University Press, 2001; p. 929: "the part of Asia south of the Himalayas which forms a peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Historically forming the whole territory of Greater India, the region is now divided into three countries named Bangladesh, India and Pakistan." The terms ''Indian subcontinent'' and ''South Asia'' are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
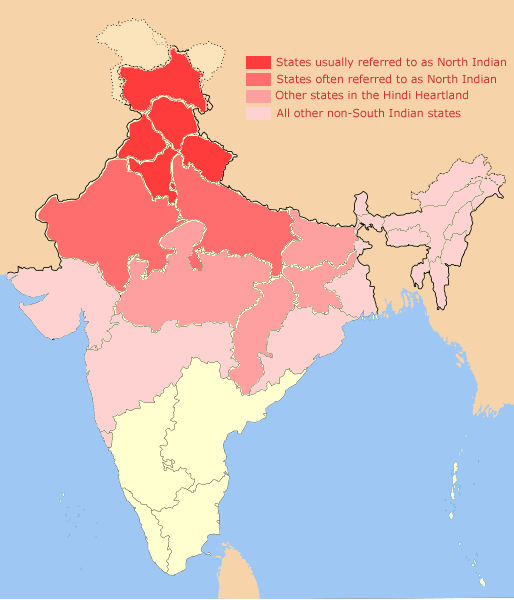
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratha
Paratha () is a flatbread native to South Asia, prevalent throughout the modern-day nations of India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Afghanistan, Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, Mauritius, Fiji, Guyana, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago where wheat is the traditional staple. ''Paratha'' is an amalgamation of the words ''parat'' and ''atta'', which literally means layers of cooked dough. Alternative spellings and names include ''parantha'', ''parauntha'', ''prontha'', ''parontay'', ''paronthi'' ( Punjabi), ''porota'' (in Bengali), ''paratha'' (in Odia, Hindi), ''palata'' (; in Myanmar), ''porotha'' (in Assamese), ''forota'' (in Sylheti), ''farata'' (in Mauritius and the Maldives), ''roti canai'', ''prata'' (in Southeast Asia), ''paratha'', ''buss-up shut'', ''oil roti'' (in the Anglophone Caribbean). History The Hindi/Urdu word ''paratha'' is derived from Sanskrit (S. पर, or परा+स्थः, or स्थितः). Recipes for various stuffed whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratha
Paratha () is a flatbread native to South Asia, prevalent throughout the modern-day nations of India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Afghanistan, Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, Mauritius, Fiji, Guyana, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago where wheat is the traditional staple. ''Paratha'' is an amalgamation of the words ''parat'' and ''atta'', which literally means layers of cooked dough. Alternative spellings and names include ''parantha'', ''parauntha'', ''prontha'', ''parontay'', ''paronthi'' ( Punjabi), ''porota'' (in Bengali), ''paratha'' (in Odia, Hindi), ''palata'' (; in Myanmar), ''porotha'' (in Assamese), ''forota'' (in Sylheti), ''farata'' (in Mauritius and the Maldives), ''roti canai'', ''prata'' (in Southeast Asia), ''paratha'', ''buss-up shut'', ''oil roti'' (in the Anglophone Caribbean). History The Hindi/Urdu word ''paratha'' is derived from Sanskrit (S. पर, or परा+स्थः, or स्थितः). Recipes for various stuffed whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
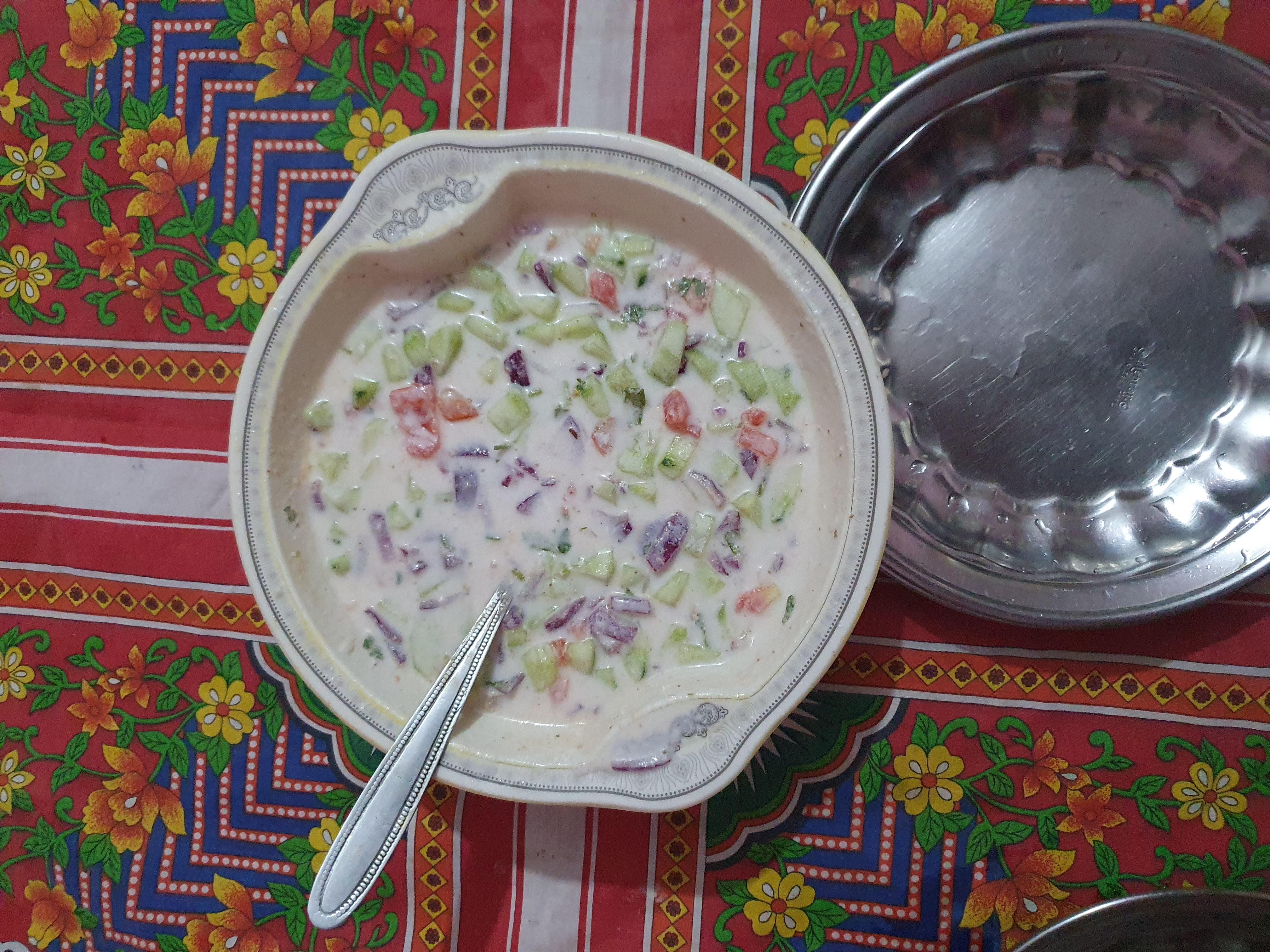
Raita
Raita is a side dish in Indian cuisine made of dahi (yogurt, often referred to as curd) together with raw or cooked vegetables, more seldom fruit, or in the case of boondi raita, with fried droplets of batter made from besan (chickpea flour, generally labeled as gram flour). The closest approximation in western cuisine is a side dish or dip, or a cooked salad. It is often referred to as a condiment, but unlike traditional western condiments like salt, pepper, mustard and horseradish that make dishes more spicy, a dish of dahi or raita has a cooling effect to contrast with spicy curries and kebabs that are the main fare of some Asian cuisines. In Indian cuisine, some type of flatbread may be eaten together with raita, chutneys and pickles. The yogurt may be seasoned with coriander, roasted cumin seeds, mint, cayenne pepper, chaat masala and other herbs and spices. Etymology The word ''raita'' first appeared in print around the 19th century; it comes from the Hindi languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bread Dishes
This is a list of bread dishes and foods, which use bread as a primary ingredient. Bread is a staple food prepared from a dough of flour and water, usually by baking. Throughout recorded history it has been popular around the world and is one of the oldest artificial foods, having been of importance since the dawn of agriculture. Bread dishes * * * * * * Bread bowl * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Bread salads * Cappon magro * Dakos * Fattoush * Panzanella Bread soups Bread soup is a simple soup that mainly consists of stale bread in a meat or vegetable broth. * * * * * * * * Jeon Jeon refers to many pancake-like dishes in Korean cuisine. * * * * * * * File:Korean pancake-Bindaetteok-04.jpg, Bindaetteok File:Korean pancake-Jindallae hwajeon-03.jpg, Hwajeon File:Korean pancake-Haemul pajeon-03.jpg, Pajeon Pancakes Paratha Paratha is a flatbread that originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Cuisine
Indian cuisine consists of a variety of regional and traditional cuisines native to India. Given the diversity in soil, climate, culture, ethnic groups, and occupations, these cuisines vary substantially and use locally available spices, herbs, vegetables, and fruits. Indian food is also heavily influenced by religion, in particular Hinduism and Islam, cultural choices and traditions. Historical events such as invasions, trade relations, and colonialism have played a role in introducing certain foods to this country. The Columbian discovery of the New World brought a number of new vegetables and fruit to India. A number of these such as potatoes, tomatoes, chillies, peanuts, and guava have become staples in many regions of India. Indian cuisine has shaped the history of international relations; the spice trade between India and Europe was the primary catalyst for Europe's Age of Discovery. Spices were bought from India and traded around Europe and Asia. Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |