|
Glyptodont
Glyptodonts are an extinct subfamily of large, heavily armoured armadillos. They arose in South America around 48 million years ago and spread to southern North America after the continents became connected several million years ago. The best-known genus within the group is ''Glyptodon''. While they were formerly considered to constitute the distinct family Glyptodontidae, in 2016, an analysis of ''Doedicurus'' Mitochondrial DNA (also known as mtDNA / mDNA) found that it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, glyptodonts and all armadillos but '' Dasypus'' were relocated to a new family, Chlamyphoridae, and glyptodonts were demoted from the former family Glyptodontidae to a subfamily. Evolution Glyptodonts first evolved during the Eocene in South America, which remained their center of species diversity. For example, an Early Miocene glyptodont with many primitive feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptotherium
''Glyptotherium'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved beast') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Early Pliocene, about 4.9 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 7,000 years ago, in the United States, Mexico, Guatemala, Costa Rica, Honduras, El Salvador, Panama, Venezuela, and Brazil. The genus was first described in 1903 by American paleontologist Henry Fairfield Osborn with the type species being, ''G. texanum,'' based on fossils that had been found in the Pliocene Blancan Beds in Llano Estacado, Texas, USA. The genus has since been discovered in many more fossil sites. Another species, ''G. cylindricum'', was named in 1912 by fossil hunter Barnum Brown on the basis of a partial carapace, teeth, and several additional fossils that had been unearthed from the Pleistocene deposits in Jalisco, Mexico. Glyptodonts were typically large, graviportal, herbivorous armadillos with armored carapaces that were made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doedicurus
''Doedicurus'', or ''Dædicurus'', is an extinct genus of glyptodont from South America containing one species, ''D. clavicaudatus''. Glyptodonts are a member of the family Chlamyphoridae, which also includes some modern armadillo species, and they are classified in the superorder Xenarthra alongside sloths and anteaters. Being a glyptodont, it was a rotund animal with heavy armor and a carapace. Averaging at an approximate , it was one of the largest glyptodonts to have ever lived. Though glyptodonts were quadrupeds, large ones like ''Doedicurus'' may have been able to stand on two legs like other xenarthrans. It notably sported a spiked tail club, which may have weighed in life, and it may have swung this in defense against predators or in fights with other ''Doedicurus'' at speeds of perhaps . ''Doedicurus'' was likely a grazer, but its teeth and mouth, like those of other glyptodonts, seem unable to have chewed grass effectively, which may indicate a slow metabolism. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
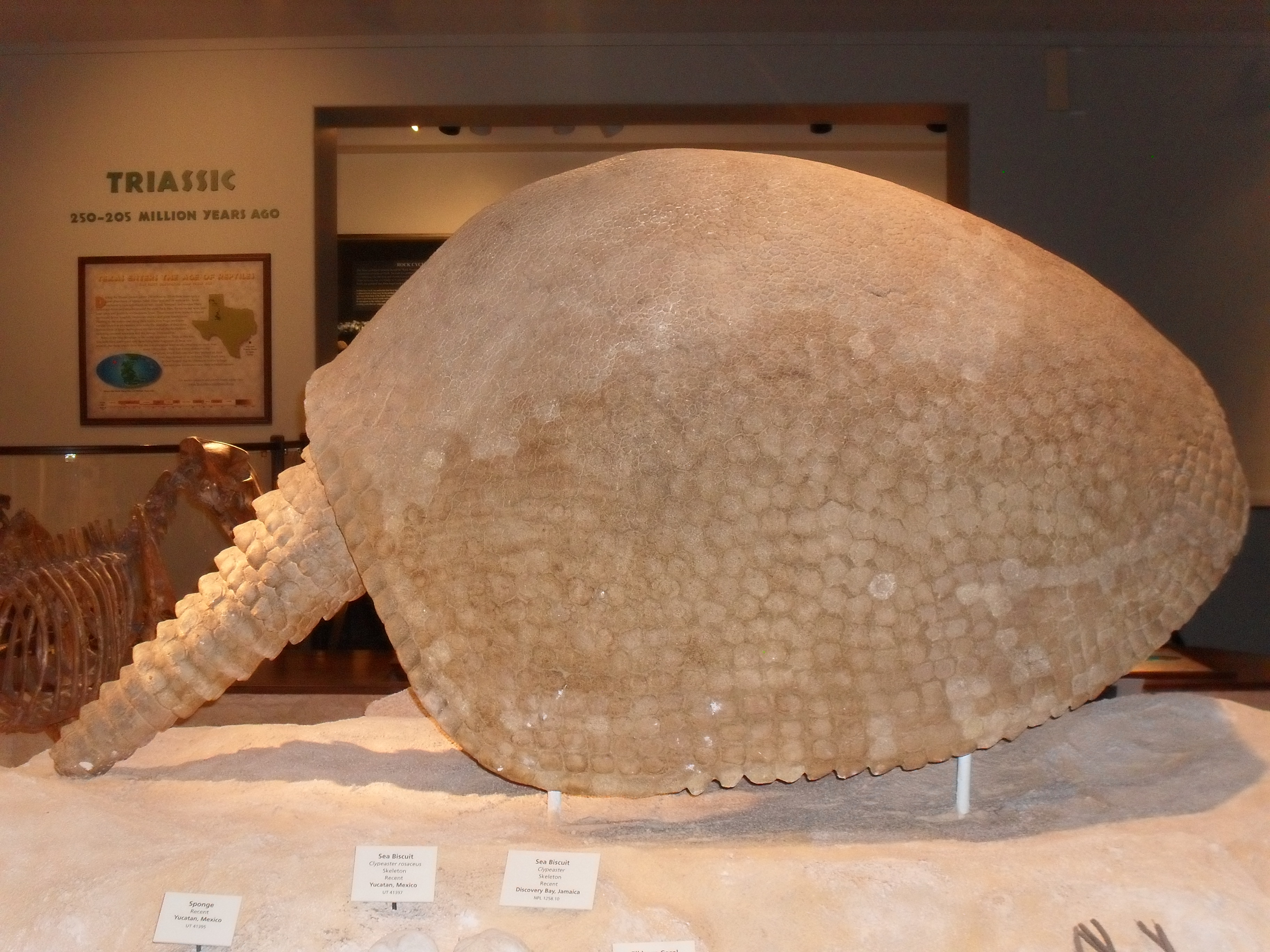
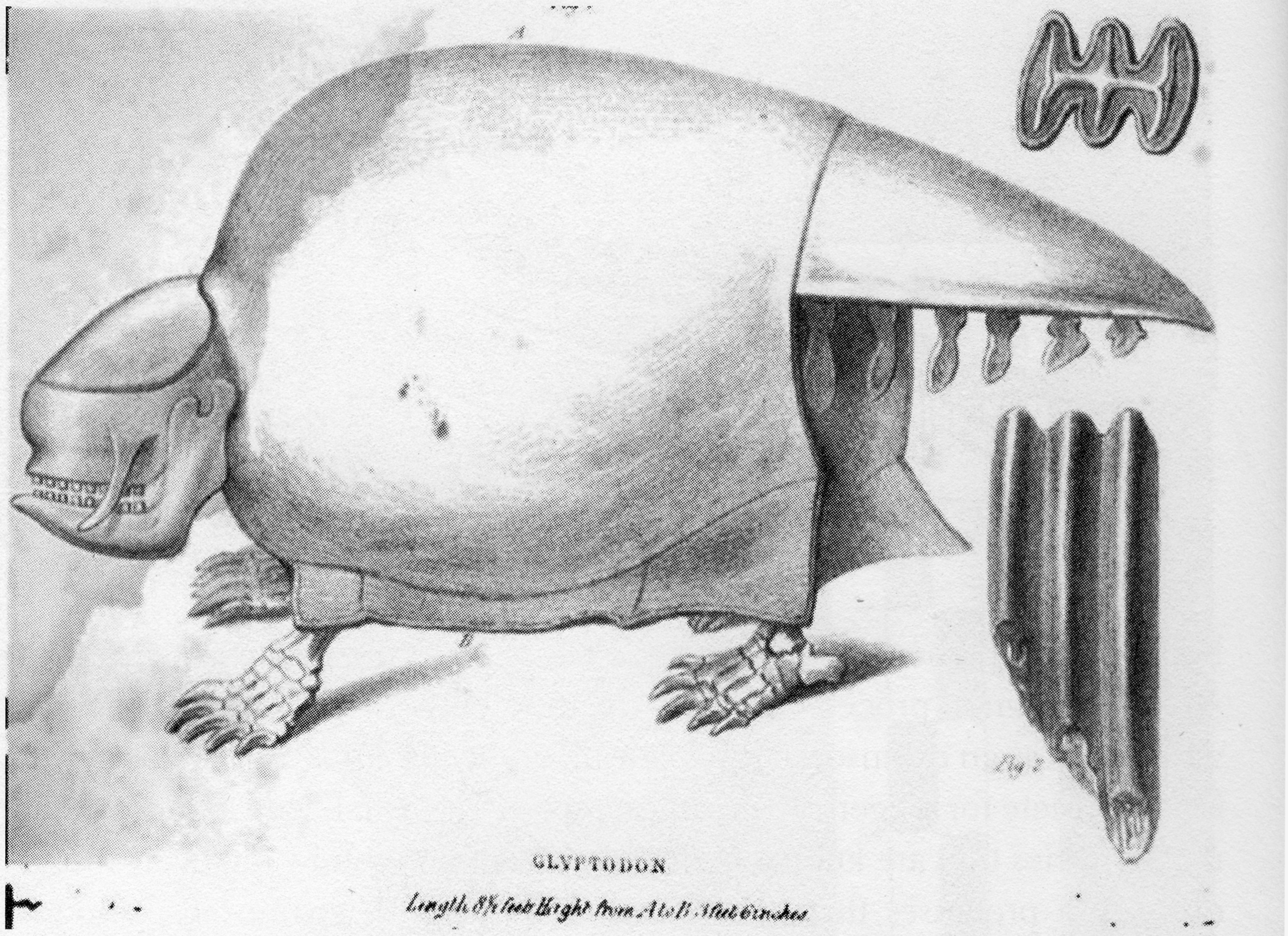
Glyptodon
''Glyptodon'' (from Greek for 'grooved or carved tooth': γλυπτός 'sculptured' and ὀδοντ-, ὀδούς 'tooth') is a genus of glyptodont (an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos) that lived from the Pleistocene, around 2.5 million years ago, to the Early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, and Colombia. It was the first named extinct cingulate and is the type genus of Glyptodontinae, and, or, Glyptodontinae. Many species have been named for the genus, though few are considered valid, and it is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. Hundreds of specimens have been referred to the genus, but the holotype, or name specimen, of the type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British paleontologist Sir Richard Owen. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle, 800–840 kg (1,760–1,850 lb). With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superfic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosclerocalyptus
''Neosclerocalyptus'' was an extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pliocene, Pleistocene, and Holocene of Southern South America, mostly Argentina. It was small compared to many Glyptodonts at only around 2 meters long and 360 kilograms. Etymology The genus name ''Neosclerocalyptus'' is a modification of the name of its synonym, ''Sclerocalyptus'', and derived from the Greek roots ''neo-'' meaning "young" or "new", ''scleros'' meaning "hard", and -''calyptos'' meaning "covering", referring to the armored carapace of the animal. The type species, ''N. ornatus'', specific name meaning is "adorned" after the patterns on the holotype osteoderms. History and taxonomy Fossils of ''Neosclerocalyptus'' were first collected by a "Sir Woodbine Parish, KH" from the Pleistocene strata near the Matanzas River in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, but where later sent to the Royal College of Surgeons in the UK, where they were later described by paleontologist Sir Richard Owen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplophorus
''Hoplophorus'' is an extinct genus of glyptodont, a subfamily of armadillos . The only confidently known species was ''H. euphractus'', found in Pleistocene deposits in Brazil, though fossils possibly from another species are known from Bolivia. History and taxonomy ''Hoplophorus euphractus'' was first described in 1837 by Danish paleontologist Peter Wilhelm Lund on the basis of fossilized osteoderms and carapace fragments unearthed in the Upper Pleistocene cave deposits in Lagoa Santa, Minas Gérais, Brazil.Lund, P. W. (1837). ''Blik paa Brasiliens dyreverden foÈr sidste jordomvaeltning''. Popp. This was one of the first glyptodonts to be described. Lund attributed many other fossils to the species over several years, including limb bones, teeth, vertebrae, foot remains, and an incomplete skull. Lund later erected 3 more ''Hoplophorus'' species based on the fossils from Lago Santa: ''H. selloi, H. minor,'' & ''H. meyeri.'' All three didn’t receive proper descriptions, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelenkura
''Kelenkura'' is an extinct genus of heavily armored mammals belonging to the subfamily Glyptodontinae, from the family Chlamyphoridae that contain most of the modern armadillos. It was a medium-sized South American animal, distantly related to ''Doedicurus''. Fossils of this genus were recovered in the Arroyo Chasicó Formation and in the Loma de Las Tapias Formation of Argentina in rocks dating back to the Late Miocene epoch. Discovery and etymology The presence of glyptodonts in the Arroyo Chasicó Formation was known from fragmentary remains since 1926. In 2005, a new, more complete specimen was unearthed from a river bed in the formation. Alfredo E. Zurita and Silvia A. Aramayo described it in 2007 as PV-UNS-260, a well preserved skeleton from the Arroyo Chasicó including a partially complete skull and carapace, a complete right femur, several caudal rings and a complete caudal tube, alongside several limb bones and isolated osteoderms. They assigned the skeleton to the al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucinepeltus
''Eucinepeltus'' (also often called, historically, ''Encinepeltus'') is an extinct genus of Glyptodont. It lived during the Early Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America. Description Like all glyptodonts, this genus was characterized by its dorsal armor composed of numerous osteoderms fused together. ''Eucinepeltus'' was larger than other basal glyptodonts such as ''Propalaehoplophorus'', with a skull reaching 20 centimeters in length, and wider than most of its relative species. The cephalic shield was composed of 11-15 large welded bony plates, presenting a central convexity often perforated. The skull was depressed and presented a rather elongated muzzle. The dental characteristics of ''Eucinepeltus'' includes lower molars increasing in size from the first to the fifth molar ; a first and second lower molars elliptical, convex in the internal side and with a large notch and a corresponding perpendicular groove in the back ; bilobed third and four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptatelus
''Glyptatelus'' is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Late Eocene to the Middle Oligocene in what is now Argentina and Bolivia. Description This genus is only known from very fragmentary remains from its carapace. From a comparison between those fossils and those of its later relatives, it is assumed that ''Glyptatelus'' was a rather small glyptodont, with a carapace made of polygonal osteoderms welded together to form a rigid structure. The shape of those osteoderms was hexagonal ; they featured a large central figure displaced a bit backwards, from which radial grooves branched off, separating some peripheral polygonal figures. In the older forms attributed to ''Glyptatelus'', the individual osteoderms usually had a diameter of 1.3 millimeters and a height of 9 millimeters, while more recent forms possessed osteoderms with a diameter of 25–30 millimeters and a height of 20 millimeters. A fragment of mandible attributed to ''Glyptatelus'' preserve a tooth divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuryurus
''Neuryurus'' is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Late Pliocene to the Early Holocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America. Description This genus, like all glyptodonts, had a heavy armor formed by osteoderms fused together, protecting most of its body. ''Neuryurus'' was large-sized, reaching three meters in length. The carapace resembled that of other glyptodonts such as ''Trachycalyptus'', with thick and rectangular-shaped osteoderms, loosely fused by a serrated suture. The outer surface of those osteoderms was evenly dotted. The tail was protected by a caudal tube ; this structure, in ''Neuryurus'', was depressed, not consolidated and mostly formed by osteoderms similar to each others. The lateral osteoderms had large elliptical structures, with a central conical prominence, reminding those of ''Hoplophorus'' and ''Panochthus''. Some marginal plates had an elevated and conical central area. The cephalic shield resembled that of ''Panoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterostemma Depressa
''Asterostemma'' is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Middle Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America. Description Like all its close relatives, ''Asterostemma'' had a carapace made of fused osteoderms, protecting most of its body. The ornamentation of its osteoderms was similar to other basal genera of glyptodonts, such as ''Propalaehoplophorus'', with clear and shallow furrows, and the central figures were rounded. Those were surrounded by a single row of peripheral figures. The caudal cuirass of ''Asterostemma'' was formed by rings and a caudal tube, forming a long and thin structure, similar to those of modern armadillos. Classification ''Asterostemma depressa'' was first described by Florentino Ameghino in 1889, based on fossil remains found in Middle Miocene terrains of Argentina. Other species attributed to this genus, such as ''A. acostae'', ''A. gigantea'', and ''A. venezolensis'' ; subsequent revisions of the fossil re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaehoplophorus
''Palaehoplophorus'' (also spelled, historically, ''Palaeohoplophorus'') is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America. Description This animal, like all glyptodonts, had a thick carapace, composed of numerous osteoderm fused together, covering a large part of its body. The plates of its carapace bore a medium-sized, depressed central figure, surrounded by a wrinkled peripheral zone, divided by barely defined furrows and irregular tubercles. Large perforations opened in the furrows around the central figure and between the peripheral figures. The tail was protected by a series of mobile osteoderm rings, presenting a similar ornamentation, and by a terminal straight and cylindrical "tube", formed by contiguous, rounded osteoderms, separated by deep grooves with large perforations, similar to those of the carapace. The terminal and lateral osteoderms were almost identical to each other. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreostemma
''Boreostemma'' is an extinct genus of glyptodonts from northern South America. Fossils assigned to the genus were first described as belonging to '' Asterostemma'' from southern South America, but have been placed in the new genus ''Boreostemma'' by Carlini et al. in 2008. The type species is ''B. pliocena''. Fossils of ''Boreostemma'' have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, in Peru and Venezuela. Etymology The genus name ''Boreostemma'' is a combination of ''stemma'', taken from '' Asterostemma'', and ''boreo'' is derived from borealis, meaning "northern", to distinguish the northern South American genus from the southern ''Asterostemma''. Species Four species have been described in the genus ''Boreostemma''.''Boreostemma'' at |