|
Glycol Cleavage
Glycol cleavage is a specific type of organic chemistry oxidation. The carbon–carbon bond in a vicinal diol (glycol) is cleaved and instead the two oxygen atoms become double-bonded to their respective carbon atoms. Depending on the substitution pattern in the diol, these carbonyls can be either ketones or aldehydes. Glycol cleavage is an important reaction in the laboratory because it is useful for determining the structures of sugars. After cleavage takes place the ketone and aldehyde fragments can be inspected and the location of the former hydroxyl groups ascertained. Reagents Periodic acid (HIO4), (diacetoxyiodo)benzene (PhI(OAc)2) and lead tetraacetate (Pb(OAc)4) are the most common reagents used for glycol cleavage, processes called the Malaprade reaction and Criegee oxidation, respectively. These reactions are most efficient when a cyclic intermediate can form, with the iodine or lead atom linking both oxygen atoms. The ring then fragments, with breakage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaprade Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Malaprade reaction or Malaprade oxidation is a glycol cleavage reaction in which a vicinal diol is oxidized by periodic acid or a periodate salt to give the corresponding carbonyl functional groups. The reaction was first reported by in 1928 and also works with β-aminoalcohols. File:Malaprade.svg, Malaprade reaction File:Glykolspaltung RMa cis trans Malaprade.svg, Malaprade reaction mechanism References See also * Criegee oxidation The Criegee oxidation is a glycol cleavage reaction in which vicinal diols are oxidized to form ketones and aldehydes using lead tetraacetate. It is analogous to the Malaprade reaction, but uses a milder oxidant. This oxidation was discovere ... {{organic-chem-stub Organic oxidation reactions Name reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxylation
Dihydroxylation is the process by which an alkene is converted into a vicinal diol. Although there are many routes to accomplish this oxidation, the most common and direct processes use a high-oxidation-state transition metal (typically osmium or manganese). The metal is often used as a catalyst, with some other stoichiometric oxidant present. In addition, other transition metals and non-transition metal methods have been developed and used to catalyze the reaction. Mechanism In the dihydroxylation mechanism, a ligand first coordinates to the metal catalyst (depicted as osmium), which dictates the chiral selectivity of the olefin. The alkene then coordinates to the metal through a +2cycloaddition, and the ligand dissociates from the metal catalyst. Hydrolysis of the olefin then yields the vicinal diol, and oxidation of the catalyst by a stoichiometric oxidant regenerates the metal catalyst to repeat the cycle. The concentration of the olefin is crucial to the enantiomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KMnO4. It is a purplish-black crystalline salt, that dissolves in water as K+ and , an intensely pink to purple solution. Potassium permanganate is widely used in the chemical industry and laboratories as a strong oxidizing agent, and also as a medication for dermatitis, for cleaning wounds, and general disinfection. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2000, worldwide production was estimated at 30,000 tonnes. Properties Potassium permanganate is the potassium salt of the tetrahedral transition metal oxo complex permanganate, in which four O2- ligands are bound to a manganese(VII) center. Structure KMnO4 forms orthorhombic crystals with constants: ''a'' = 910.5 pm, ''b'' = 572.0 pm, ''c'' = 742.5 pm. The overall motif is similar to that for barium sulfate, with which it forms solid solutions. In the solid (as in solution), each MnO4− centre is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycol Cleavage
Glycol cleavage is a specific type of organic chemistry oxidation. The carbon–carbon bond in a vicinal diol (glycol) is cleaved and instead the two oxygen atoms become double-bonded to their respective carbon atoms. Depending on the substitution pattern in the diol, these carbonyls can be either ketones or aldehydes. Glycol cleavage is an important reaction in the laboratory because it is useful for determining the structures of sugars. After cleavage takes place the ketone and aldehyde fragments can be inspected and the location of the former hydroxyl groups ascertained. Reagents Periodic acid (HIO4), (diacetoxyiodo)benzene (PhI(OAc)2) and lead tetraacetate (Pb(OAc)4) are the most common reagents used for glycol cleavage, processes called the Malaprade reaction and Criegee oxidation, respectively. These reactions are most efficient when a cyclic intermediate can form, with the iodine or lead atom linking both oxygen atoms. The ring then fragments, with breakage of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a larger hydrocarbon backbone. It is one factor in determining a molecule's properties and reactivity. A side chain is also known as a pendant chain, but a pendant group (side group) has a different definition. Conventions The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl (saturated hydrocarbon) group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon groups in structure diagrams, X, Y, or Z are often used. History The ''R'' symbol was introduced by 19th-century French chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt, who advocated its adoption on the grounds that it would be widely recognizable and intelligible given its correspondence in multiple European languages to the initial letter of "root" or "residue": ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Intermediate
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation. When their existence is indicated, reactive intermediates can help explain how a chemical reaction takes place. Most chemical reactions take more than one elementary step to complete, and a reactive intermediate is a high-energy, yet stable, product that exists only in one of the intermediate steps. The series of steps together make a reaction mechanism. A reactive intermediate differs from a reactant or product or a simple reaction intermediate only in that it cannot usually be isolated but is sometimes observable only through fast spectroscopic methods. It is stable in the sense that an elementary reaction forms the reactive intermediate and the elementary reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
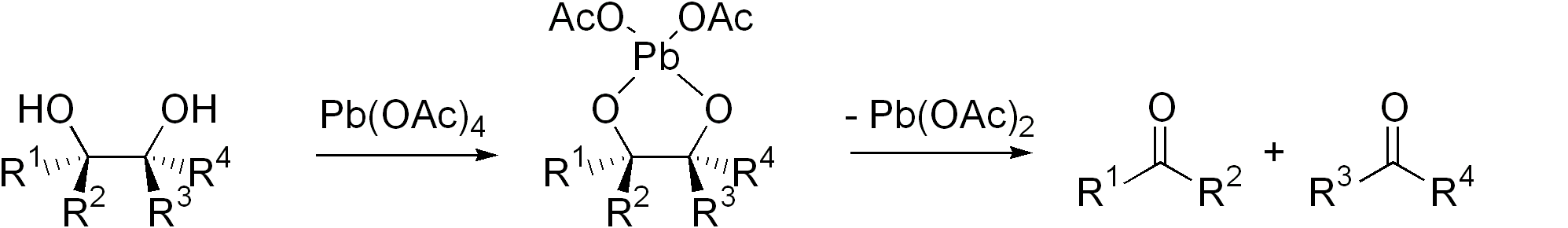
Criegee Oxidation
The Criegee oxidation is a glycol cleavage reaction in which vicinal diols are oxidized to form ketones and aldehydes using lead tetraacetate. It is analogous to the Malaprade reaction, but uses a milder oxidant. This oxidation was discovered by Rudolf Criegee and coworkers and first reported in 1931 using ethylene glycol as the substrate. The rate of the reaction is highly dependent on the relative geometric position of the two hydroxyl groups, so much so that diols that are ''cis'' on certain rings can be reacted selectively as opposed to those that are ''trans'' on them. It was heavily stressed by Criegee that the reaction must be run in anhydrous solvents, as any water present would hydrolyze the lead tetraacetate; however, subsequent publications have reported that if the rate of oxidation is faster than the rate of hydrolysis, the cleavage can be run in wet solvents or even aqueous solutions. For example, glucose, glycerol, mannitol, and xylose can all undergo a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(IV) Acetate
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an organometallic compound with chemical formula . It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis. Structure In the solid state the lead(IV) centers are coordinated by four acetate ions, which are bidentate, each coordinating via two oxygen atoms. The lead atom is 8 coordinate and the O atoms form a flattened trigonal dodecahedron. Preparation It is typically prepared by treating of red lead with acetic acid and acetic anhydride (), which absorbs water. The net reaction is shown: :Pb3O4 + 4 Ac2O -> Pb(OAc)4 + 2 Pb(OAc)2 The remaining lead(II) acetate can be partially oxidized to the tetraacetate: :2 Pb(OAc)2 + Cl2 -> Pb(OAc)4 + PbCl2 Reagent in organic chemistry Lead tetraacetate is a strong oxidizing agent, a source of acetyloxy groups and a general reagent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicinal (chemistry)
In chemistry the descriptor vicinal (from Latin ''vicinus'' = neighbor), abbreviated ''vic'', describes any two functional groups bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms (i.e., in a 1,2-relationship). Relation of atoms in a molecule For example, the molecule 2,3-dibromobutane carries two vicinal bromine atoms and 1,3-dibromobutane does not. Mostly, the use of the term vicinal is restricted to two ''identical'' functional groups. Likewise in a ''gem-''dibromide the prefix ''gem'', an abbreviation of geminal, signals that both bromine atoms are bonded to the ''same'' atom (i.e., in a 1,1-relationship). For example, 1,1-dibromobutane is geminal. While comparatively less common, the term hominal has been suggested as a descriptor for groups in a 1,3-relationship. Like other such descriptors as syn, anti, exo or endo, the description ''vicinal'' helps explain how different parts of a molecule are related to each other either structurally or spatially. The vicinal adjective is sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Diacetoxyiodo)benzene
(Diacetoxyiodo)benzene, also known as phenyliodine(III) diacetate (PIDA) is a hypervalent iodine chemical with the formula . It is used as an oxidizing agent in organic chemistry. Preparation This reagent was originally prepared by Conrad Willgerodt by reacting iodobenzene with a mixture of acetic acid and peracetic acid: :CHI + CHCOH + CHCOH → CHI(OCCH) + HO PIDA can also be prepared from iodosobenzene and glacial acetic acid: :CHIO + 2 CHCOH → CHI(OCCH) + HO More recent preparations direct from iodine, acetic acid, and benzene have been reported, using either sodium perborate or potassium peroxydisulfate as the oxidizing agent: : CH + I + 2 CHCOH + KSO → CHI(OCCH) + KI + HSO + KHSO The PIDA molecule is termed hypervalent as its iodine atom (technically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Acid
Periodic acid ( ) is the highest oxoacid of iodine, in which the iodine exists in oxidation state +7. Like all periodates it can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula , and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula . Periodic acid was discovered by Heinrich Gustav Magnus and C. F. Ammermüller in 1833. Synthesis Modern industrial scale production involves the oxidation of a solution of sodium iodate under alkaline conditions, either electrochemically on a anode, or by treatment with chlorine: : (counter ions omitted for clarity) ''E''° = -1.6 V : Orthoperiodic acid can be dehydrated to give metaperiodic acid by heating to 100 °C under reduced pressure. : Further heating to around 150 °C gives iodine pentoxide () rather than the expected anhydride ''diiodine heptoxide'' (). Metaperiodic acid can also be prepared from various orthoperiodates by treatment with dilute nitric acid. Properties Orthoperiodic acid has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |