|
Global Aphasia
Global aphasia is a severe form of nonfluent aphasia, caused by damage to the left side of the brain, that affects Language processing in the brain, receptive and Expressive language disorder, expressive language skills (needed for both written and oral language) as well as auditory and visual comprehension.Brookshire, R. H. (2007). Introduction to neurogenic communication disorders (Seventh edition.). St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier. Acquired impairments of communicative abilities are present across all language modalities, impacting language production, comprehension, and repetition.Goodglass, H., and Kaplan, E. (1983). The assessment of aphasia and related disorders. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger. Patients with global aphasia may be able to verbalize a few short utterances and use non-word neologisms,Manasco, H. M. (2014). Introduction to Neurogenic Communication Disorders. Burlington, MA: Jones & Barlett Learning. but their overall production ability is limited. Their ability t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
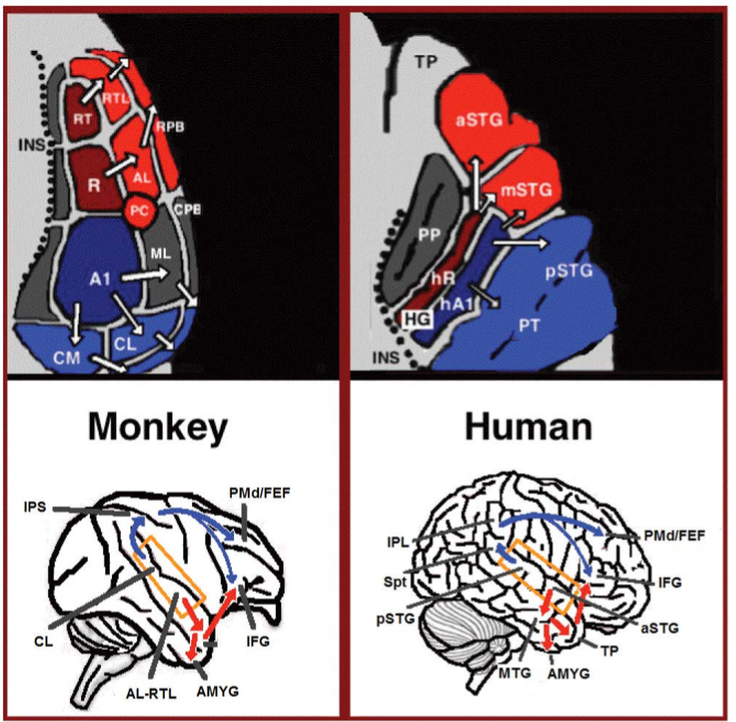
Language Processing In The Brain
Language processing refers to the way humans use words to communicate ideas and feelings, and how such communications are processed and understood. Language processing is considered to be a uniquely human ability that is not produced with the same grammatical understanding or systematicity in even human's closest primate relatives. Throughout the 20th century the dominant model for language processing in the brain was the Geschwind-Lichteim-Wernicke model, which is based primarily on the analysis of brain damaged patients. However, due to improvements in intra-cortical electrophysiological recordings of monkey and human brains, as well non-invasive techniques such as fMRI, PET, MEG and EEG, a dual auditory pathway has been revealed and a two-streams model has been developed. In accordance with this model, there are two pathways that connect the auditory cortex to the frontal lobe, each pathway accounting for different linguistic roles. The auditory ventral stream pathway is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressive Language Disorder
Expressive language disorder is a communication disorder in which there are difficulties with verbal and written expression. It is a specific language impairment characterized by an ability to use expressive spoken language that is markedly below the appropriate level for the mental age, but with a language comprehension that is within normal limits. There can be problems with vocabulary, producing complex sentences, and remembering words, and there may or may not be abnormalities in articulation. Careful diagnosis is also important because "atypical language development can be a secondary characteristic of other physical and developmental problems that may first manifest as language problems". Models of language production Willem Levelt outlined the currently accepted theory of speech production. Words are produced after the concept waiting to be produced is conceptualized, related words are selected, encoded and the sound waves of speech are produced. Association with language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
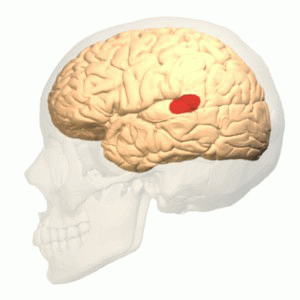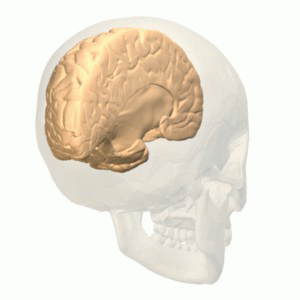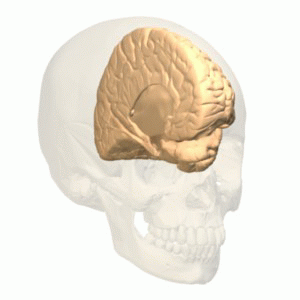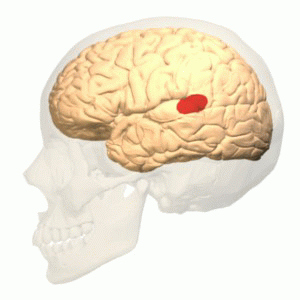
Broca's Area
Broca's area, or the Broca area (, also , ), is a region in the frontal lobe of the dominant Cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere, usually the left, of the Human brain, brain with functions linked to speech production. Language processing in the brain, Language processing has been linked to Broca's area since Pierre Paul Broca reported impairments in two patients. They had lost the ability to speak after injury to the posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pars triangularis) (BA45) of the brain. Since then, the approximate region he identified has become known as Broca's area, and the deficit in language production as Broca's aphasia, also called expressive aphasia. Broca's area is now typically defined in terms of the pars opercularis and pars triangularis of the inferior frontal gyrus, represented in Korbinian Brodmann, Brodmann's Brodmann area, cytoarchitectonic map as Brodmann area 44 and Brodmann area 45 of the dominant hemisphere. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wernicke's Area
Wernicke's area (; ), also called Wernicke's speech area, is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex that are linked to speech, the other being Broca's area. It is involved in the comprehension of written and spoken language, in contrast to Broca's area, which is primarily involved in the production of language. It is traditionally thought to reside in Brodmann area 22, which is located in the superior temporal gyrus in the dominant cerebral hemisphere, which is the left hemisphere in about 95% of right-handed individuals and 70% of left-handed individuals. Damage caused to Wernicke's area results in receptive, fluent aphasia. This means that the person with aphasia will be able to fluently connect words, but the phrases will lack meaning. This is unlike non-fluent aphasia, in which the person will use meaningful words, but in a non-fluent, telegraphic manner. Structure Wernicke's area is traditionally viewed as being located in the posterior section of the superior tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiparesis
Hemiparesis, or unilateral paresis, is weakness of one entire side of the body (''wikt:hemi-#Prefix, hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia is, in its most severe form, complete paralysis of half of the body. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia can be caused by different medical conditions, including congenital causes, trauma, tumors, or stroke.Detailed article about hemiparesis at Disabled-World.com Signs and symptoms Depending on the type of hemiparesis diagnosed, different bodily functions can be affected. Some effects are expected (e.g., partial paralysis of a limb on the affected side). Other impairments, though, can at first seem completely non-related to the limb weakness but are, in fact, a direct result of the damage to the affected side of the brain. |
Apraxia Of Speech
Apraxia of speech (AOS), also called verbal apraxia, is a speech sound disorder affecting an individual's ability to translate conscious speech plans into motor plans, which results in limited and difficult speech ability. By the definition of apraxia, AOS affects volitional (willful or purposeful) movement pattern. However, AOS usually also affects automatic speech. Individuals with AOS have difficulty connecting speech messages from the brain to the mouth. AOS is a loss of prior speech ability resulting from a brain injury such as a stroke or progressive illness. Developmental verbal dyspraxia (DVD), also known as childhood apraxia of speech (CAS) and developmental apraxia of speech (DAS), is an inability to utilize motor planning to perform movements necessary for speech during a child's language learning process. Although the causes differ between AOS and DVD, the main characteristics and treatments are similar. Presentation Apraxia of speech (AOS) is a neurogenic commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexia (condition)
Dyslexia, also known until the 1960s as word blindness, is a disorder characterized by reading below the expected level for one's age. Different people are affected to different degrees. Problems may include difficulties in spelling words, reading quickly, writing words, "sounding out" words in the head, pronouncing words when reading aloud and understanding what one reads. Often these difficulties are first noticed at school. The difficulties are involuntary, and people with this disorder have a normal desire to learn. People with dyslexia have higher rates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), developmental language disorders, and difficulties with numbers. Dyslexia is believed to be caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Some cases run in families. Dyslexia that develops due to a traumatic brain injury, stroke, or dementia is sometimes called "acquired dyslexia" or alexia. The underlying mechanisms of dyslexia result from differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Word Deafness
Auditory verbal agnosia (AVA), also known as pure word deafness, is the inability to comprehend speech. Individuals with this disorder lose the ability to understand language, repeat words, and write from dictation. Some patients with AVA describe hearing spoken language as meaningless noise, often as though the person speaking was doing so in a foreign language. However, spontaneous speaking, reading, and writing are preserved. The maintenance of the ability to process non-speech auditory information, including music, also remains relatively more intact than spoken language comprehension. Individuals who exhibit pure word deafness are also still able to recognize non-verbal sounds. The ability to interpret language via lip reading The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ..., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agraphia
Agraphia is an acquired neurological disorder causing a loss in the ability to communicate through writing, either due to some form of motor dysfunction or an inability to spell. The loss of writing ability may present with other language or neurological disorders; disorders appearing commonly with agraphia are alexia, aphasia, dysarthria, agnosia, acalculia and apraxia. The study of individuals with agraphia may provide more information about the pathways involved in writing, both language related and motoric. Agraphia cannot be directly treated, but individuals can learn techniques to help regain and rehabilitate some of their previous writing abilities. These techniques differ depending on the type of agraphia. Agraphia can be broadly divided into central and peripheral categories. Central agraphias typically involve language areas of the brain, causing difficulty spelling or with spontaneous communication, and are often accompanied by other language disorders. Peripheral agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (clinical)
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homonymous Hemianopsia
Hemianopsia, or hemianopia, is a visual field loss on the left or right side of the vertical midline. It can affect one eye but usually affects both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia (or homonymous hemianopia) is hemianopic visual field loss on the same side of both eyes. Homonymous hemianopsia occurs because the right half of the brain has visual pathways for the left hemifield of both eyes, and the left half of the brain has visual pathways for the right hemifield of both eyes. When one of these pathways is damaged, the corresponding visual field is lost. Signs and symptoms Paris as seen with right homonymous hemianopsia Mobility can be difficult for people with homonymous hemianopsia. "Patients frequently complain of bumping into obstacles on the side of the field loss, thereby bruising their arms and legs." People with homonymous hemianopsia often experience discomfort in crowds. "A patient with this condition may be unaware of what he or she cannot see and frequently bumps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Cerebral Artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral artery, cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortex, insular cortices. The left and right MCAs rise from trifurcations of the internal carotid artery, internal carotid arteries and thus are connected to the anterior cerebral artery, anterior cerebral arteries and the posterior communicating artery, posterior communicating arteries, which connect to the posterior cerebral artery, posterior cerebral arteries. The MCAs are not considered a part of the Circle of Willis. Structure The middle cerebral artery divides into four segments, named by the region they supply as opposed to order of branching as the latter can be somewhat variable: *M1: The ''sphenoidal' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |