|
Glenorchy, New Zealand
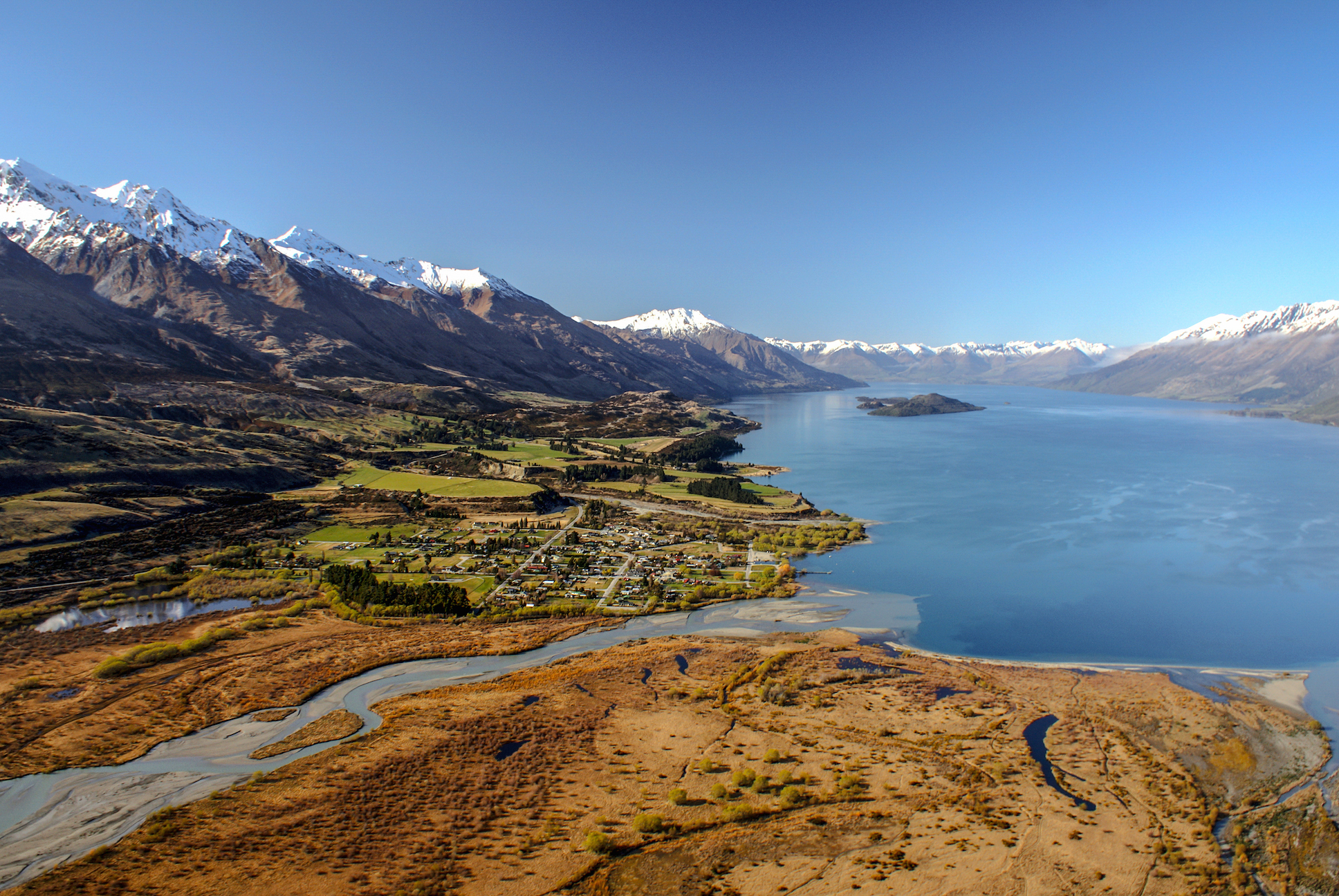
Glenorchy is a small settlement at the northern end of Lake Wakatipu in the South Island region of Otago, New Zealand. It is approximately by road or boat from Queenstown, the nearest large town. There are two pubs, a café and a range of small shops in the town catering mainly to tourists but also to the small resident population. There is also a small airstrip which caters to small planes. The locality of Paradise is nearby. The Dart River / Te Awa Whakatipu and Rees River flow into the head of Lake Wakatipu next to Glenorchy. Naming Glenorchy was named after Glen Orchy, a valley in Argyll, Scotland. Demographics Glenorchy is described by Statistics New Zealand as a rural settlement. It covers . It is part of the much larger Glenorchy statistical area. Glenorchy settlement had a population of 318 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 57 people (21.8%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 126 people (65.6%) since the 2006 census. There were 129 househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of New Zealand
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions () for local government in New Zealand, local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils (the top tier of local government), and five are administered by Unitary authority#New Zealand, unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authorities (the second tier of local government) that also perform the functions of regional councils. The Chatham Islands#Government, Chatham Islands Council is not a region but is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation. Current regions History and statutory basis The regional councils are listed in Part 1 of Schedule 2 of the Local Government Act 2002 (New Zealand), Local Government Act 2002, along with reference to the ''New Zealand Gazette, Gazette'' notices that established them in 1989. The Act requires regional councils to promote sustainable developmentthe social, economic, environmental and cultural well-bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 New Zealand Census
The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048, – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 2006 census. The 2013 census forms were the same as the forms developed for the 2011 census which was cancelled due to the February 2011 major earthquake in Christchurch. There were no new topics or questions. New Zealand's next census was conducted in March 2018. Collection methods The results from the post-enumeration survey showed that the 2013 census recorded 97.6 percent of the residents in New Zealand on census night. However, the overall response rate was 92.9 percent, with a non-response rate of 7.1 percent made up of the net undercount and people who were counted in the census but had not received a form. Results Population and dwellings Population counts for New Zealand regions. Note: All figures are for the census usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, Driving (horse), driving, and Equestrian vaulting, vaulting. This broad description includes the use of horses for practical working animal, working purposes, transportation, recreational activities, artistic or cultural exercises, and animals in sport, competitive sport. Overview of equestrian activities Horses are horse training, trained and ridden for practical working purposes, such as in Mounted police, police work or for controlling herd animals on a ranch. They are also used in Horse#Sport, competitive sports including dressage, endurance riding, eventing, reining, show jumping, tent pegging, equestrian vaulting, vaulting, polo, horse racing, driving (horse), driving, and rodeo (see additional equestrian sports listed later in this article for more examples). Some popular forms of competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetboat
A jetboat is a boat propelled by a jet of water ejected from the back of the craft. Unlike a powerboat or motorboat that uses an external propeller in the water below or behind the boat, a jetboat draws the water from under the boat through an intake and into a pump-jet inside the boat, before expelling it through a nozzle at the stern. The modern jetboat was developed by New Zealand engineer Sir William Hamilton in the mid-1950s. His goal was a boat to run up the fast-flowing rivers of New Zealand that were too shallow for propellers. Previous attempts at waterjet propulsion had very short lifetimes, generally due to the inefficient design of the units and the fact that they offered few advantages over conventional propellers. Unlike these previous waterjet developments, such as Campini's and the Hanley Hydrojet, Hamilton had a specific need for a propulsion system to operate in very shallow water, and the waterjet proved to be the ideal solution. The popularity of the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fly Fishing
Fly fishing is an angling method that uses a light-weight lure—called an artificial fly—to catch fish. The fly is cast using a fly rod, reel, and specialized weighted line. The light weight requires casting techniques significantly different from other forms of casting. The flies may resemble natural invertebrates, bait-fish, or other food organisms. Fly fishing can be done in fresh or saltwater. North Americans usually distinguish freshwater fishing between cold-water species (trout, salmon) and warm-water species, notably bass. In Britain, where natural water temperatures vary less, the distinction is between game fishing for trout and salmon versus coarse fishing for other species. Techniques for fly fishing differ with habitat (lakes and ponds, small streams, large rivers, bays and estuaries, and open ocean.) Author Izaak Walton called fly fishing "The Contemplative Man's Recreation". Overview In fly fishing, fish are caught by using artificial flies that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyoning
Canyoning (canyoneering in the United States, kloofing in South Africa) is a type of mountaineering that involves travelling in canyons using a variety of techniques that may include other outdoor activities such as walking, scrambling, climbing, jumping, abseiling (rappelling), and swimming. Although non-technical descents such as hiking down a canyon (''canyon hiking'') are often referred to as ''canyoneering'', the terms ''canyoning'' and ''canyoneering'' are more often associated with technical descents — those that require abseils (rappels) and ropework, technical climbing or down-climbing, technical jumps, and/or technical swims. Canyoning is frequently done in remote and rugged settings and often requires navigational, route-finding, and other wilderness travel skills. Canyons that are ideal for canyoning are often cut into the bedrock stone, forming narrow gorges with numerous drops, beautifully sculpted walls, and sometimes spectacular waterfalls. Most canyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenstone And Caples Tracks
The Greenstone and Caples Tracks form a tramping (hiking) circuit which is located in the South Island of New Zealand. Each track can be completed by itself and are linked by the McKellar Saddle while the loop also links to several other tracks including the New Zealand Great Walk of the Routeburn Track as well as the Mavora Lakes Conservation Park tracks. All of these areas are part of the Te Wāhipounamu/South-West New Zealand World Heritage Area. Ownership and access The Caples Track follows the Caples River up the privately owned Caples Valley while the Greenstone Track follows the Greenstone River in the Greenstone Valley which is also privately owned. Much of the area is owned by the local tribe of the Ngāi Tahu Ngāi Tahu, or Kāi Tahu, is the principal Māori (tribe) of the South Island. Its (tribal area) is the largest in New Zealand, and extends from the White Bluffs / Te Parinui o Whiti (southeast of Blenheim), Mount Mahanga and Kahurangi Point ... whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Great Walks
The New Zealand Great Walks are a set of popular tramping tracks developed and maintained by the Department of Conservation. They are New Zealand's premier tracks, through areas of some of the best scenery in the country, ranging from coastlines with beaches to dense rain forests and alpine terrain. The tracks are maintained to a high standard, making it easier for visitors to explore some of the most scenic parts of New Zealand's backcountry. The walks range from length to in length and take between 3 and 6 days to complete, with the Whanganui Journey on river being long over 5 days. Only the Tongariro Northern Circuit and the Kepler Track are loop walks, all other Great Walks requiring transport to return to the starting point. History The Great Walks network was established by the Department of Conservation in 1992. The network was established both as a way to advertise hiking in New Zealand, but also as a means of managing and conserving the most popular tracks which we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
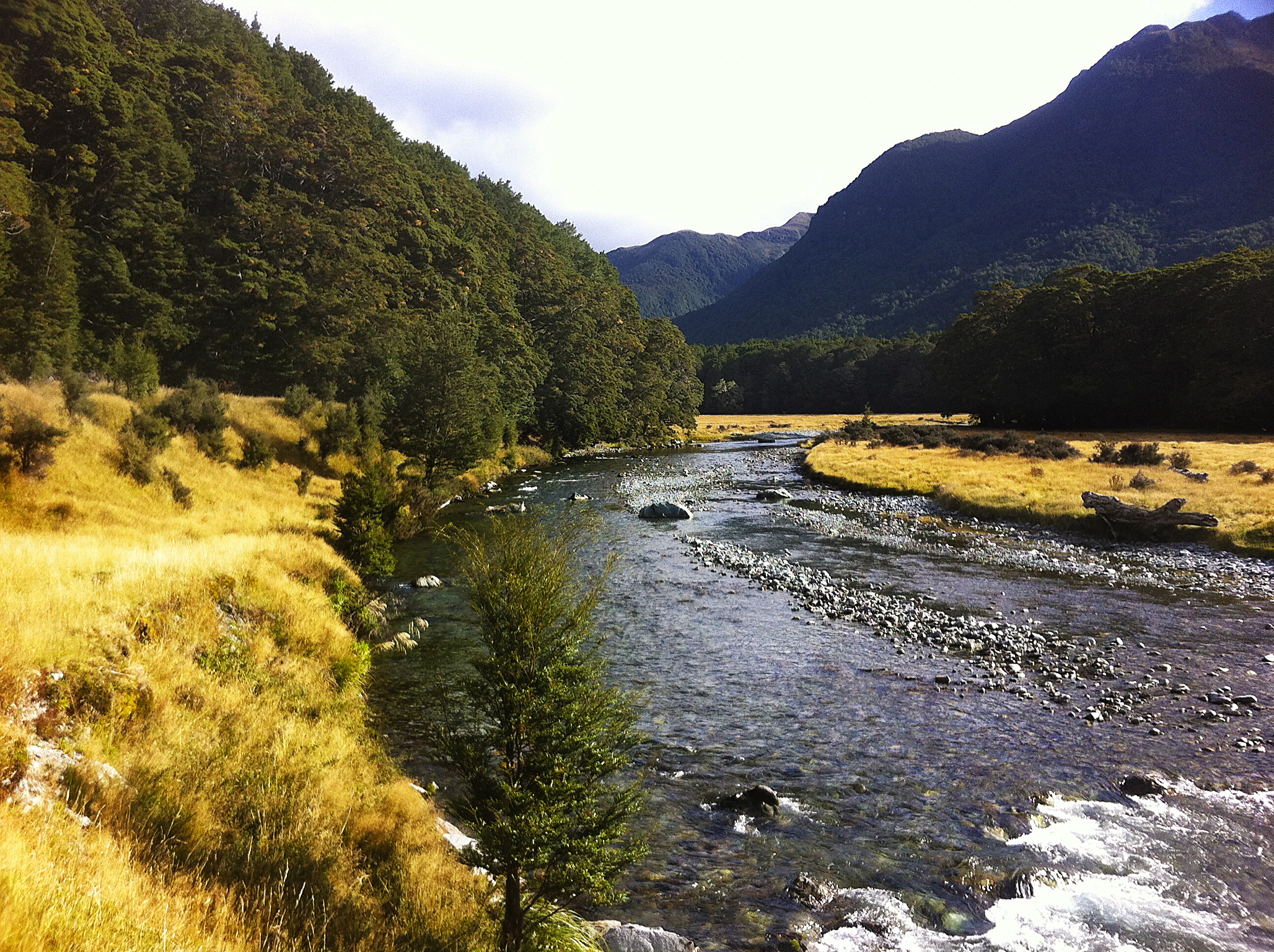
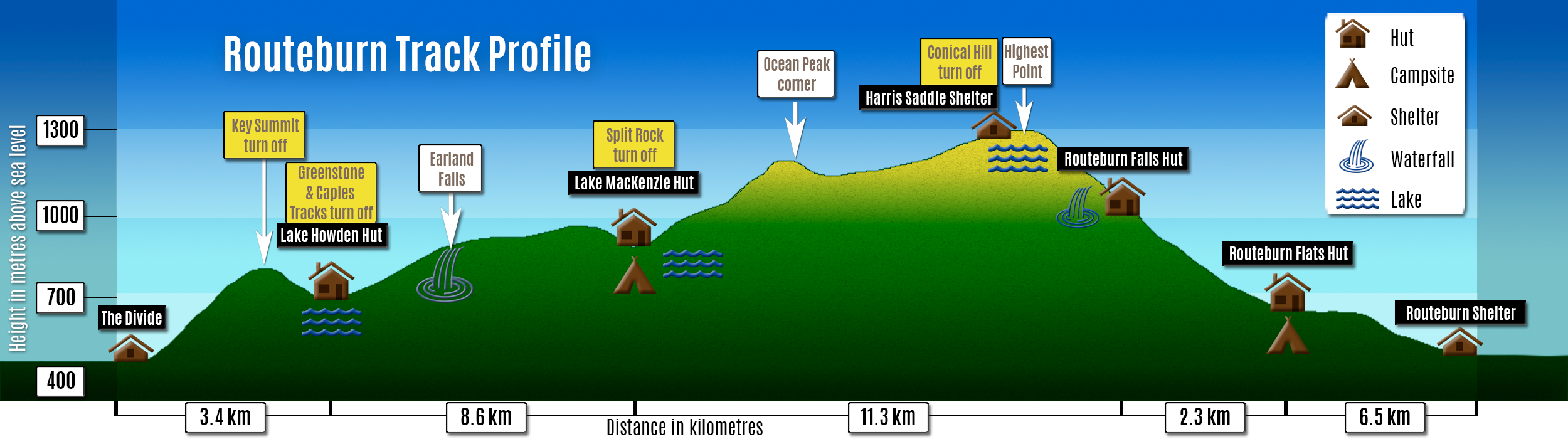
Routeburn Track
The Routeburn Track is a world-renowned, 32 km tramping (hiking) track found in the South Island of New Zealand. The track can be done in either direction, starting on the Queenstown side of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana, at the northern end of Lake Wakatipu or on the Te Anau side, at the Divide, several kilometres from the Homer Tunnel to Milford Sound / Piopiotahi. The New Zealand Department of Conservation classifies this track as a Great Walk and maintains three huts along the track: Routeburn Flats Hut, Routeburn Falls Hut, and Lake Mackenzie Hut; in addition there is an emergency shelter at Harris Saddle. The track overlaps both the Mount Aspiring and Fiordland National Parks, with the border and highest point being the Harris Saddle. There is access to another tramping area called the Greenstone and Caples Tracks from Lake Howden near The Divide. This area gets much less rain than Milford Sound / Piopiotahi, and the forests are very different, es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiordland National Park
Fiordland National Park occupies the southwest corner of the South Island of New Zealand. It is by far the largest of the 13 national parks in New Zealand, with an area of , and a major part of the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage Site. The park is administered by the Department of Conservation. of Fiordland were set aside as a national reserve in 1904, following suggestions by then-future Prime Minister Thomas Mackenzie and Southland Commissioner of Crown Lands, John Hay, that the region should be declared a national park. The area had already become a destination for trampers, following the opening up of the Milford Track from Lake Te Anau to Milford Sound in 1889 by New Zealand explorers Quintin McKinnon and Donald Sutherland, which received significant publicity from a 1908 article in the London Spectator describing it as the "Finest Walk in the World". The Fiordland "public reserve" was created as a park administered by the Department of Lands and Survey - in practical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Aspiring National Park
Mount Aspiring National Park is in the Southern Alps of the South Island of New Zealand, north of Fiordland National Park, situated in Otago and Westland regions. The park forms part of the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage site. Geography Established in 1964 as New Zealand's tenth national park, Mount Aspiring National Park covers at the southern end of the Southern Alps, directly to the west of Lake Wānaka, and is popular for tramping, walking and mountaineering. Mount Aspiring / Tititea, elevation above sea level, gives the park its name. Other prominent peaks within the park include Mount Pollux, elevation , and Mount Brewster, elevation . The Haast Pass, one of the three principal road routes over the Southern Alps, crosses the north-eastern corner of the park. History Landsborough Station added In April 2005 the Nature Heritage Fund purchased private land in the Landsborough River valley as an addition to the park. Milford Sound tunnel proposal In 2006, the Milford Dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A History of Walking'', 101-24. NYU Press, 2004. Accessed March 1, 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt9qg056.7. Religious pilgrimages have existed much longer but they involve walking long distances for a spiritual purpose associated with specific religions. "Hiking" is the preferred term in Canada and the United States; the term "walking" is used in these regions for shorter, particularly urban walks. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, the word "walking" describes all forms of walking, whether it is a walk in the park or backpacking in the Alps. The word hiking is also often used in the UK, along with rambling , hillwalking, and fell walking (a term mostly used for hillwalking in northern England). The term bushwalking is end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |