|
Glejser Test
In statistics, the Glejser test for heteroscedasticity, developed in 1969 by Herbert Glejser, regresses the residuals on the explanatory variable that is thought to be related to the heteroscedastic variance. After it was found not to be asymptotically valid under asymmetric disturbances, similar improvements have been independently suggested by Im, and Machado and Santos Silva. Steps for using the Glejser method Step 1: Estimate original regression with ordinary least squares and find the sample residuals ''e''''i''. Step 2: Regress the absolute value , ''e''''i'', on the explanatory variable that is associated with the heteroscedasticity. : \begin , e_i, & = \gamma_0 + \gamma_1 X_i + v_i \\ pt, e_i, & = \gamma_0 + \gamma_1 \sqrt + v_i \\ pt, e_i, & = \gamma_0 + \gamma_1 \frac 1 + v_i \end Step 3: Select the equation with the highest ''R''2 and lowest standard errors to represent heteroscedasticity. Step 4: Perform a t-test on the equation selected from step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteroscedasticity
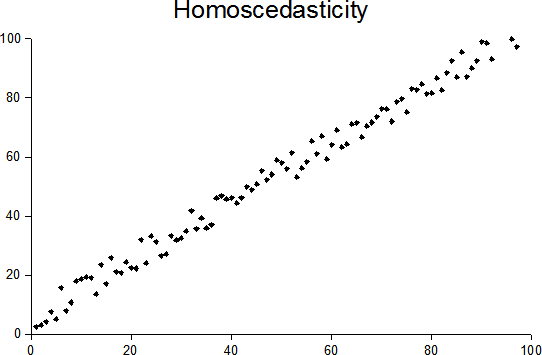
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical tests of significance that assume that the modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is still unbiased in the presence of heteroscedasticity, it is inefficient and generalized least squares should be used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Glejser
Herbert may refer to: People Individuals * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert Name * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket (''Great Expectations'' character), Pip's close friend and roommate in the Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the ''estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explanatory Variable
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical function), on the values of other variables. Independent variables, in turn, are not seen as depending on any other variable in the scope of the experiment in question. In this sense, some common independent variables are time, space, density, mass, fluid flow rate, and previous values of some observed value of interest (e.g. human population size) to predict future values (the dependent variable). Of the two, it is always the dependent variable whose variation is being studied, by altering inputs, also known as regressors in a statistical context. In an experiment, any variable that can be attributed a value without attributing a value to any other variable is called an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Econometrics
The ''Journal of Econometrics'' is a scholarly journal in econometrics. It was first published in 1973. Its current managing editors are Serena Ng and Elie Tamer, Torben Andersen and Xiaohong Chen serve as editors. The journal publishes work dealing with estimation and other methodological aspects of the application of statistical inference to economic data, as well as papers dealing with the application of econometric techniques to economics. The journal also publishes a supplement to the Journal of Econometrics which is called "Annals of Econometrics". Each issue of the Annals includes a collection of papers on a single topic selected by the editor of the issue. See also * ''Econometrics Journal'' References External links Homepage Econometrics, Journal of Econometrics journals Econometrics Econometrics is the application of Statistics, statistical methods to economic data in order to give Empirical evidence, empirical content to economic relationships.M. Hashem P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinary Least Squares
In statistics, ordinary least squares (OLS) is a type of linear least squares method for choosing the unknown parameters in a linear regression model (with fixed level-one effects of a linear function of a set of explanatory variables) by the principle of least squares: minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed dependent variable (values of the variable being observed) in the input dataset and the output of the (linear) function of the independent variable. Geometrically, this is seen as the sum of the squared distances, parallel to the axis of the dependent variable, between each data point in the set and the corresponding point on the regression surface—the smaller the differences, the better the model fits the data. The resulting estimator can be expressed by a simple formula, especially in the case of a simple linear regression, in which there is a single regressor on the right side of the regression equation. The OLS estimator is consiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Hypothesis
In scientific research, the null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim that no difference or relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. The null hypothesis is that any experimentally observed difference is due to chance alone, and an underlying causative relationship does not exist, hence the term "null". In addition to the null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is also developed, which claims that a relationship does exist between two variables. Basic definitions The ''null hypothesis'' and the ''alternative hypothesis'' are types of conjectures used in statistical tests, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions or making decisions on the basis of data. The hypotheses are conjectures about a statistical model of the population, which are based on a sample of the population. The tests are core elements of statistical inference, heavily used in the interpretation of scientific experimental data, to separate scientific claims fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R (programming Language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinformaticians and statisticians for data analysis and developing statistical software. Users have created packages to augment the functions of the R language. According to user surveys and studies of scholarly literature databases, R is one of the most commonly used programming languages used in data mining. R ranks 12th in the TIOBE index, a measure of programming language popularity, in which the language peaked in 8th place in August 2020. The official R software environment is an open-source free software environment within the GNU package, available under the GNU General Public License. It is written primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself (partially self-hosting). Precompiled executables are provided for various operating systems. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHAZAM (software)
SHAZAM is a comprehensive econometrics and statistics package for estimating, testing, simulating and forecasting many types of econometrics and statistical models. SHAZAM was originally created in 1977 by Kenneth White. Compatibility SHAZAM Version 11 is available for all Windows platforms (server, workstation or desktop) from Windows XP or later. Data management All SHAZAM editions read and write both fixed and free format text formats using the READ and FORMAT statements. Data can be stored by observation (row) or by variable (column) with or without variable names. Through the supplied Windows Environment formats such as comma-separated values (CSV), Microsoft Excel (both XLS and XLSX) may also be read and written. SHAZAM Professional Edition contains comprehensive data import capabilities through its Data Connector and SQL editor allowing the import of machine data source such as tab, space or comma separated text formats, other file-based proprietary binary formats (inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
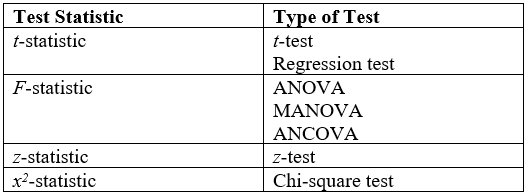
Statistical Tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |