|
Gleichenia Polypodioides
''Gleichenia polypodioides'' (L.) Sm., commonly known as coral fern, kystervaring ('kyster' meaning 'coastal' and of possible Scandinavian derivation) or ystervaring (meaning 'iron fern' in Afrikaans) due to its glabrous, brown, wiry stipes. The species is widespread in south- and east tropical Africa, southern Africa and the western Indian Ocean region. It occurs naturally in a broad coastal belt in South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Angola, Malawi, Burundi, Tanzania, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Mauritius, Réunion, Amsterdam Island and Madagascar, and was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1771 under the name ''Onoclea polypodioides''. Often forming dense and impenetrable thickets, sometimes over large areas, this rhizomatous perennial is an important pioneer in disturbed areas such as pine plantations. It is often mistakenly seen as an exotic invader rather than as a useful rehabilitation plant, a source of peat and growing medium, while showing exceptional resistance to herbicides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Smith (botanist)
__NOTOC__ Sir James Edward Smith (2 December 1759 – 17 March 1828) was an English botanist and founder of the Linnean Society. Early life and education Smith was born in Norwich in 1759, the son of a wealthy wool merchant. He displayed a precocious interest in the natural world. During the early 1780s he enrolled in the medical course at the University of Edinburgh where he studied chemistry under Joseph Black and natural history under John Walker. He then moved to London in 1783 to continue his studies. Smith was a friend of Sir Joseph Banks, who was offered the entire collection of books, manuscripts and specimens of the Swedish natural historian and botanist Carl Linnaeus following the death of his son Carolus Linnaeus the Younger. Banks declined the purchase, but Smith bought the collection for the bargain price of £1,000. The collection arrived in London in 1784, and in 1785 Smith was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. Academic career Between 1786 and 1788 Smit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Friedrich Von Gleichen
Wilhelm Friedrich von Gleichen-Rußwurm (1717–1783), Stablemaster of the Margrave of Bayreuth, was a German biologist. In 1778 he developed a process of staining micro-organisms with indigo and carmine (''Abhandlung über die Saamen - und Infusionsthierchen, und über die Erzeugung, nebst mikroskopischen Beobachtungen des Saamens der Thiere in verschiedenen Infusionen'' - Treatise on seed and infusoria, and their production, along with microscopic observations of the semen of animals in different suspensions). The fern genus ''Gleichenia'' was named in his honour. Publications''Drosophila : a contribution to its morphology and development'' - W. F. von Gleichen, 1764A description of Drosophila melanogaster ''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with Ch ... edited in 1764 by Johan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karatara
Karatara is a town in Knysna Local Municipality in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Settlement and forestry station on the Karatara River which flows southwards into Swartvlei. It is situated 5 km west of Barrington and some 40 km northwest of Knysna Knysna () is a town with 76,150 inhabitants (2019 mid-year estimates) in the Western Cape province of South Africa. and is one of the destinations on the loosely defined Garden Route tourist route. It lies at 34° 2' 6.3168'' S and 23° 2' 47 .... It was founded in 1941. The name is of Khoekhoen origin and probably means 'horse hill', after a hillock to the north. Previously the Karatara River was known as the Tsao or Witterivier. References Populated places in the Knysna Local Municipality {{WesternCape-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloukrans Pass (Western Cape)
The Bloukrans Pass is a pass through the ravine of the Bloukrans River on the R102 road between Plettenberg Bay and Jeffreys Bay in South Africa. The Bloukrans River forms the boundary between the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces. The pass no longer serves as the main route, as it has been bypassed by the Bloukrans Bridge which carries the N2 national road. The pass underwent major repairs during 2011 on the Western Cape side after flood damage in November 2007. Since November 2007, the pass is permanently closed to traffic, although pedestrians and bicycles are able to utilise the pass for their respective purposes. The only way for motorists to travel between the two provinces in this region is by using the N2 national route (Bloukrans Bridge The Bloukrans Bridge is an arch bridge located near Nature's Valley, Western Cape, South Africa. Constructed by Concor between February 1980 and June 1983, the bridge stands at a height of 216m above the Bloukrans River. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Zambesiaca
''Flora Zambesiaca'' is an ongoing botanical project aimed at achieving a full account of the flowering plants and ferns of the Zambezi River basin covering Zambia, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and the Caprivi Strip, and is published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. The work is published in parts or whole volumes as and when the relevant families are completed, and is currently (2012) over the halfway mark. Some 24 500 plant species have been described so far. The majority of the line illustration plates in the first volume were by Miss L. M. Ripley and Miss G. W. Dalby. The ''Flora Zambesiaca'' project was set in motion in 1950 by Arthur Wallis Exell when he returned to the British Museum from his wartime activities with the Government Communications Headquarters at Bletchley Park Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorus
A sorus (pl. sori) is a cluster of sporangia (structures producing and containing spores) in ferns and fungi. A coenosorus (plural coenosori) is a compound sorus composed of multiple, fused sori. Etymology This New Latin word is from Ancient Greek σωρός (''sōrós'' 'stack, pile, heap'). Structure In lichens and other fungi, the sorus is surrounded by an external layer. In some red algae, it may take the form of depression into the thallus. In ferns, the sori form a yellowish or brownish mass on the edge or underside of a fertile frond. In some species, they are protected during development by a scale or film of tissue called the indusium, which forms an umbrella-like cover. Lifecycle significance Sori occur on the sporophyte generation, the sporangia within producing haploid meiospores. As the sporangia mature, the indusium shrivels so that spore release is unimpeded. The sporangia then burst and release the spores. As an aid to identification The shape, arrangemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaflet (botany)
A leaflet (occasionally called foliole) in botany is a leaf-like part of a compound leaf. Though it resembles an entire leaf, a leaflet is not borne on a main plant stem or branch, as a leaf is, but rather on a leaf, petiole or a branch of the leaf. Compound leaves are common in many plant families and they differ widely in morphology (biology), morphology. The two main classes of compound leaf morphology are Leaf shape, palmate and pinnate. For example, a ''Cannabis, hemp'' plant has palmate compound leaves, whereas some species of ''Acacia sensu lato, Acacia'' have pinnate leaves. The ultimate free division (or leaflet) of a compound leaf, or a pinnate subdivision of a multipinnate leaf is called a pinnule or pinnula. Image:Ветвь акации.jpg, Pinnate leaf of a Fabaceae, legume with 10 leaflets Image:Mimosa Pudica.gif, ''Mimosa pudica'' folding leaflets inward. See also * Compound leaf References Plant morphology {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulcus (morphology)
In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus (pl. ''sulci'') is a furrow or fissure (Latin ''fissura'', plural ''fissurae''). It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles (including the heart), as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth. In invertebrate zoology, a sulcus is a fold, groove, or boundary, especially at the edges of sclerites or between segments. In pollen a grain that is grooved by a sulcus is termed sulcate. Examples in anatomy Liver *Ligamentum teres hepatis fissure *Ligamentum venosum fissure *Portal fissure, found in the under-surface of the liver *Transverse fissure of liver, found in the lower surface of the liver *Umbilical fissure, found in front of the liver Lung *Azygos fissure, of ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glabrousness
Glabrousness (from the Latin ''glaber'' meaning "bald", "hairless", "shaved", "smooth") is the technical term for a lack of hair, down, setae, trichomes or other such covering. A glabrous surface may be a natural characteristic of all or part of a plant or animal, or be due to loss because of a physical condition, such as alopecia universalis in humans, which causes hair to fall out or not regrow. In botany Glabrousness or otherwise, of leaves, stems, and fruit is a feature commonly mentioned in plant keys; in botany and mycology, a ''glabrous'' morphological feature is one that is smooth and may be glossy. It has no bristles or hair-like structures such as trichomes. In anything like the zoological sense, no plants or fungi have hair or wool, although some structures may resemble such materials. The term "glabrous" strictly applies only to features that lack trichomes at all times. When an organ bears trichomes at first, but loses them with age, the term used is ''glabresce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
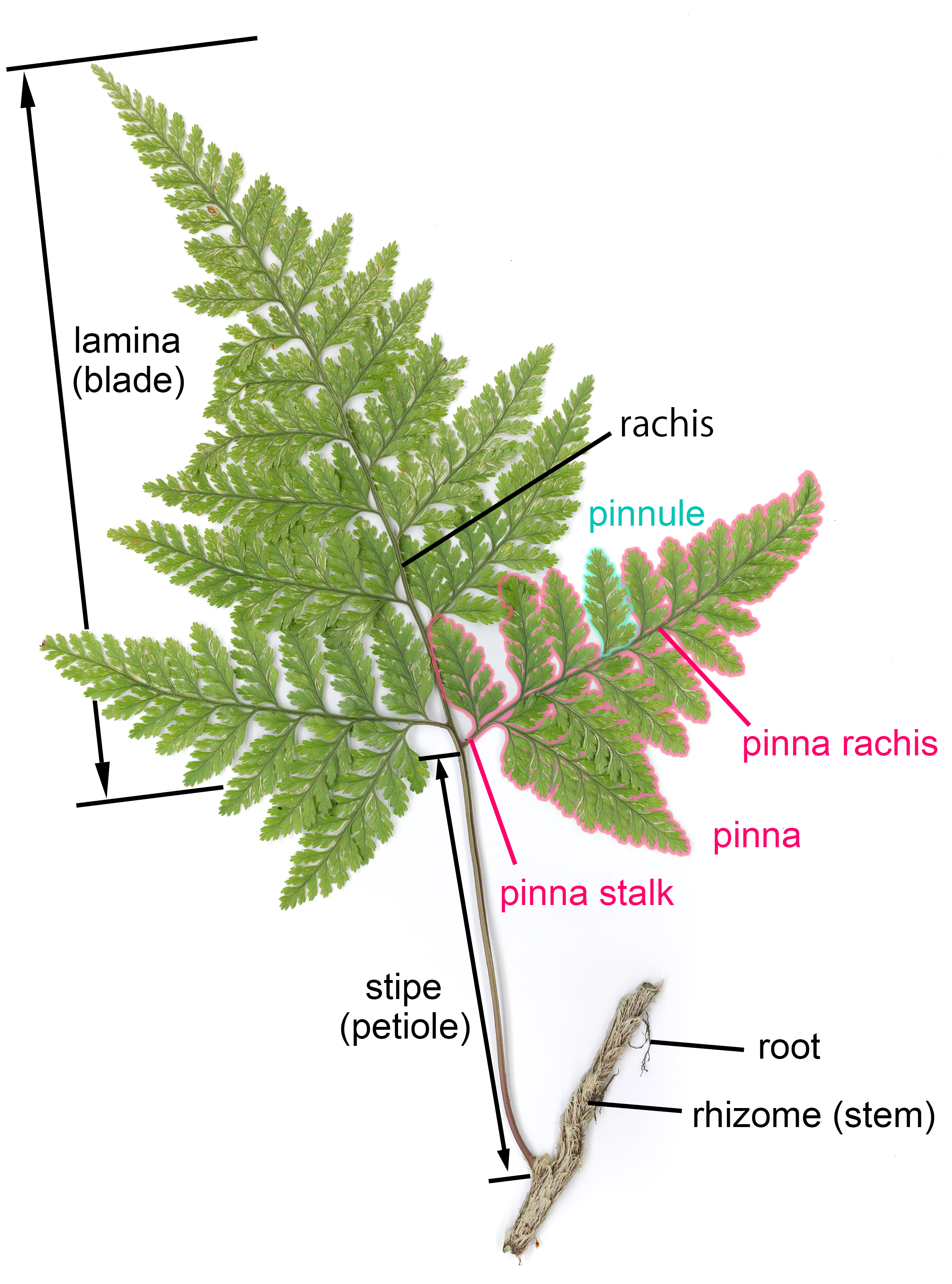
Frond
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves. Fronds have particular terms describing their components. Like all leaves, fronds usually have a stalk connecting them to the main stem. In botany, this leaf stalk is generally called a petiole, but in regard to fronds specifically it is called a stipe, and it supports a flattened blade (which may be called a lamina), and the continuation of the stipe into this portion is called the rachis. The blades may be simple (undivided), pinnatifid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |