|
Glass Solder
Glass frit bonding, also referred to as glass soldering or seal glass bonding, describes a wafer bonding technique with an intermediate glass layer. It is a widely used encapsulation technology for surface micro-machined structures, e.g., accelerometers or gyroscopes. This technique utilizes low melting-point glass ("glass solder") and therefore provides various advantages including that viscosity of glass decreases with an increase of temperature. The viscous flow of glass has effects to compensate and planarize surface irregularities, convenient for bonding wafers with a high roughness due to plasma etching or deposition. A low viscosity promotes hermetically sealed encapsulation of structures based on a better adaption of the structured shapes. Further, the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the glass material is adapted to silicon. This results in low stress in the bonded wafer pair. The glass has to flow and wet the soldered surfaces well below the temperature where d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafer Bonding
Wafer bonding is a packaging technology on wafer-level for the fabrication of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), microelectronics and optoelectronics, ensuring a mechanically stable and hermetically sealed encapsulation. The wafers' diameter range from 100 mm to 200 mm (4 inch to 8 inch) for MEMS/NEMS and up to 300 mm (12 inch) for the production of microelectronic devices. Smaller wafers were used in the early days of the microelectronics industry, with wafers being just 1 inch in diameter in the 1950s. Overview In microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS), the package protects the sensitive internal structures from environmental influences such as temperature, moisture, high pressure and oxidizing species. The long-term stability and reliability of the functional elements depend on the encapsulation process, as does the overall device cost. The package has to fulfill the following r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
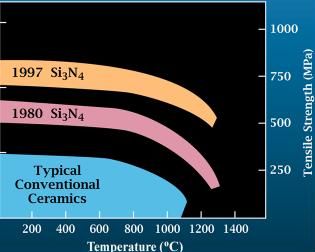
Silicon Nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot . It is very hard (8.5 on the mohs scale). It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications. Production Silicon nitride is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere: :3 Si + 2 → The silicon sample weight increases progressively due to the chemical combination of silicon and nitrogen. Without an iron catalyst, the reaction is complete after several hours (~7), when no further weight increase due to nitrogen absorption (per gram of silicon) is detected. In addition to , several other silicon nitride phases (with chemica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer, to protect selected areas of it during subsequent etching, deposition, or implantation operations. Typically, ultraviolet light is used to transfer a geometric design from an optical mask to a light-sensitive chemical ( photoresist) coated on the substrate. The photoresist either breaks down or hardens where it is exposed to light. The patterned film is then created by removing the softer parts of the coating with appropriate solvents. Conventional photoresists typically consists of three components: resin, sensitizer, and solvent. Photolithography processes can be classified according to the type of light used, such as ultraviolet, deep ultraviolet, extreme ultraviolet, or X-ray. The wavelength of light used determines the minimum feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Printing
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink (or dye) onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One colour is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multi-coloured image or design. Traditionally, silk was used in the process. Currently, synthetic threads are commonly used in the screen printing process. The most popular mesh in general use is made of polyester. There are special-use mesh materials of nylon and stainless steel available to the screen-printer. There are also different types of mesh size which will determine the outcome and look of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Printing
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink (or dye) onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One colour is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multi-coloured image or design. Traditionally, silk was used in the process. Currently, synthetic threads are commonly used in the screen printing process. The most popular mesh in general use is made of polyester. There are special-use mesh materials of nylon and stainless steel available to the screen-printer. There are also different types of mesh size which will determine the outcome and look of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Coating
Spin coating is a procedure used to deposit uniform thin films onto flat substrates. Usually a small amount of coating material is applied on the center of the substrate, which is either spinning at low speed or not spinning at all. The substrate is then rotated at speed up to 10,000 rpm to spread the coating material by centrifugal force. A machine used for spin coating is called a spin coater, or simply spinner. Rotation is continued while the fluid spins off the edges of the substrate, until the desired thickness of the film is achieved. The applied solvent is usually volatile, and simultaneously evaporates. The higher the angular speed of spinning, the thinner the film. The thickness of the film also depends on the viscosity and concentration of the solution, and the solvent. Pioneering theoretical analysis of spin coating was undertaken by Emslie et al., and has been extended by many subsequent authors (including Wilson et al., who studied the rate of spreading in spin coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Window
The optical window is a range of wavelengths that are not blocked by the earth's atmosphere. The window runs from around 300 nanometers (ultraviolet-B) up into the range the human eye can detect, roughly 400–700 nm and continues up to approximately 2 μm. Sunlight mostly reaches the ground through the optical atmospheric window; the sun is particularly active in most of this range (44% of the radiation emitted by the sun falls within the visible spectrum and 49% falls within the infrared spectrum). Definition The earth's atmosphere is not totally transparent and is in fact 100% opaque to many wavelengths (see plot of Earth's opacity); the wavelength ranges to which it is transparent are called atmospheric windows. Disambiguation of the term 'optical spectrum' Although the word ''optical'', deriving from Ancient Greek ὀπτῐκός (optikós, “of or for sight”), generally refers to something visible or visual, the term ''optical spectrum'' is used to describe th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Sensor
A pressure sensor is a device for pressure measurement of gases or liquids. Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually stated in terms of force per unit area. A pressure sensor usually acts as a transducer; it generates a signal as a function of the pressure imposed. For the purposes of this article, such a signal is electrical. Pressure sensors are used for control and monitoring in thousands of everyday applications. Pressure sensors can also be used to indirectly measure other variables such as fluid/gas flow, speed, water level, and altitude. Pressure sensors can alternatively be called pressure transducers, pressure transmitters, pressure senders, pressure indicators, piezometers and manometers, among other names. Pressure sensors can vary drastically in technology, design, performance, application suitability and cost. A conservative estimate would be that there may be over 50 technologies and at least 300 compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leakage Current
In electronics, leakage is the gradual transfer of electrical energy across a boundary normally viewed as insulating, such as the spontaneous discharge of a charged capacitor, magnetic coupling of a transformer with other components, or flow of current across a transistor in the "off" state or a reverse-polarized diode. In capacitors Gradual loss of energy from a charged capacitor is primarily caused by electronic devices attached to the capacitors, such as transistors or diodes, which conduct a small amount of current even when they are turned off. Even though this off current is an order of magnitude less than the current through the device when it is on, the current still slowly discharges the capacitor. Another contributor to leakage from a capacitor is from the undesired imperfection of some dielectric materials used in capacitors, also known as ''dielectric leakage''. It is a result of the dielectric material not being a perfect insulator and having some non-zero conductivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivation (chemistry)
Passivation, in physical chemistry and engineering, refers to coating a material so it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating, created by chemical reaction with the base material, or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. As a technique, passivation is the use of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to create a shield against corrosion. Passivation of silicon is used during fabrication of microelectronic devices. In electrochemical treatment of water, passivation reduces the effectiveness of the treatment by increasing the circuit resistance, and active measures are typically used to overcome this effect, the most common being polarity reversal, which results in limited rejection of the fouling layer. When exposed to air, many metals naturally form a hard, relatively inert surface layer, usually an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Material
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field (for example, if the field is moving parallel to the positive ''x'' axis, the negative charges will shift in the negative ''x'' direction). This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polaris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frit
A frit is a ceramic composition that has been fused, quenched, and granulated. Frits form an important part of the batches used in compounding enamels and ceramic glazes; the purpose of this pre-fusion is to render any soluble and/or toxic components insoluble by causing them to combine with silica and other added oxides.''Dictionary of Ceramics'' (3rd Edition) Edited by Dodd, A. Murfin, D. Institute of Materials. 1994. However, not all glass that is fused and quenched in water is frit, as this method of cooling down very hot glass is also widely used in glass manufacture. According to the '' OED'', the origin of the word "frit" dates back to 1662 and is "a calcinated mixture of sand and fluxes ready to be melted in a crucible to make glass". Nowadays, the unheated raw materials of glass making are more commonly called "glass batch". In antiquity, frit could be crushed to make pigments or shaped to create objects. It may also have served as an intermediate material in the man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)